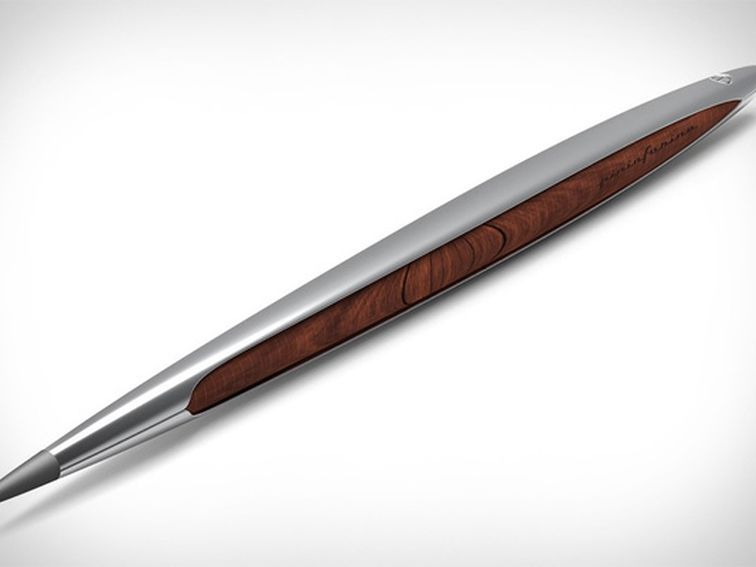
Car design firm Pininfarina has designed an inkless pen with a metal nib that will write without ever running out.
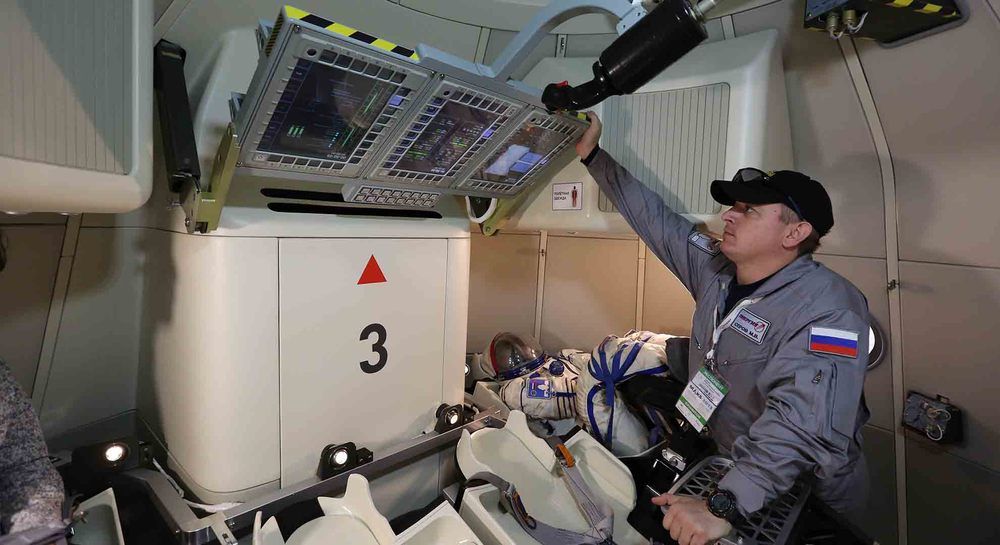



Industrial designer Vladimir Pirojkov was called upon to work on the interior design for a new spacecraft for the Russian Space Agency. Here he talks about the experience.
Can you tell us a little about your background?
My roots are in the transportation industry. I graduated from Art Center College of Design in Switzerland. My first job was as a Citroen interior designer in Paris. After six years I moved to Nice in the south of France to join the Toyota Europe Design Development Centre as senior interior designer. It was a great experience, where many countries and cultures met and learned from each other. We worked on projects for show cars and some for on-the-road production vehicles. In 2007, I returned to Russia to work on the future of the world.
