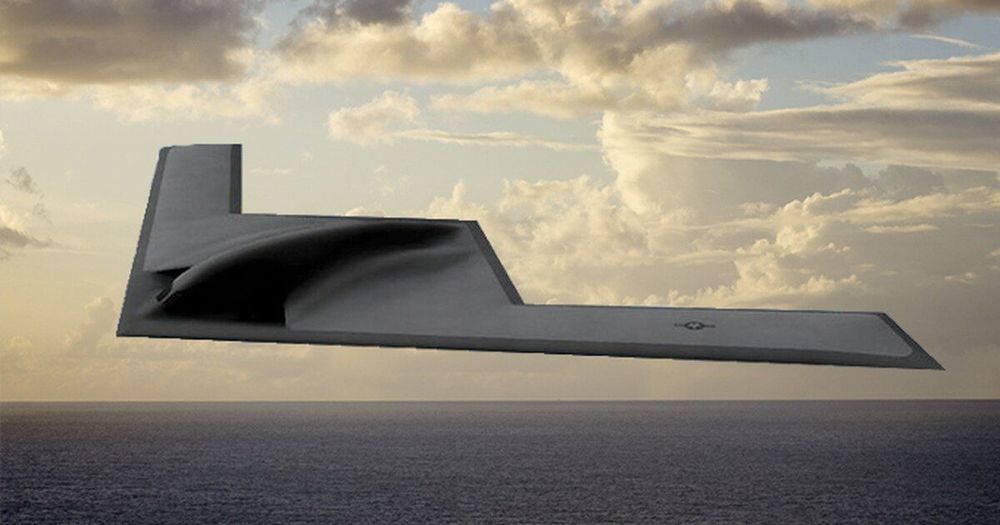
The future looks stealthy and unmanned.



Have a good day group 😅.
On Thursday, Donald Trump raised a few eyebrows as he spoke at the White House daily briefing on the coronavirus. Like us previously He reportedly suggested using UV lights or injecting disinfectants into a person affected by the virus.
Oddly enough, Trump’s suggestion not only sparked a conversation, as many people ignored him, but also prompted RB, the makers of Lysol and Dettol, to release a statement to assure everyone that their products are NOT for internal use, despite Trump’s suggestion.
On Friday, the company released the statement in its official website and said: “As a world leader in health and hygiene products, we must be clear that under no circumstances should our disinfectant products be administered to the human body (by injection, ingestion, or any other route). As with all products, our disinfectant products and hygiene should only be used as intended and in accordance with usage guidelines. Read label and safety information. We have a responsibility to provide consumers with access to accurate and up-to-date information as advised by leading health experts public ”.

In the constant battle against the spread of infectious diseases, scientists are continually on the hunt for new weapons that specifically target pathogenic microbes. Now, investigators from the Center for Radiological Research at Columbia University Irving Medical Center (CUIMC) believe they may have found a new, low-cost solution to eradicating airborne viruses in indoor public spaces. The research team found that continuous low doses of far ultraviolet C (far-UVC) light can kill airborne flu viruses without harming human tissues. The findings from the new study—published today in Scientific Reports in an article entitled “Far-UVC Light: A New Tool to Control the Spread of Airborne-Mediated Microbial Diseases”—suggests that use of overhead far-UVC light in hospitals, doctors’ offices, schools, airports, airplanes, and other public spaces could provide a powerful check on seasonal influenza epidemics, as well as influenza pandemics.
Scientists have known for decades that broad-spectrum UVC light, which has a wavelength of between 200 to 400 nanometers (nm), is highly effective at killing bacteria and viruses by destroying the molecular bonds that hold their DNA together. This conventional UV light is routinely used to decontaminate surgical equipment.
“Unfortunately, conventional germicidal UV light is also a human health hazard and can lead to skin cancer and cataracts, which prevents its use in public spaces,” explained senior study investigator David Brenner, Ph.D., director of the Center for Radiological Research and professor at CUIMC.

:oooo.
SOUTHERN UNITED STATES — Over 20 tornadoes touched down in the southern United States Wednesday, April 22 and more are expected Thursday, April 23. At one point, there were four distinct supercells on radar producing a tornado in Oklahoma.
Many of these storms lasted for hours and the threat for severe weather on Thursday, April 23 is aimed at the southeast.
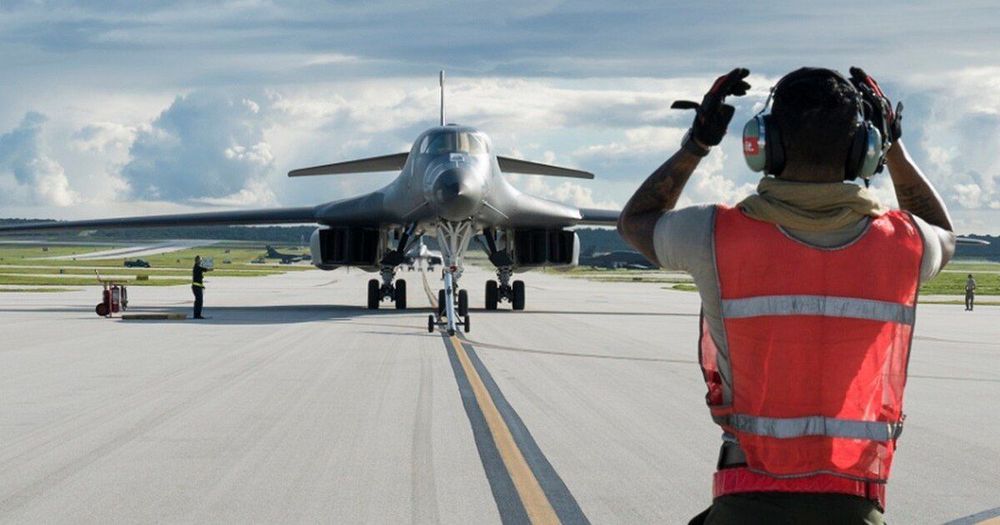

