The industry showed out in spades for this year’s list, highlighting devices in medical AI, surgical robotics, wearables, and femtech, among others.


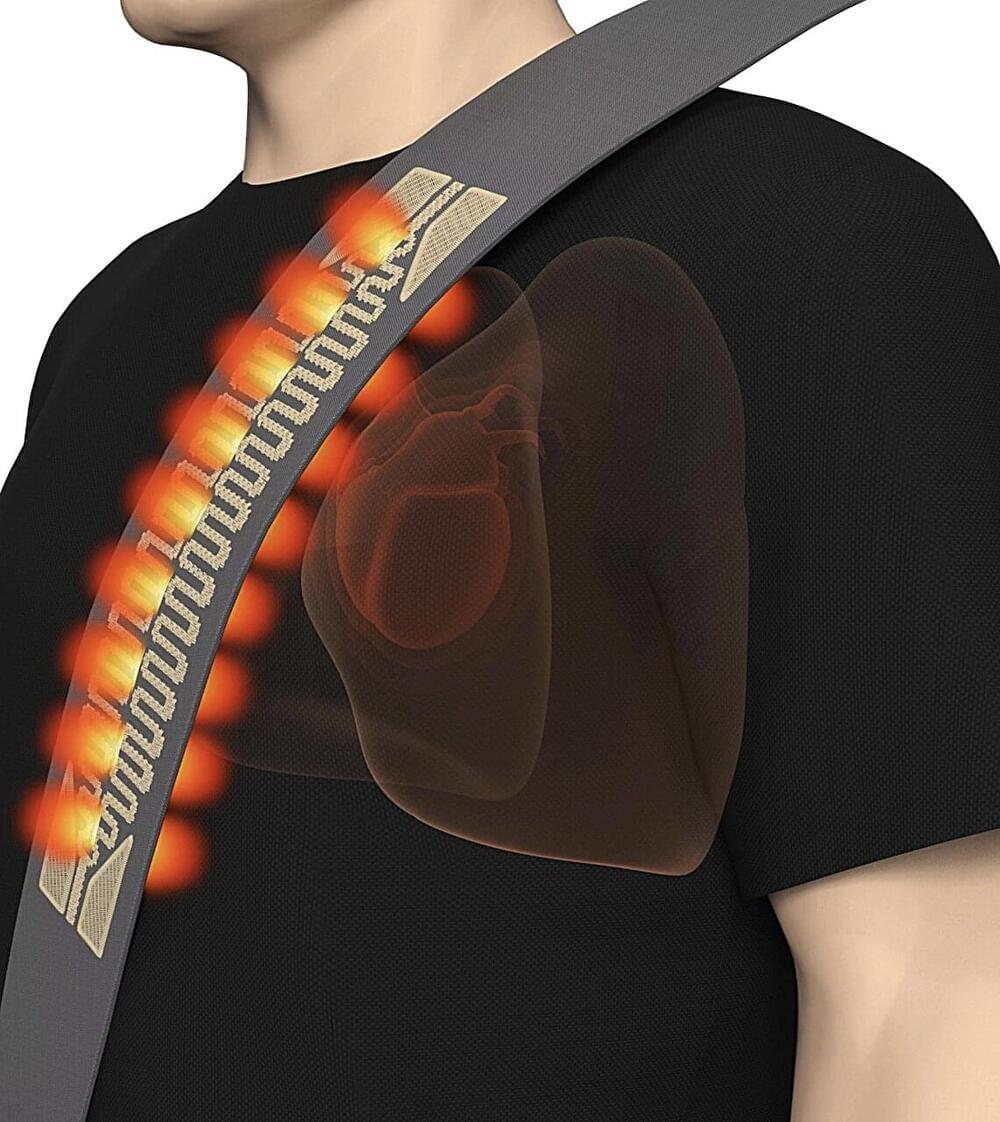
Over the past decades, electronics and biomedical engineers have developed increasingly sophisticated biosensors, devices that can pick up biological signals from human users. These sensors, which are generally embedded in wearable or implantable technologies, often do not perform as well in settings where users are moving a lot, such as within a vehicle.
Researchers at the National University of Singapore and Tsinghua University have recently developed a new sensor that can pick up and track biological signals, such as the heartbeat and respiration, without being in contact with the body of users. This sensor, presented in a paper published in Nature Electronics, could be used to pick up the cardiopulmonary signals of humans while they are in dynamic and closed environments, such as a plane cabin, a moving car or a bus.
“Monitoring drivers’ alertness or stress is essential for road safety,” Xi Tian, co-author of the paper, told Tech Xplore. “Existing sensors designed to measure physiological markers of fatigue, such as heart rate and respiration, face challenges in moving vehicles due to the unpredictable vibrational noise. To overcome these challenges, our research focused on developing an automotive biosensor capable of non-contact and reliable health monitoring in dynamic environments.”
