This portable device turns seawater into drinking water.



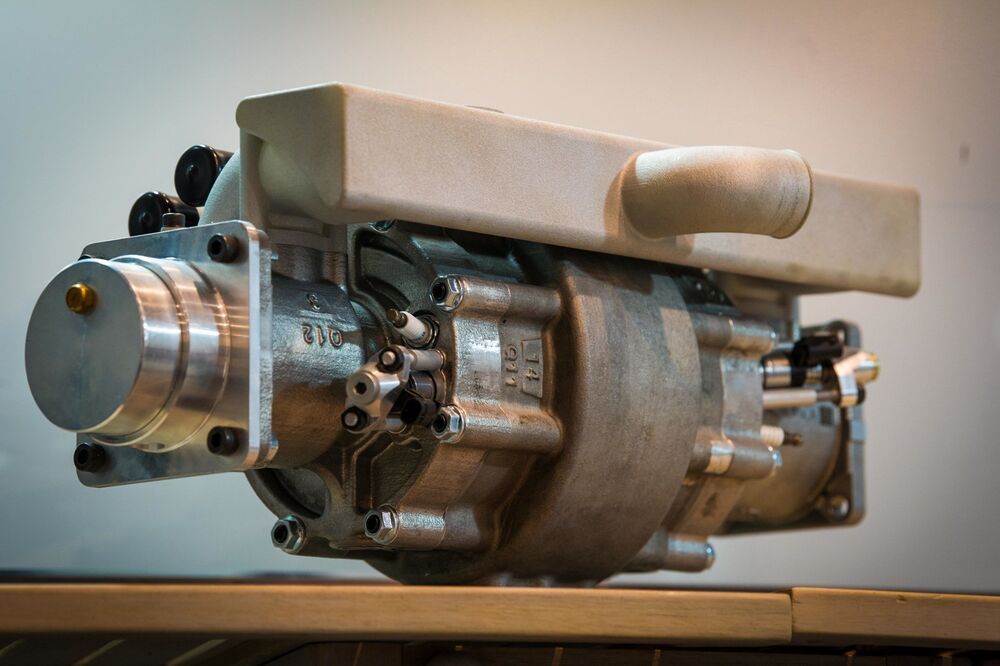
Israel’s Aquarius Engines this week gave the world a first look at the tiny hydrogen engine it hopes can supplant gas engine-generators and hydrogen fuel cells in future electrified vehicles. Weighing just 22 lb (10 kg), the simple engine uses a single moving piston to develop power. Beyond vehicles, Aquarius is developing the engine for use as an off-grid micro-generator.
First created in 2014, Aquarius’ efficient single-piston linear engine has a single central cylinder in which the piston moves between two engine heads. In previous iterations, Aquarius used more conventional fossil fuels to create combustion, but now it’s turning attention to emissions-slashing hydrogen. The company says Austrian engineering firm AVL-Schrick recently completed third-party testing, verifying that a modified version of the engine can operate purely on hydrogen.
“It was always our dream at Aquarius Engines to breathe oxygen into hydrogen technology as the fuel of the future,” explains Aquarius chairman Gal Fridman. “From initial tests, it appears that our hydrogen engine, that doesn’t require costly hydrogen fuel-cells, could be the affordable, green and sustainable answer to the challenges faced by global transport and remote energy production.”

Home batteries are becoming increasingly popular ways to store solar energy to power houses at night, but what if one could make the whole house a battery? Rechargeable cement batteries prove the idea is possible, even if it has a long way to go to be affordable.
Dr Emma Zhang of Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, mixed 0.9 percent carbon fibers into cement and poured it over a metal-coated carbon fiber mesh to make concrete blocks. In the journal Buildings, Zhang and colleagues report that with iron anodes and nickel cathodes these blocks become rechargeable batteries.
At 0.8 Watthours per liter, Zhang’s battery is hundreds of times less energy-dense than a lithium-ion battery, and completely useless for transportation purposes. However, it stores about ten times more energy than previous rechargeable concrete batteries. These, Zhang said in a statement; “Showed very low performance,” forcing her and colleagues to seek new ideas on how to produce the electrodes.