The path forward begins with admitting the nation has a bomber shortfall. Retiring more aircraft exacerbates the problem. Nor is this just an Air Force problem. Bombers are national assets essential to our security strategy and must be prioritized accordingly. If other services have excess funds to invest in ideas like a 1,000-mile-range cannon when thousands of strike aircraft, various munitions and remotely piloted aircraft can fill the exact same mission requirements, it is time for a roles and missions review to direct funding toward the most effective, efficient options. Bombers would compete well in such an assessment. Ultimately, the solution demands doubling down on the B-21 program.
There comes a point where you cannot do more with less. Given the importance of bombers to the nation, rebuilding the bomber force is not an option — it is an imperative.
Retired U.S. Air Force Maj. Gen. Larry Stutzriem served as a fighter pilot and held various command positions. He concluded his service as the director of plans, policy and strategy at North American Aerospace Defense Command and U.S. Northern Command. He is currently the director of studies at the Mitchell Institute for Aerospace Studies, where Douglas Birkey is the executive director. Birkey researches issues relating to the future of aerospace and national security, and he previously served as the Air Force Association’s director of government relations.
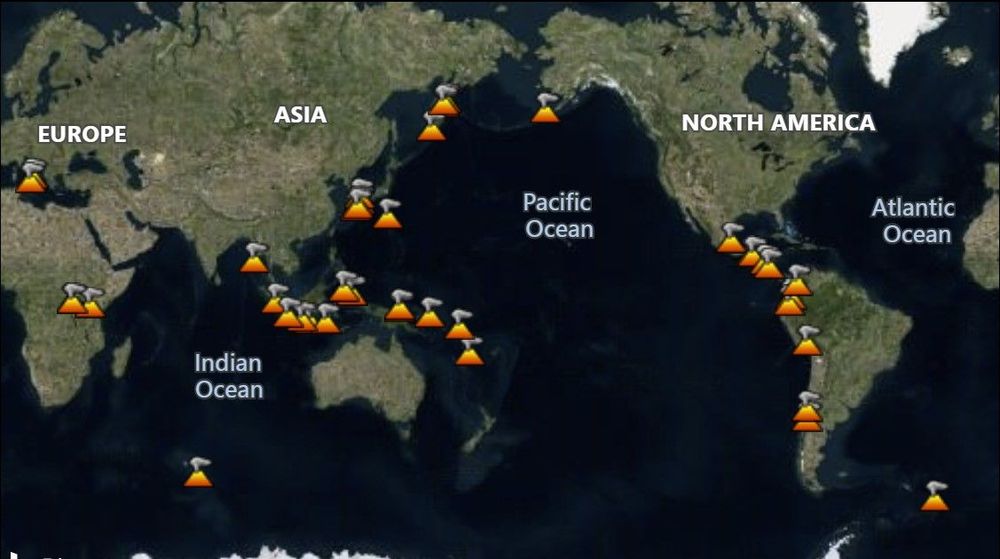
Volcano activity update.
Although detailed statistics are not kept on daily activity, generally there are around 20 volcanoes actively erupting at any particular time.
Overall there are 45 volcanoes with ongoing eruptions as of the Stop Dates indicated, and as reported through the last data update (17 April 2020) and shown in the diagram below.
Just a reminder that yesterday was the 30th anniversary of the Redoubt volcanic eruption on April 21, 1990. Here a picture:

While we might often take our sense of touch for granted, for researchers developing technologies to restore limb function in people paralyzed due to spinal cord injury or disease, re-establishing the sense of touch is an essential part of the process. And on April 23 in the journal Cell, a team of researchers at Battelle and the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center report that they have been able to restore sensation to the hand of a research participant with a severe spinal cord injury using a brain-computer interface (BCI) system. The technology harnesses neural signals that are so miniscule they can’t be perceived and enhances them via artificial sensory feedback sent back to the participant, resulting in greatly enriched motor function.
“We’re taking subperceptual touch events and boosting them into conscious perception,” says first author Patrick Ganzer, a principal research scientist at Battelle. “When we did this, we saw several functional improvements. It was a big eureka moment when we first restored the participant’s sense of touch.”
The participant in this study is Ian Burkhart, a 28-year-old man who suffered a spinal cord injury during a diving accident in 2010. Since 2014, Burkhart has been working with investigators on a project called NeuroLife that aims to restore function to his right arm. The device they have developed works through a system of electrodes on his skin and a small computer chip implanted in his motor cortex. This setup, which uses wires to route movement signals from the brain to the muscles, bypassing his spinal cord injury, gives Burkhart enough control over his arm and hand to lift a coffee mug, swipe a credit card, and play Guitar Hero.
Stephen Wolfram is a cult figure in programming and mathematics. He is the brains behind Wolfram Alpha, a website that tries to answer questions by using algorithms to sift through a massive database of information. He is also responsible for Mathematica, a computer system used by scientists the world over.
Last week, Wolfram launched a new venture: the Wolfram Physics Project, an ambitious attempt to develop a new physics of our Universe.
The new physics, he declares, is computational. The guiding idea is that everything can be boiled down to the application of simple rules to fundamental building blocks.