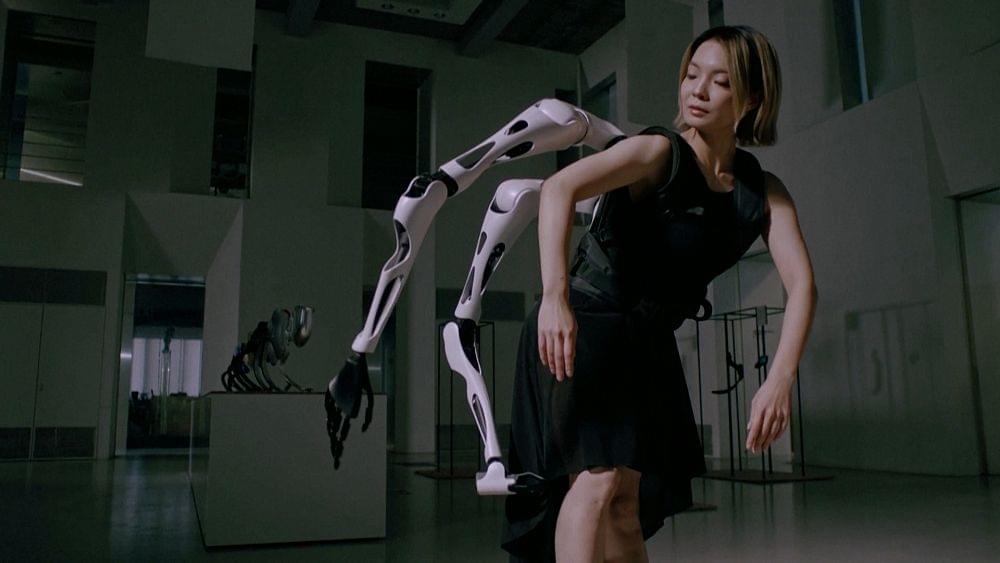
Breakthrough research represents “the missing link that will enable wearables to control genes in the not-so-distant future,” researchers say.



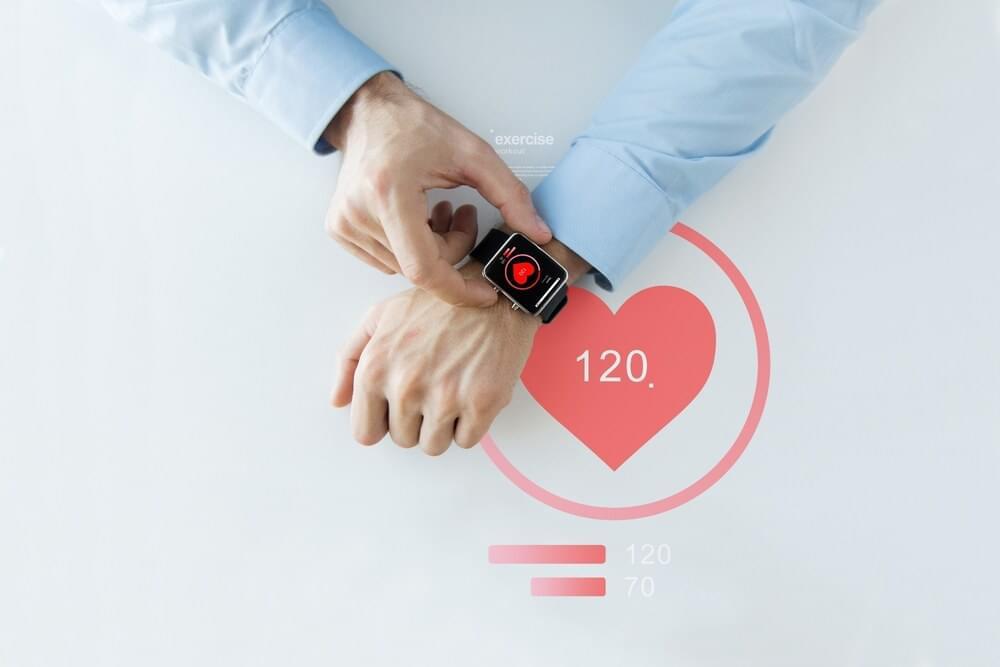
Not surprisingly, the Intelligence Community (IC), Department of Defense (DoD), and first responders at the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) and other agencies are also interested in wearable electronics. With its Smart Electrically Powered and Networked Textile Systems (SMART ePANTS) program, the Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity (IARPA) is delivering the largest single investment ever made1 to make Advanced Smart Textiles2 (AST) a reality.
According to SMART ePANTS Program Manager, Dr. Dawson Cagle, developing clothing with sensor systems that can record audio, video, and geolocation data would significantly improve the capabilities of IC, DoD, DHS staff, and others working in dangerous or high-stress environments, such as crime scenes and arms control inspections. Dr. Cagle also asserted that ASTs could collect information one doesn’t notice, which would increase job effectiveness.
Summary: Researchers created a revolutionary tiny and efficient thermoelectric device, which can help amputees feel temperature with their phantom limbs.
Known as the wearable thin-film thermoelectric cooler (TFTEC), this device is lightweight, incredibly fast, and energy-efficient, potentially revolutionizing applications such as prosthetics, augmented reality haptics, and thermally-modulated therapeutics. Additionally, this technology has potential in industries like electronics cooling and energy harvesting in satellites.
The study conducted to test the TFTEC demonstrated its ability to elicit cooling sensations in phantom limbs, doing so significantly faster, with more intensity, and less energy than traditional thermoelectric technology.

