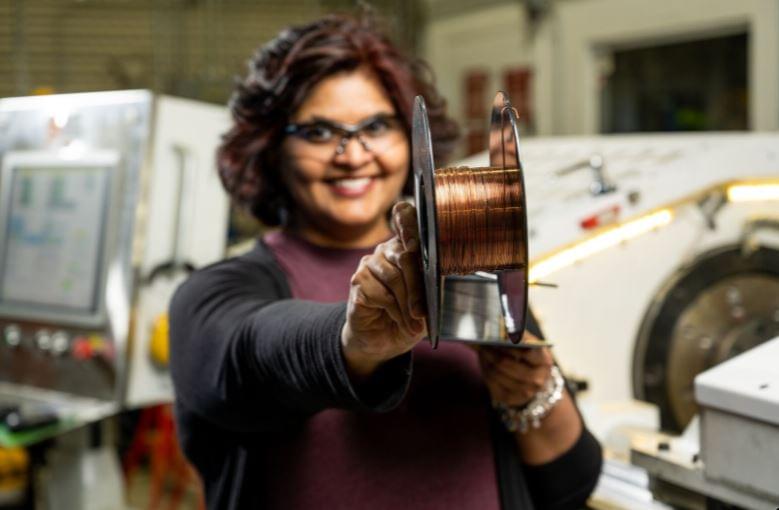
A common carbon compound is enabling remarkable performance enhancements when mixed in just the right proportion with copper to make electrical wires. It’s a phenomenon that defies conventional wisdom about how metals conduct electricity.
The findings, reported in the journal Materials & Design, could lead to more efficient electricity distribution to homes and businesses, as well as more efficient motors to power electric vehicles and industrial equipment. The team has applied for a patent for the work, which was supported by the Department of Energy (DOE) Advanced Materials and Manufacturing Technologies Office.
Materials scientist Keerti Kappagantula and her colleagues at DOE’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory discovered that graphene, single layers of the same graphite found in pencils, can enhance an important property of metals called the temperature coefficient of resistance.