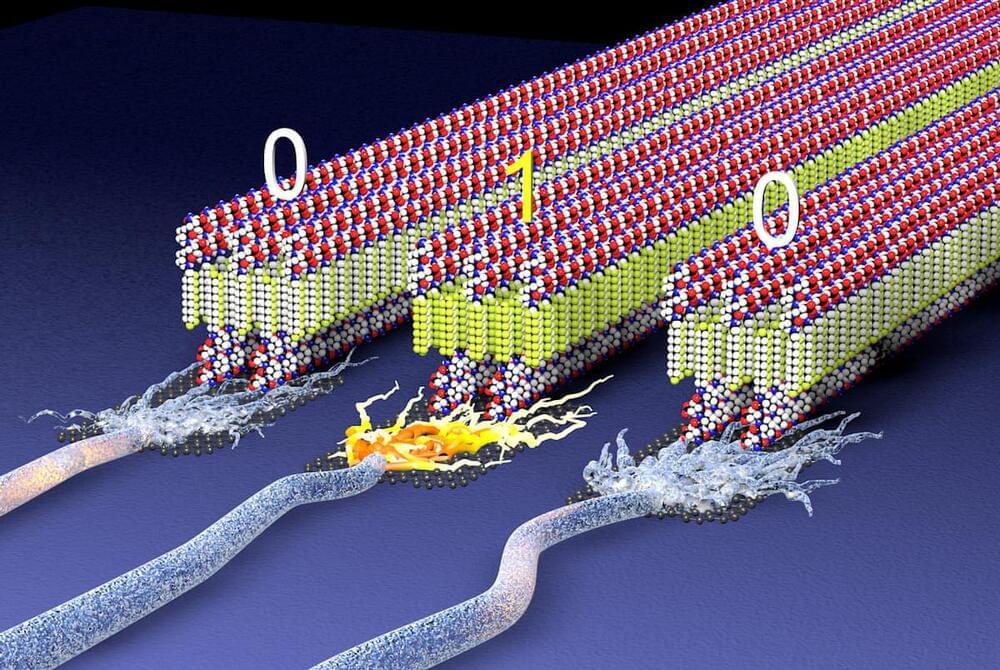
Step aside, hard and rigid materials — a new soft, sustainable electroactive material is here, ready to unlock new possibilities for medical devices, wearable technology, and human-computer interfaces.
Using peptides and a snippet of the large molecules in plastics, Northwestern University materials scientists have developed materials made of tiny, flexible nano-sized ribbons that can be charged just like a battery to store energy or record digital information. Highly energy efficient, biocompatible, and made from sustainable materials, the systems could give rise to new types of ultralight electronic devices while reducing the environmental impact of electronic manufacturing and disposal.
The study was recently published in the journal Nature.

A research team, led by Professor Hoon Eui Jeong from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at UNIST has introduced an innovative magnetic composite artificial muscle, showcasing an impressive ability to withstand loads comparable to those of automobiles. This material achieves a stiffness enhancement of more than 2,700 times compared to conventional systems. The study is published in Nature Communications.
Soft artificial muscles, which emulate the fluidity of human muscular motion, have emerged as vital technologies in various fields, including robotics, wearable devices, and biomedical applications. Their inherent flexibility allows for smoother operations; however, traditional materials typically exhibit limitations in rigidity, hindering their ability to lift substantial weights and maintain precise control due to unwanted vibrations.
To overcome these challenges, researchers have employed variable rigid materials that can transition between hard and soft states. Yet, the available range for stiffness modulation has remained constrained, along with inadequate mechanical performance.
If you’ve ever seen yourself through a thermal imaging camera, you’ll know that your body produces lots of heat. This is in fact a waste product of our metabolism. Every square foot of the human body gives off heat equivalent to about 19 matches per hour.
Unfortunately, much of this heat simply escapes into the atmosphere. Wouldn’t it be great if we could harness it to produce energy? My research has shown this would indeed be possible. My colleagues and I are discovering ways of capturing and storing body heat for energy generation, using eco-friendly materials.
The goal is to create a device that can both generate and store energy, acting like a built-in power bank for wearable tech. This could allow devices such as smart watches, fitness trackers, or GPS trackers to run much longer, or even indefinitely, by harnessing our body heat.
Future wearables won’t need to get under your skin.