In a recent perspective piece published in the Nature Medicine Journal, researchers discussed the current achievements, challenges, and potential opportunities in using digital technologies, such as remote medicine and wearables in geriatric medicine and care.
Study: Digital health for aging populations. Image Credit: GroundPicture/Shutterstock.com.
Imagine a wearable patch that tracks your vital signs through changes in the color display, or shipping labels that light up to indicate changes in temperature or sterility of food items.
These are among the potential uses for a new flexible display created by UBC researchers and announced recently in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
“This device is capable of fast, realtime and reversible color change,” says researcher Claire Preston, who developed the device as part of her master’s in electrical and computer engineering at UBC. “It can stretch up to 30 percent without losing performance. It uses a color-changing technology that can be used for visual monitoring. And it is relatively cheap to manufacture.”
An Israeli startup has developed a wearable device that can predict the likelihood of an imminent stroke through changes in the carotid artery’s blood flow, potentially helping early intervention and preventing disablity.
Strokes are most commonly caused by a clot blocking the essential supply of blood to the brain, and according to the World Health Organization are the second leading cause of death and the leading cause of disability across the globe.
Over 100 million people have experienced a stroke worldwide, with one in four adults experiencing one in their lifetime. And for 50 percent of them, that means some form of lasting disability.

A new study by researchers at the University of Cambridge reveals a surprising discovery that could transform the future of electrochemical devices. The findings offer new opportunities for the development of advanced materials and improved performance in fields such as energy storage, brain-like computing, and bioelectronics.
Electrochemical devices rely on the movement of charged particles, both ions and electrons, to function properly. However, understanding how these charged particles move together has presented a significant challenge, hindering progress in creating new materials for these devices.
In the rapidly evolving field of bioelectronics, soft conductive materials known as conjugated polymers are used for developing medical devices that can be used outside of traditional clinical settings. For example, this type of materials can be used to make wearable sensors that monitor patients’ health remotely or implantable devices that actively treat disease.

Gas accidents such as toxic gas leakage in factories, carbon monoxide leakage of boilers, or toxic gas suffocation during manhole cleaning continue to claim lives and cause injuries. Developing a sensor that can quickly detect toxic gases or biochemicals is still an important issue in public health, environmental monitoring, and military sectors. Recently, a research team at POSTECH has developed an inexpensive, ultra-compact wearable hologram sensor that immediately notifies the user of volatile gas detection.
[Professor Junsuk Rho’s research team at POSTECH develops wearable gas sensors that display instantaneous visual holographic alarm.].

