Amsterdam-based Squad Mobility’s solar powered electric two-seater quickly caught our fancy the last time we covered it. Now the Squad Solar City Car is back with updated design options for the solar-powered microcar.
Category: sustainability – Page 538

No Joke — Algeria Plans 4 Gigawatt, 5 Year Solar Power Initiative
Make no small plans. That seems to be the logic among the leaders of Algeria.
For some perspective, I just wrote about the corporate behemoth Amazon, which hopes to get to 100% renewable electricity by 2025 (firm target of 2030) and has a whopping total of 31 utility-scale wind and solar power plants built or planned that add up to 2,900 MW of total power capacity. That’s 2.3 gigawatts (GW). Algeria is talking about building 4 gigawatts of solar power capacity in 5 years. That’s a pretty stunning target.
Algeria does have a population of 44 million, making it the 32nd most populous country in the world. It also has ample sunshine. Nonetheless, 4 GW means increasing the country’s solar power capacity 10 times over, and that solar power capacity hasn’t changed much in the past 3 years.
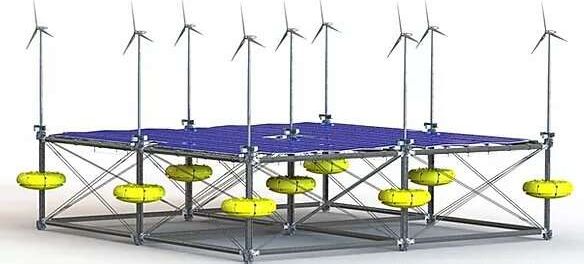
German firm introducing game-changing solar-wind-wave energy platform
A German power firm will launch demonstrations of a one-of-a-kind, triple-threat power generating platform off Iraklio, Greece, later this year.
SINN Power has been testing wave energy converter modules for five years. Buoys attached to steel frame components generate energy as waves push them up and down. The modular nature of the platform is unique in the industry.
“The modular design has been a key element since we started developing maritime technologies that allow flexibility and a wide variety of applications,” according to SINN Power CEO Philipp Sinn. “The floating platform can supply renewable energy to islands across the world … and contribute to the worldwide implementation of offshore wind farms.”
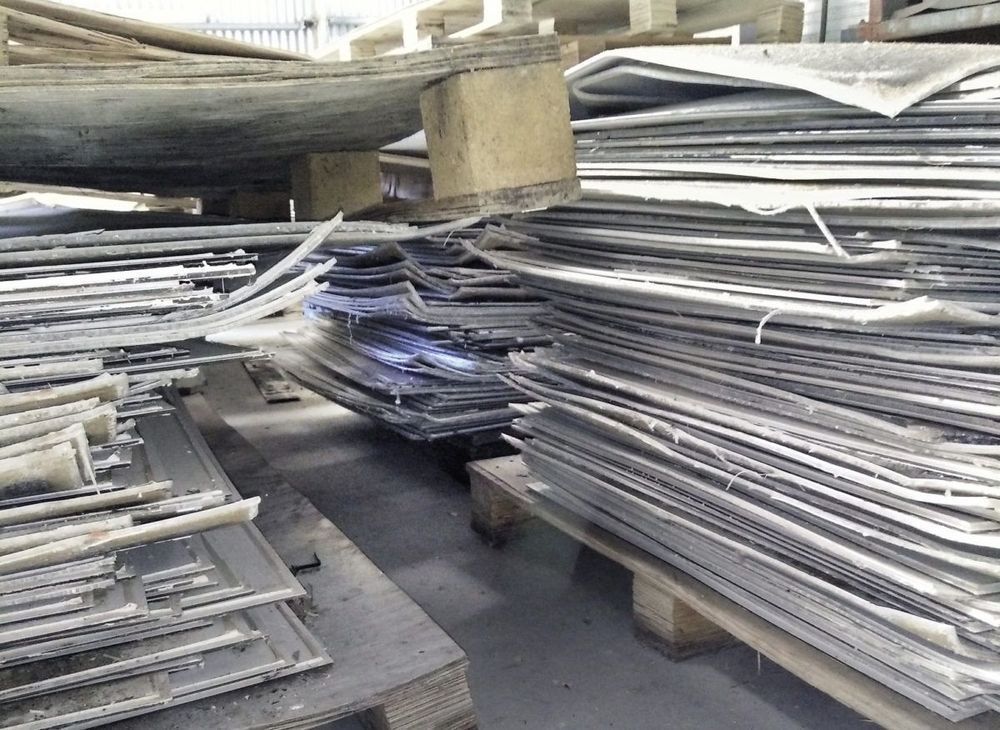

Solar panel recycling: Turning ticking time bombs into opportunities
Australia has certainly demonstrated its appetite for solar power. Now, with the average lifespan of a solar panel being approximately 20 years, many installations from the early 2000’s are set to reach end-of-life. Will they end up in landfill or be recycled? The cost of recycling is higher than landfill, and the value of recovered materials is smaller than the original, so there’s limited interest in recycling. But given the presence of heavy metals, such as lead and tin, if waste is managed poorly, we’re on track for another recycling crisis. A potential time bomb could present itself as an opportunity, however, if the global EV industry showed an interest in the recovered solar products.

