SpaceX and NASA are planning a triumphant return to American human spaceflight on May 27, with the SpaceX Demo-2 mission for its Crew Dragon spacecraft. This is the final step required for Crew Dragon to become certified for human flight, after which it’ll enter into regular operational service ferrying people (and some cargo) to the International Space Station on behalf of the U.S. and some of its allies.
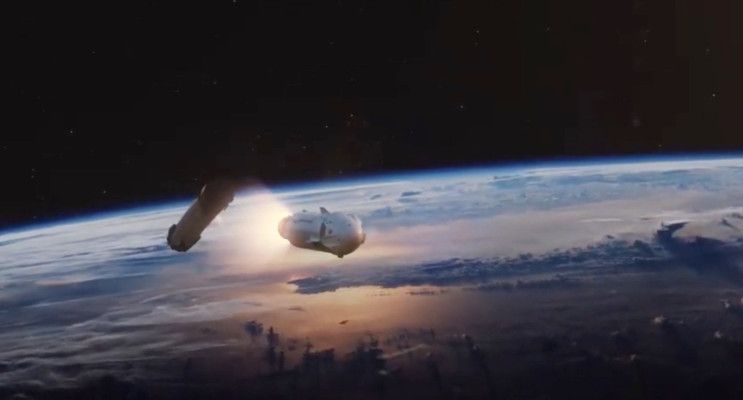
The animation above shows how SpaceX and NASA envision the mission going, from the astronauts stepping out of their ride to the launch pad (a Tesla Model X badged with NASA logos past and present), their trip across the bridge linking the launch tower to the Falcon 9 that will take them up and their spacecraft’s separation from the rocket and subsequent docking procedure with the ISS.
SpaceX and NASA have done plenty of preparation to get to this point, including running a full uncrewed original demo mission that more or less followed this exact flow, just without any actual astronauts on board. That mission also included the undocking of the Crew Dragon capsule, and its return to Earth, with a parachute-assisted splashdown in the ocean.