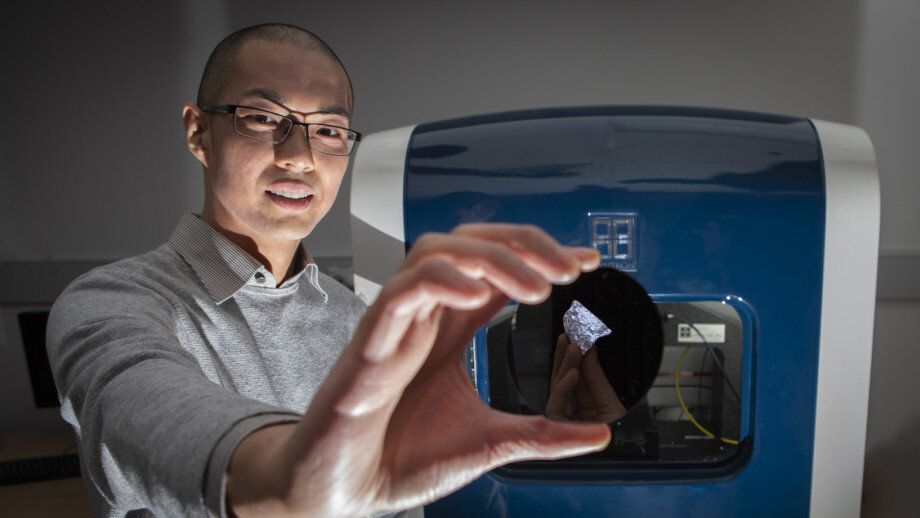
An international research team led by The Australian National University (ANU) has made a new type of silicon that better uses sunlight and promises to cut the cost of solar technology.
The researchers say their world-first invention could help reduce the costs of renewable electricity below that of existing coal power stations, as well as lead to more efficient solar cells.
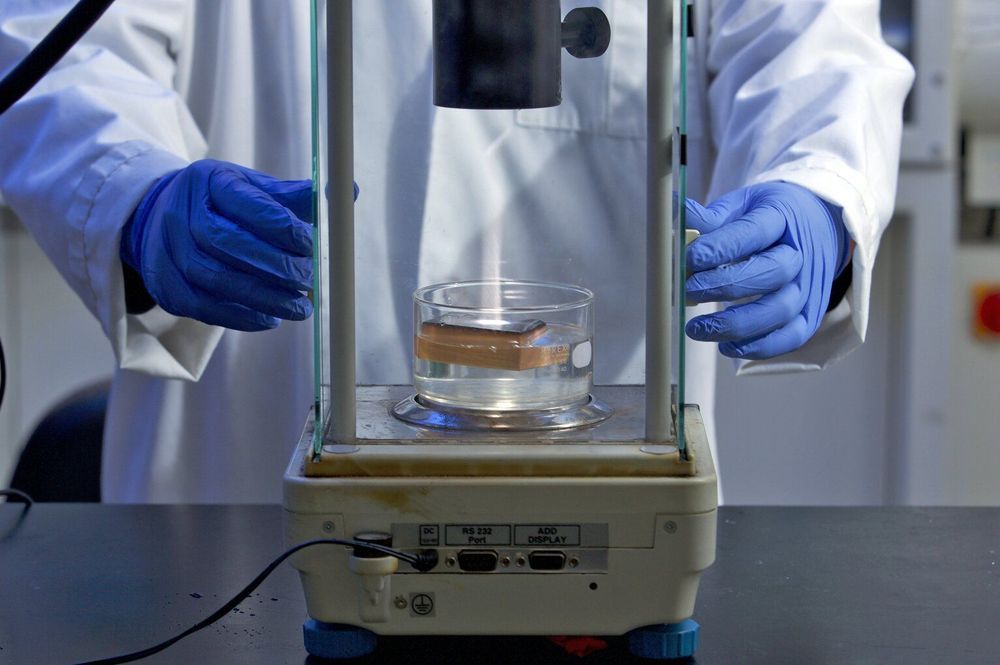
Senior researcher ANU Professor Jodie Bradby said silicon was used as the raw material for solar cells because of its abundance, low-cost and non-toxicity.