Building a sustainable human presence on other worlds should be open to all. Comparing the journey to violent conquest doesn’t help.



No matter how abundant or renewable, solar power has a thorn in its side. There is still no cheap and efficient long-term storage for the energy that it generates.
The solar industry has been snagged on this branch for a while, but in the past year alone, a series of four papers has ushered in an intriguing new solution.
Scientists in Sweden have developed a specialised fluid, called a solar thermal fuel, that can store energy from the sun for well over a decade.
On Wednesday, November 7, NASA will launch its Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) spacecraft to study the ionosphere. This boundary lies between space and Earth, being home to a “sea” of charged electrons and ions; it reacts to both lower atmosphere weather and solar energy, the result being space weather. NASA’s ICON will study this, offering unprecedented scientific data.


Ha…which would be the bigger challenge? 🤔.
The growing mistrust and hostility towards global intuitions must be overcome if the world is to successfully tackle the environmental challenges it faces, the head of the University of Sussex’s global sustainability research centre has warned.
Professor Joseph Alcamo, Director of the Sussex Sustainability Research Programme (SSRP), said high-quality research and closer engagement with citizens around the world was needed to overcome the growing zeitgeist that viewed organisations such as the UN as meddling amid a geopolitical backdrop of cancelled treaties, neglected obligations and frozen negotiations.
Delivering his keynote speech at the 2018 Utrecht Conference on Earth System Governance this morning, Prof Alcamo said: To many people earth system governance is not beautiful, it is worrisome, it means loss of control over their lives, and this mistrust is a big part of the national retrenchment going on.
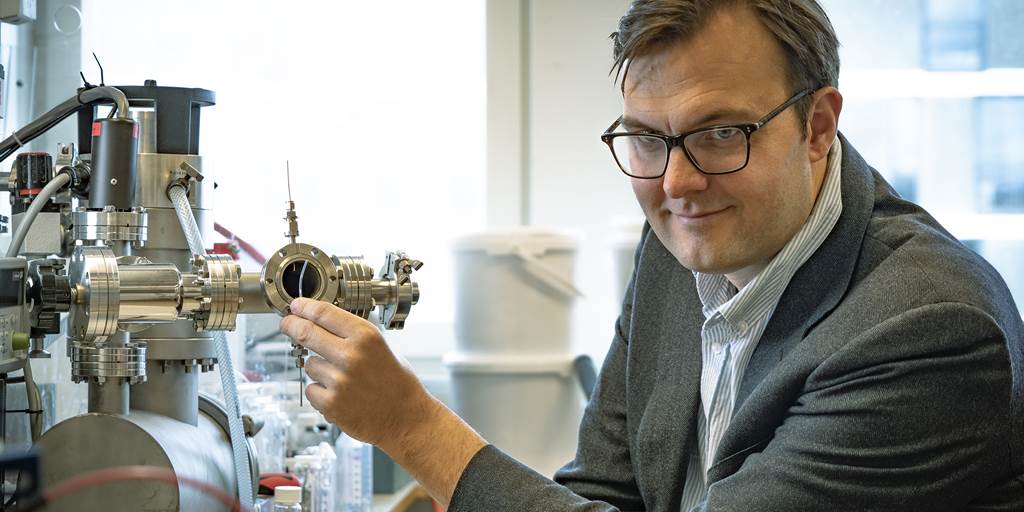
What if we could bottle solar energy so it could be used to power our homes and factories even when the sun doesn’t shine?
Scientists have spent decades looking for a way do just that, and now researchers in Sweden are reporting significant progress. They’ve developed a specialized fluid that absorbs a bit of sunlight’s energy, holds it for months or even years and then releases it when needed. If this so-called solar thermal fuel can be perfected, it might drive another nail in the coffin of fossil fuels — and help solve our global-warming crisis.
Unlike oil, coal and natural gas, solar thermal fuels are reusable and environmentally friendly. They release energy without spewing carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
The future is both glorious and horrifying. As we continue to expand our technological footprint in the hopes of creating wonder, several issues remain fixed with a trajectory towards disaster. From climate change to the mass extinction of several animal species, there’s no doubt that we’re heading into ruin if we’re to keep this up.
As our technology continues to advance to the point of bringing the dead back to life, how will our own species react to a growing new population of animals that can die and live again?
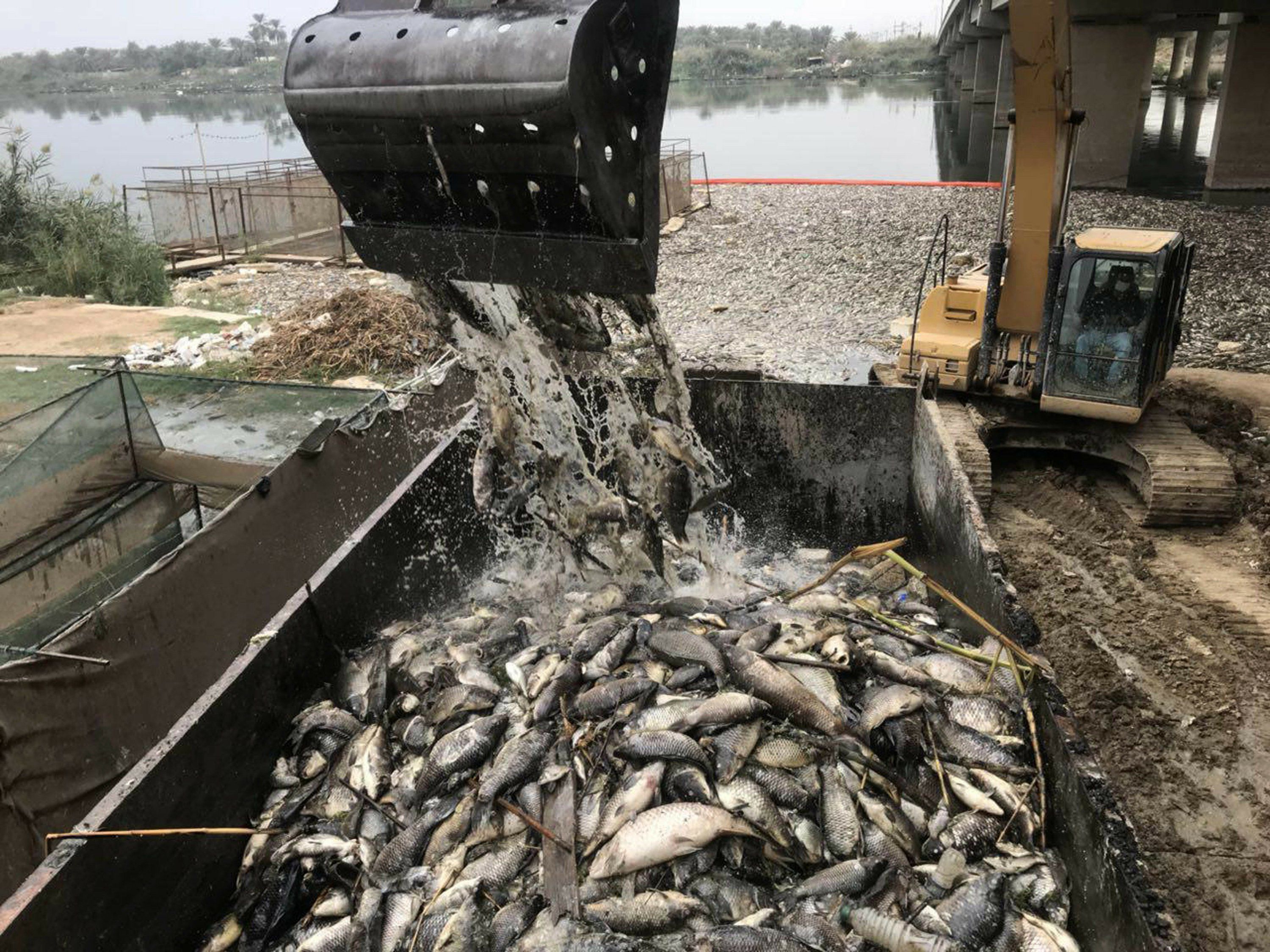