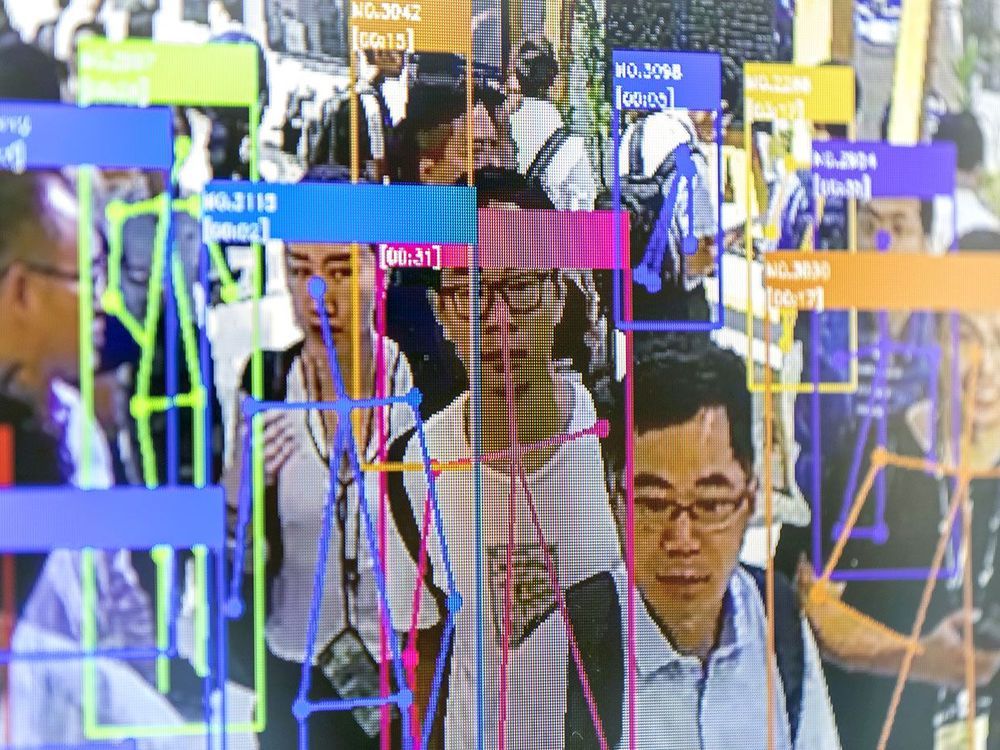

I’m excited to share my new opinion piece on AI facial recognition and privacy for IEEE Spectrum:
The views expressed here are solely those of the author and do not represent positions of IEEE Spectrum or the IEEE.
Many people seem to regard facial-recognition software in much the same way they would a nest of spiders: They recognize, in some abstract way, that it probably has some benefits. But it still gives them the creeps.
It’s time for us to get over this squeamishness and embrace face recognition as the life-enhancing—indeed, life–saving—technology that it is. In many cities, closed-circuit cameras increasingly monitor streets, plazas, and parks around the clock. Meanwhile, the price of recognition software is decreasing, while its capabilities are increasing.
I welcome these trends. I want my 9-year-old daughter tracked while she walks alone to school. I want a face scanner at Starbucks to simply withdraw the payment for my coffee from my checking account. I want to board a plane without fumbling for a boarding pass. Most of all, I want murderers or terrorists recognized as they walk on a city street and before they can cause further mayhem.
Among the hardest games to play, we find the waiting game. The lore of the DeLorean being produced once again has been floating around the watercooler for some time now. Most recently, rumors pointed to 2016 being the return of the DMC 12. However, due to changes in regulations, it would appear as if the revival wouldn’t exactly be legal. Let’s just say that low-volume auto manufacturers have some hurdles to jump over. These regulations would make the hurdles impossible for DeLorean.
That all changed.
Hagerty tells us that “According to SEMA, the final regulations will allow low-volume automakers to sell up to 325 cars each year that resemble production vehicles manufactured at least 25 years ago.”
NASA is sharing information about its myco-architecture program, in which experimental fungus-based building technologies could be the feasible future of Mars habitats. “Science fiction often imagines our future on Mars and other planets as run by machines, with metallic cities and flying cars rising above dunes of red sand,” NASA says. “But the reality may be even stranger.”
The myco-architecture (myco is the prefix meaning “fungus”) NASA is excited about isn’t only a new way to make furniture, although it can do that, the agency says. Mushroom House—not its real name—is an integrated habitat with layers. The tough, complex fibers made by fungal mycelia are building blocks of furniture, interior walls, and the innermost layer of the outer shell.
Zero to 658 in 50 seconds without emissions.
The Bloodhound LSR team has announced plans to challenge for the land speed record using a zero-emissions rocket as part of the next phase of its programme, following successful high-speed tests in South Africa last November.
The land speed record car has returned to the UK Land Speed Centre, Bloodhound’s HQ in Gloucestershire, after having successfully completed its crucial high-speed tests in South Africa.
These tests took place on the Hakskeenpan: a dry lake bed in the Kalahari Desert, during which the land speed record vehicle notched speeds of 628mph (1,010km/h), placing the Bloodhound LSR car, unofficially, as the sixth-fastest car of all time.