New Plant-Based Bottles Made From Plant Sugar Degrade in a Year
A new “all-plant” drink bottle is underway at a Netherlands biochemicals company. These bottles are made from sustainable crops and decompose within a year.
The bottle is made from plant sugars instead of traditional fossil fuels. Avantium is the company behind the bottle. They have already found support from beer company Carlsberg, who plans to sell a plant-plastic lined cardboard bottle in future beverage releases. Coca-Cola and Danone have also backed the product.
Avantium’s chief executive, Tom van Aken told the Guardian that the plan should be finalized by the end of the year, with the bottles hitting supermarket shelves by 2023. “This plastic has very attractive sustainability credentials because it uses no fossil fuels, and can be recycled – but would also degrade in nature much faster than normal plastics do,” says Van Aken.
Watch cyclists charge Tesla Model X with human power
A group of cyclists managed to charge a Tesla Model X electric SUV with their own power.
One of the best things about electric vehicles is that you get to choose where the energy powering your car comes from.
Even if your choices are somewhat limited, there are still a lot more options than with gasoline and diesel vehicles, which will of course each only take their own fuel.
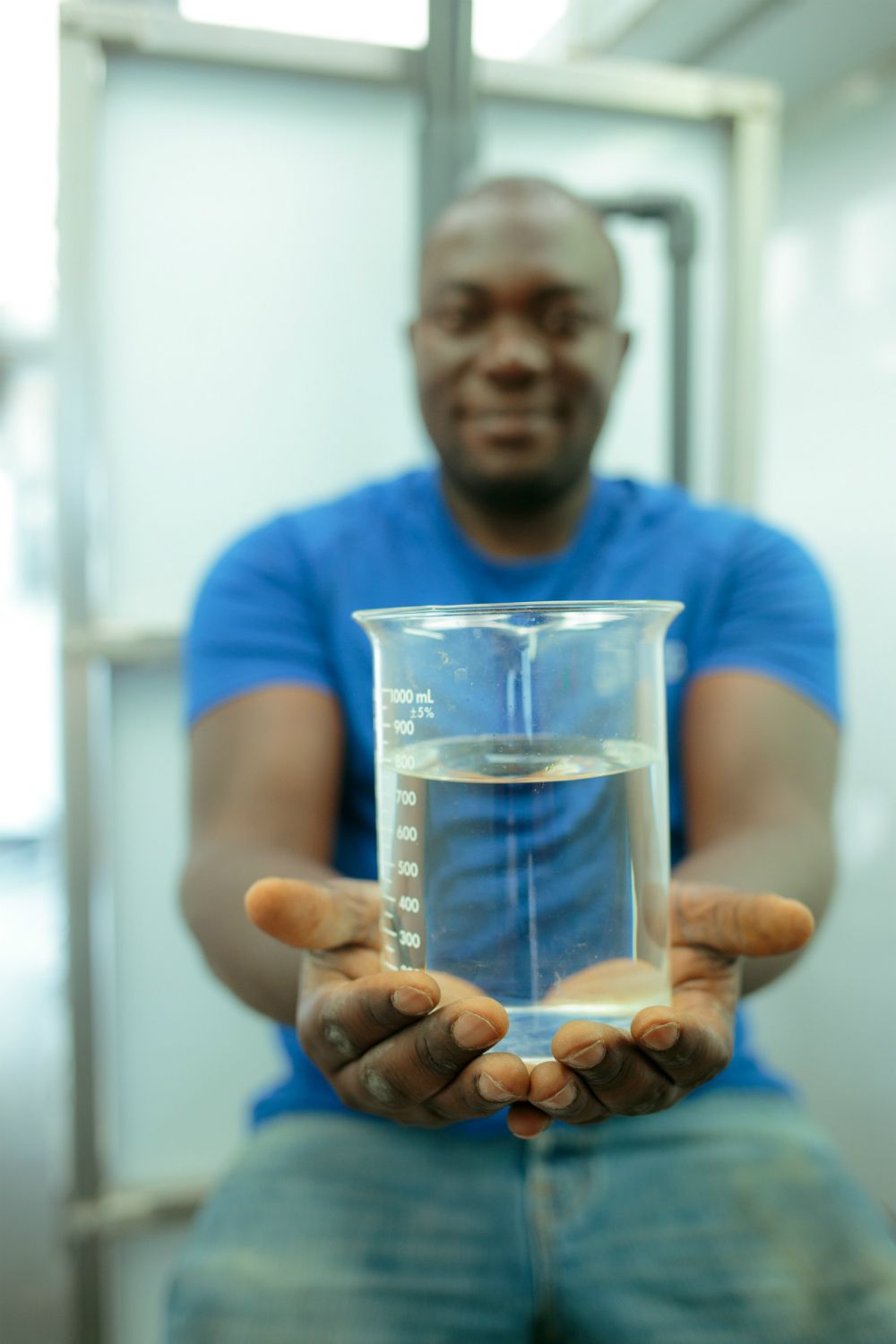



Purified: Two sips into my Centurion Pilsner at a beer garden in Denver, I hiccupped
Hoppy beers do that to me. This beer was different. The water used for the brew came not from a river, a reservoir, or even a well. Instead, the water was sourced from a wastewater treatment plant located along the South Platte River. This simple fact didn’t bother me at all.
To be clear, I’m not a risk taker. Never skydived. Never paddled down Class V rapids. Never swallowed goldfish on a dare. But from what I’ve learned about purification processes for reclaimed water, drinking this limited-edition beer was eminently safe. The pilsner, blonde and translucent, like a Coors, looked and tasted like any number of beers made from water freshly obtained from creeks and rivers tumbling from Colorado’s mountain peaks. As for the strawberry-kiwi wheat beer ordered by my companion, I would have nothing of it. “That’s not beer,” I harrumphed, “that’s a fruit bowl. Undrinkable.”
I was at Declaration Brewing Co., located in Denver’s Overland neighborhood. The brewery and also a winery, InVINtions, located in Greenwood Village, were part of a regional effort. Water for the one-time specialty beverages produced by both came from the PureWater Colorado Demonstration Project. In the demonstration that was conducted in spring of 2018, water providers, engineering companies and water reuse advocates collaborated to showcase direct potable reuse treatment technologies. The water was treated using five different processes until it met federal and state drinking water standards, suitable for human consumption.