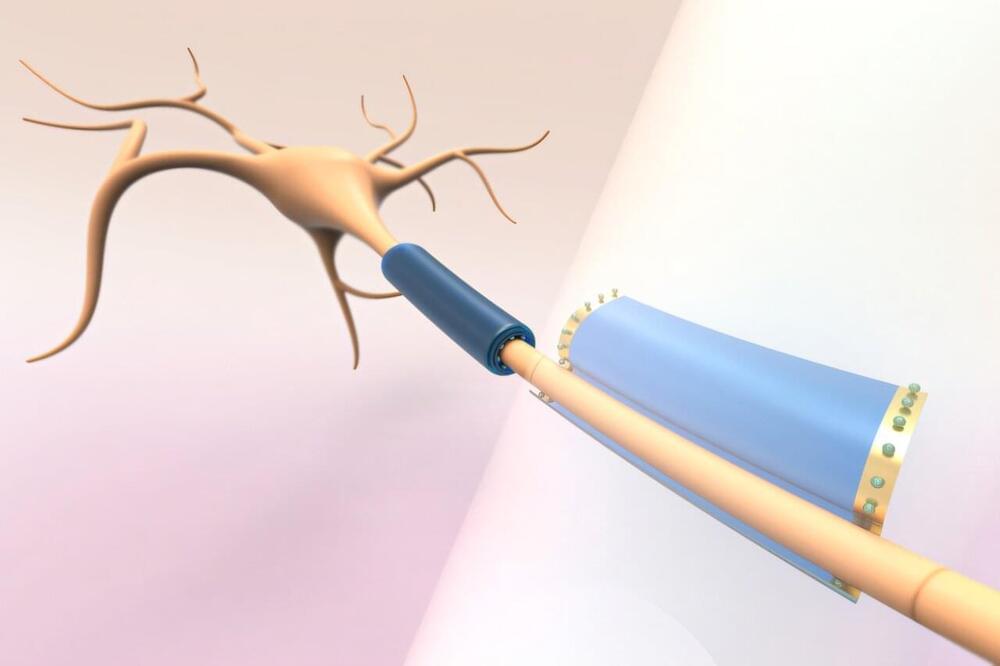
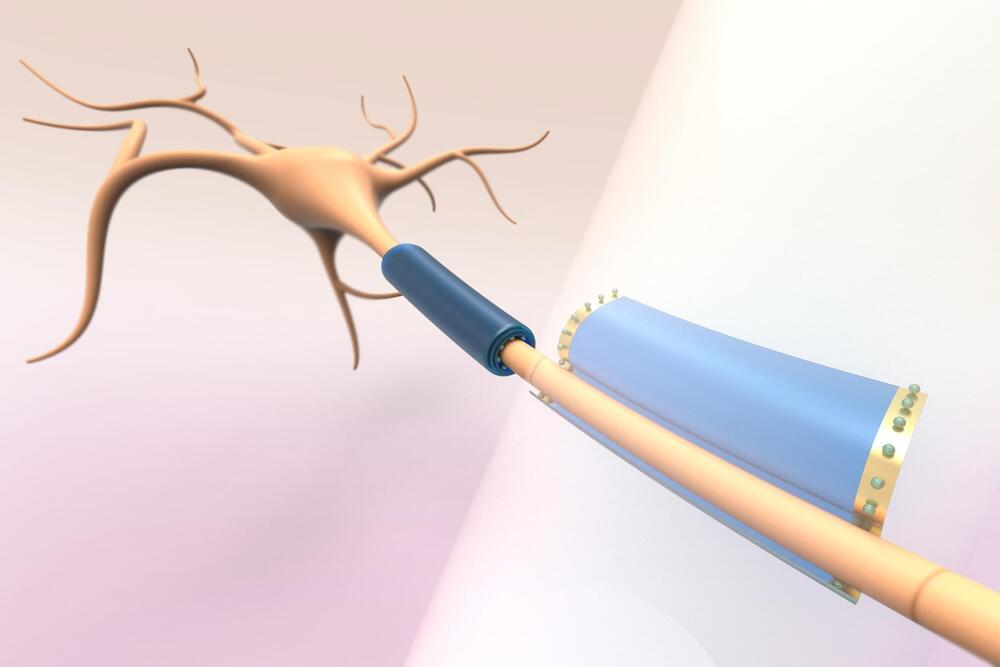
MIT researchers have developed a battery-free, subcellular-sized device made of polymer designed to measure and modulate a neuron’s electrical and metabolic activity. When the device is activated by light, it can gently wrap around the neuron cell’s axons and dendrites without damaging the cells.
Scientists want to inject thousands of these tiny wireless devices into a patient’s central nervous system and then actuate them noninvasively using light. The light would penetrate the tissue and allow precise control of the devices, and thereby restore function in cases of neuronal degradation like multiple sclerosis (MS).
The MIT researchers developed these thin-film devices from a azobenzene, a soft polymer that readily reacts to light. Thin sheets of azobenzene roll into a cylinder when exposed to light, which enables them to wrap around cells. Researchers can control the direction and diameter of the rolling by changing the intensity and polarization of the light, producing a microtube with a diameter smaller than one micrometer.
Researchers develop nanomaterial textiles for wireless power, allowing real-time data transmission without the need for bulky batteries.