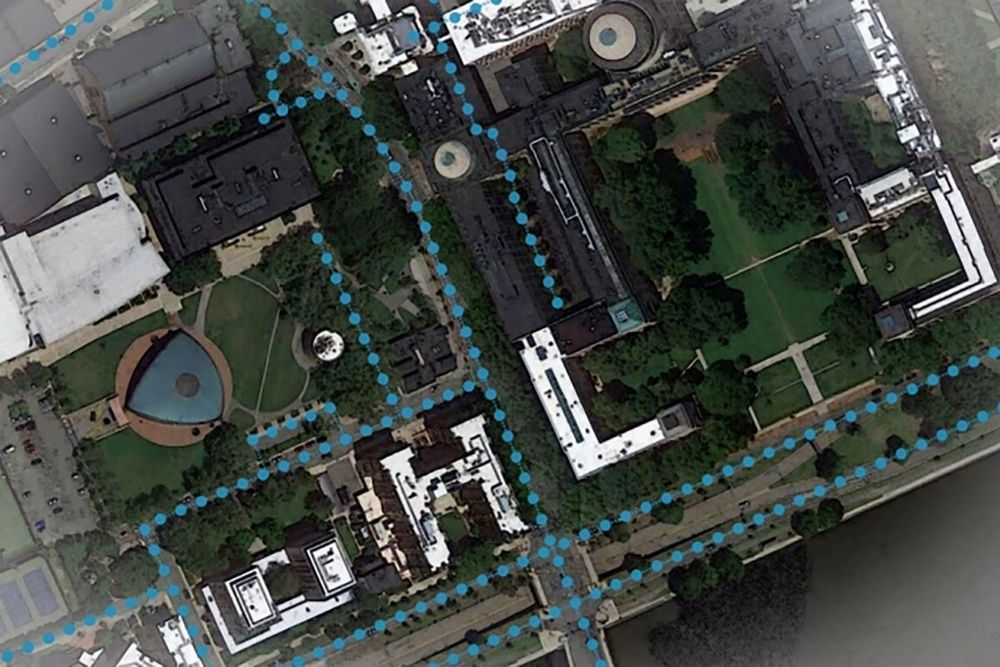
In-car satnav systems and mobile mapping apps have made it much easier to travel from one place to another without getting lost, but a new innovation promises to help fix a remaining pain point – getting in the right lane at intersections.
Today’s mapping apps aren’t always much help if you’re at an unfamiliar intersection and aren’t sure exactly where on the road your car is supposed to be: the apps often don’t have the detail or the knowledge to warn you in good time about changing lanes.
The system developed by researchers at MIT and the Qatar Computing Research Institute uses satellite imagery to augment existing mapping data, but the smart part is applying artificial intelligence to work out the layout of roads hidden by trees and buildings.
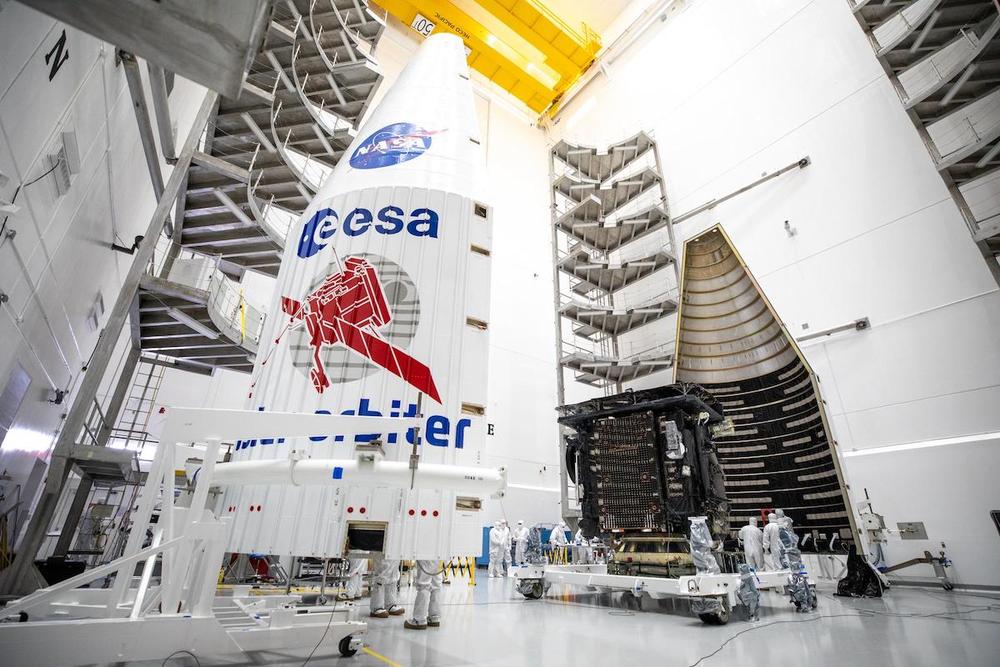

The Airbus-built Solar Orbiter spacecraft has been closed up inside the payload fairing of a United Launch Alliance Atlas 5 rocket in preparation for liftoff from Cape Canaveral in February on a joint mission between the European Space Agency and NASA.
Technicians inside the Astrotech payload processing facility encapsulated the Solar Orbiter spacecraft — designed with thermal shielding to protect against the heat of the sun — inside the Atlas 5’s payload fairing Jan. 20. The spacecraft inside the Atlas 5 rocket’s 4-meter-diameter (13.1-foot) aerodynamic nose shroud will soon travel to ULA’s Vertical Integration Facility, where crane will hoist the payload package atop the launcher.
Valued at nearly $1.7 billion, the Solar Orbiter mission will travel closer to the sun than Mercury, where it will join NASA’s Parker Solar Probe for tandem observations of the solar wind and giant solar eruptions that can affect communications and electrical grids on Earth, plus satellite operations.