A story from Salon on transhumanism:
While we have a rare combination of candidates with a real chance of taking the White House — a woman, a Jewish socialist and a real estate magnate — there’s another you probably haven’t heard about: a Transhumanist.
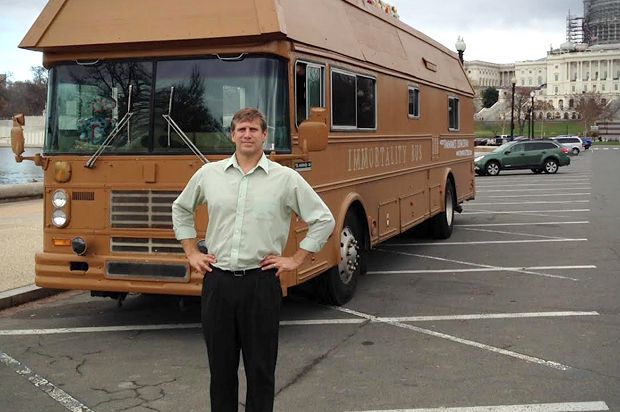
Zoltan Istvan, 43, the leader and founder of the Transhumanist party, has entered the race as a third-party candidate promising the “facilitation of immortality.” Istvan, who lives in California, first made headlines when he set out on a cross-country campaign tour in a bus shaped like a hearse last September. His main philosophy: enliven America’s technological advancement by combining humans with machines, to improve and prolong life.
In U.S politics, the two traditional parties have consistently dominated the electorate. In fact, Sen. Bernie Sanders is the only Independent in Congress, every other House member belongs to either the Democratic or Republican Party. But historically the country has had a history of fringe candidates, which typically get a few thousand votes in presidential elections. In 1992, billionaire businessman Ross Perot, who ran on the Reform Party, won 18.9% of the vote, the best finish by a non-major party candidate in a presidential election since Teddy Roosevelt won 27.5% of the vote in 1912. While Perot’s Reform Party, like practically all third parties, has failed to emerge as a contender since then, candidates like him have had a significant impact on electoral outcomes.
Zoltan Istvan is still an ambiguity for most of the political world, and the Transhumanist party in its early stages of development, but there is something to be said about how his policies could predict the way the political landscape might change in the decades to come.
Read more