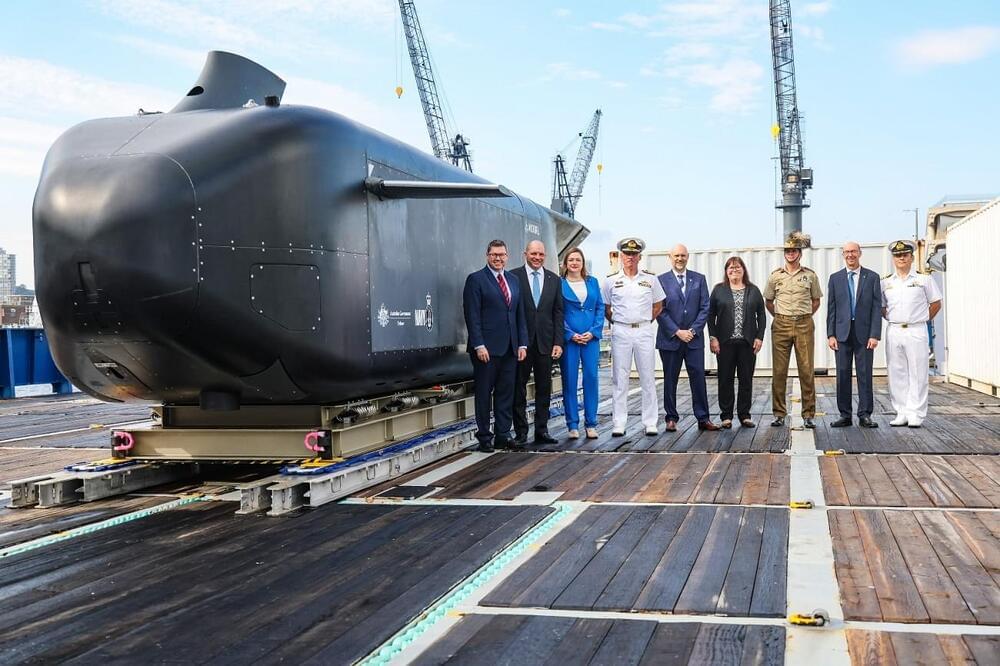
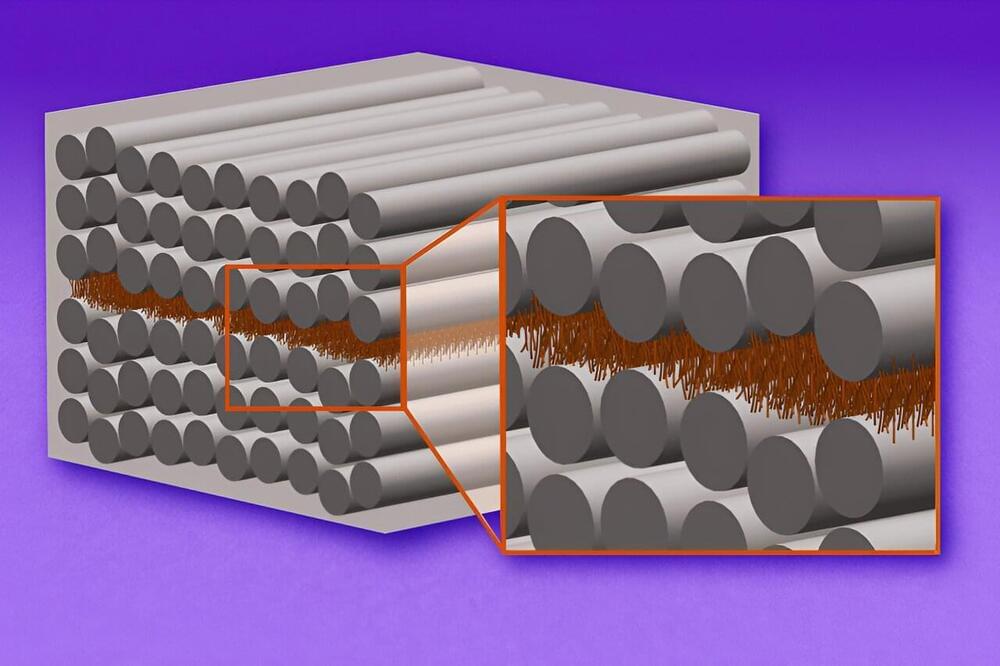
Anduril, the Royal Australian Navy (RAN), the Advanced Strategic Capabilities Accelerator (ASCA) and Defence Science and Technology Group (DSTG) are pleased to unveil the first Ghost Shark manufactured prototype and announce that the Ghost Shark program is ahead of schedule and on budget. As Anduril moves to deliver an operationally relevant capability within a fraction of traditional defence timelines, early creation and testing of the first Ghost Shark has been critical for rapid learning and iteration. It’s a momentous advancement in the $140M co-development contract between RAN, DSTG and Anduril to design and develop the three ‘Ghost Shark’ extra-large autonomous undersea vehicles (XL-AUV) in three years in Australia. Ghost Shark is a modular, multi-purpose capability that can flexibly respond to the Australian Defence Force’s mission requirements, creating an agile force multiplier for Defence.
Dr Shane Arnott, Senior Vice President Engineering, Anduril Industries said: “Moving at the speed of relevance is Anduril’s signature. For Ghost Shark, we have assembled a unique high-powered engineering team of 121 people from the best-of-Australia, across tech, resources and defence, to fuel this progress. We have 42 Australian companies currently working on Ghost Shark, which is being designed, engineered and manufactured in Australia. We plan to manufacture at scale in Australia for the Royal Australian Navy, and then for export to our allies and partners around the world. Using novel scaled agile development techniques, we are combining both tech and defence sector development practices – and it’s paying big dividends. Ghost Shark is a program that we as Australians can be very proud of.”
David Goodrich OAM, Executive Chairman and CEO Anduril Australia said: “The timeline we set to design and produce three Ghost Sharks in three years in Australia, by Australians for the ADF, was extremely ambitious. I am excited to report that we are ahead of schedule and, importantly for a Defence program, we are on budget. We’re moving incredibly quickly on this program in lockstep with our ASCA, DSTG and the RAN partners. The strategic leadership and innovation insights provided by Prof Tanya Monro, Prof Emily Hilder and Vice Admiral Mark Hammond are key to our success.”