HINDIYAH, Iraq (AP) — Iraqi officials and fishermen are at a loss to explain how hundreds of tons of carp have suddenly died in fish farms in the Euphrates River, fueling anxieties about soaring water pollution.
Local authorities used excavators to skim dead fish from the river surface near the town of Hindiyah, 80 kilometers (50 miles) south of Baghdad, where residents and local farmers have long complained about substandard water management.
The fish were being farmed in cages for sale in domestic markets, where grilled carp is considered a national dish, called masgouf.


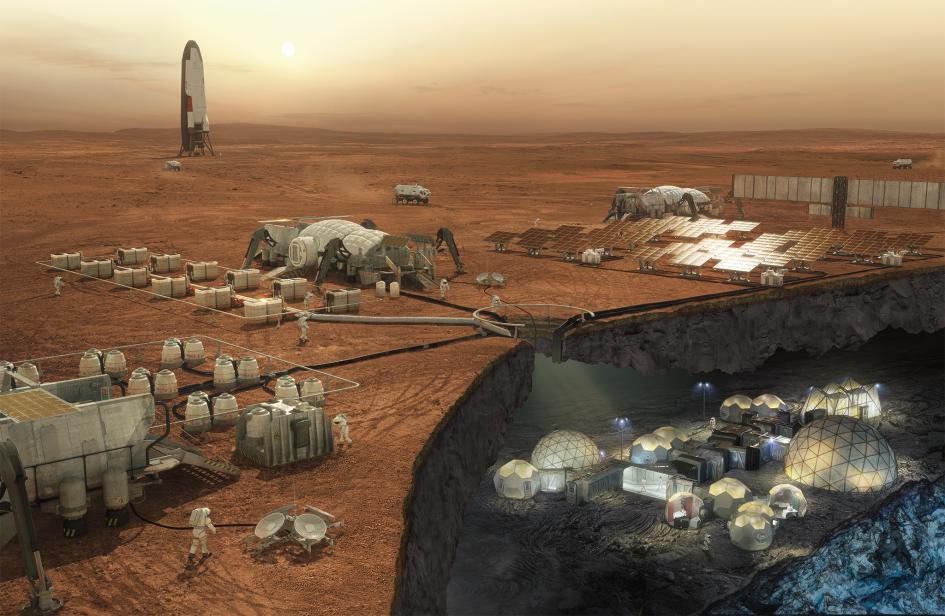
Over the past few months, I was part of a study funded by the United Launch Alliance and supported by a large group of technologists to determine if we can mine water on the Moon and turn it into rocket fuel, and to do it economically. The final report can be downloaded here.
Why Mine Water on the Moon?
The lunar water would be launched off the Moon and delivered to a “gas station” in Earth orbit. This propellant depot will use solar energy to turn the water into rocket fuel. Then, space tugs can refill their tanks so they can repeatedly boost spacecraft from Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO) (where the launch rocket throws them) into Geosynchronous Orbit (GEO) where they can begin operating.