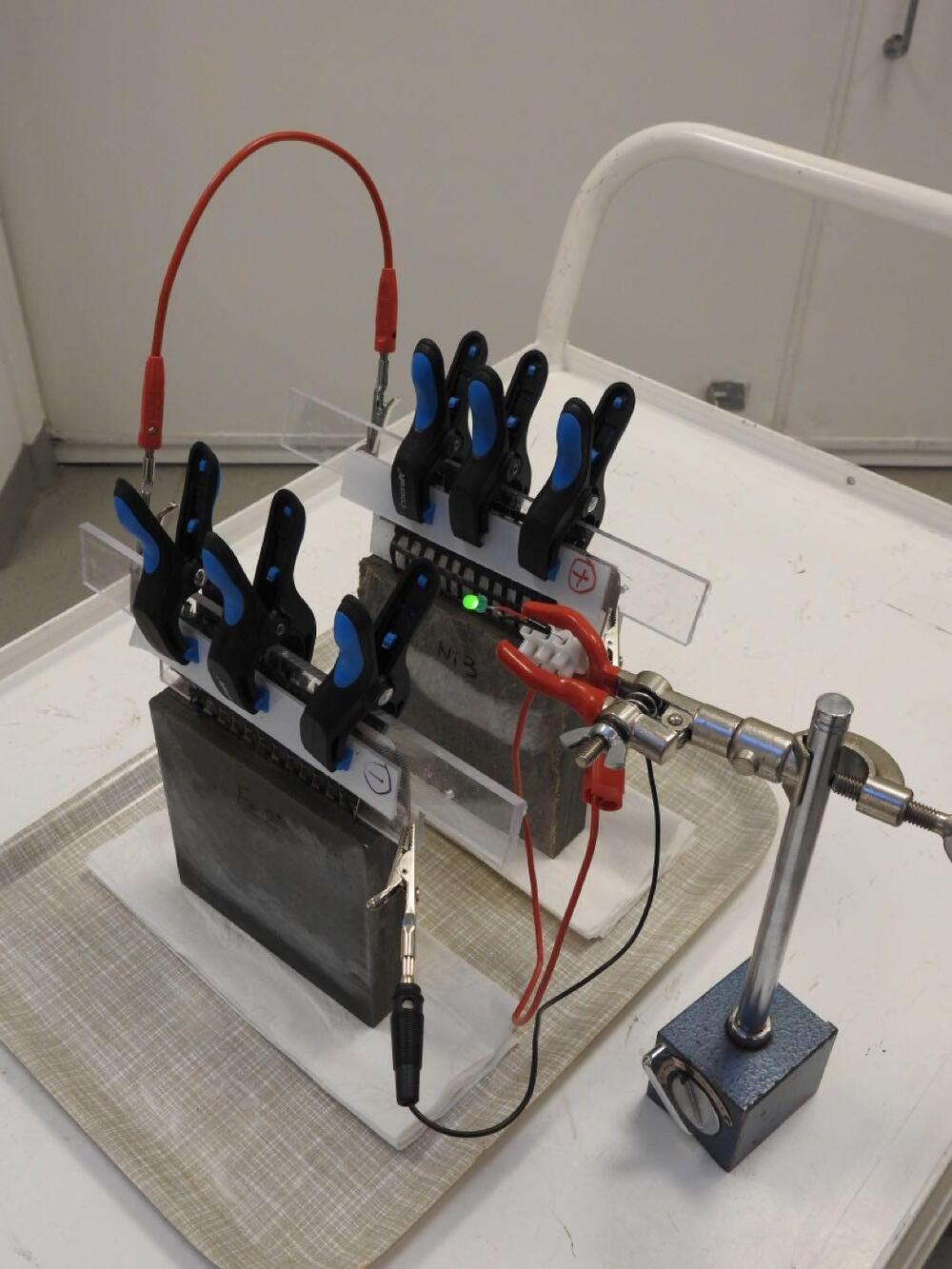
One of the more interesting areas of battery research centers on how these devices can not just store energy, but also double as structural components. We’ve seen some impressive examples of this that could be worked into electric vehicles, and now scientists in Sweden have applied this type of thinking to big buildings, demonstrating a novel type of cement-based battery that could see large structures constructed from functional concrete.
The research was carried out at Chalmers University of Technology, where scientists were working on developing more sustainable building materials, with a particular focus on concrete. As the world’s most widely-used material and one that is very energy intensive to produce, we’re seeing a lot of research into how the carbon footprint of concrete could be reduced, and the authors of this new study have come up with an interesting potential solution.
Like regular concrete, it starts with a cement-based mixture, but one spiked with small amounts of short carbon fibers to add conductivity and flexural strength. Also incorporated into the mix are a pair of carbon fiber meshes, one coated in iron to act as the battery’s anode and the other coated in nickel to act as the cathode. As the battery’s two electrodes, these ferry electrons back and forward as the device is charged and discharged.
Audacious French company Nawa showed off a concept bike in 2019, claiming its supercapacitor-hybrid battery pack could massively boost power and urban range for electric motorcycles. Now, it seems we’ll get a chance to see if the numbers stack up.
We’ve been following Nawa since 2018, when we first spoke to these guys about the potential benefits of using powerful ultracapacitors alongside energy-dense lithium batteries to extend the range and boost the peak power of electric vehicles.
The company wrapped the idea up into a futuristic-looking concept bike for CES 2020, and put some outrageous figures to its claims. Using a 9-kWh lithium battery, you would expect to get around 180 km (110 miles) of urban riding out of a full charge. The Nawa Racer proposed that adding a 0.1-kWh ultracapacitor to the system would boost that range up to around 300 km (180 miles), while unlocking some serious acceleration power to boot.

Click on photo to start video.
This interactive map tracks all the known space junk orbiting Earth. (via BBC World Service.
More on sustainability in space 🚀 https://bbc.in/3n9VQ95

Plastic pollution has become one of the most pressing environmental issues now that the rapidly increased production of disposable plastic products is far beyond the world’s capacity for recycling and upcycling waste plastics. Although recent studies have provided a few catalytic strategies for producing value-added fuel and chemical products from polyethylene (PE) waste, the kinetic rates and/or selectivities are unsatisfactory, even with extended processing time (24 h) and high temperatures (280°C). This work reports a liquid-phase catalytic hydrogenolysis process that highly efficiently converts high-density PE to jet-fuel-and lubricant-range hydrocarbons under relatively mild conditions. The application of this efficient liquid-phase catalytic hydrogenolysis process could provide a promising approach for selectively producing high-value products, such as lubricants, from waste PE and other polyolefin polymers.
Dr. Thomas Lovejoy, is an innovative conservation biologist, who is Founder and President of the non-profit Amazon Biodiversity Center, the renowned Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project, and the person who coined the term “biological diversity”.
Dr. Lovejoy currently serves as Professor in the department of Environmental Science and Policy at George Mason University, and as a senior fellow at the United Nations Foundation based in Washington, DC.
Dr. Lovejoy has also served as the World Bank’s chief biodiversity advisor and the lead specialist for environment for Latin America and the Caribbean, the first Biodiversity Chair of the H. John Heinz III Center for Science, Economics and the Environment, President of the Heinz Center, and chair of the Scientific Technical Advisory Panel (STAP) for the Global Environment Facility (GEF), the multibillion-dollar funding mechanism for developing countries in support of their obligations under international environmental conventions.
Spanning the political spectrum, Dr. Lovejoy has served on science and environmental councils under the Reagan, Bush, and Clinton administrations. At the core of these many influential positions are seminal ideas, which have formed and strengthened the field of conservation biology.
In the 1980s, Dr. Lovejoy brought international attention to the world’s tropical rainforests, and in particular, the Brazilian Amazon, where he has worked since 1965.
With multiple co-edited books (including Biodiversity and Climate Change: Transforming the Biosphere; Drones for Conservation — Field Guide for Photographers, Researchers, Conservationists and Archaeologists; Costa Rican Ecosystems; Climate Change and Biodiversity; On the Edge: The State and Fate of the World’s Tropical Rainforests), Dr. Lovejoy is credited as a founder of the field of climate change biology. He also founded the series Nature, the popular long-term series on public television.
Tune in to find out about how we’re furthering our mission to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.
0:00 Opening Film.
1:26 Introduction, Sundar Pichai.
7:07 Workspace.
34:54 Safer With Google.
43:00 Helpful Information.
1:13:30 Design + Android.
1:41:29 Health.
1:50:43 Sustainability.
To watch this keynote interpreted in American Sign Language (ASL), please click here:
Tweet with us on Twitter: https://twitter.com/google.
Follow us on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/google.
Join us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/Google