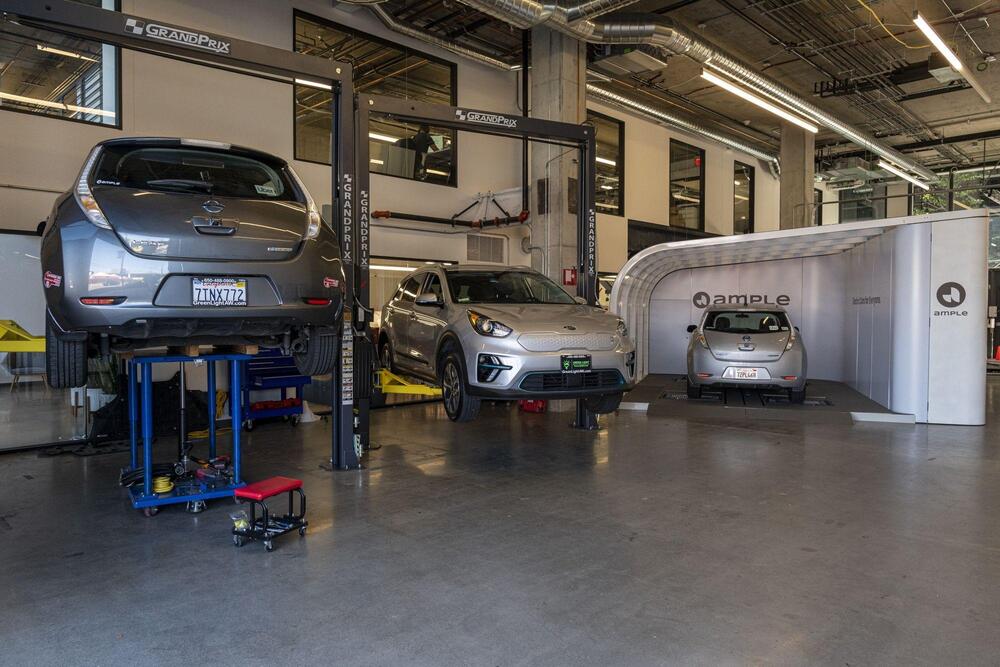
(Bloomberg) — On a Wednesday afternoon in May, an Uber driver in San Francisco was about to run out of charge on his Nissan Leaf. Normally this would mean finding a place to plug in and wait for a half hour, at least. But this Leaf was different.
Instead of plugging in, the driver pulled into a swapping station near Mission Bay, where a set of robot arms lifted the car off of the ground, unloaded the depleted batteries and replaced them with a fully charged set. Twelve minutes later the Leaf pulled away with 32 kilowatt hours of energy, enough to drive about 130 miles, for a cost of $13.
A swap like this is a rare event in the U.S. The Leaf’s replaceable battery is made by Ample, one of the only companies offering a service that’s more popular in markets in Asia. In March, Ample announced that it had deployed five stations around the Bay Area. Nearly 100 Uber drivers are using them, the company says, making an average of 1.3 swaps per day. Ample’s operation is tiny compared to the 100000 public EV chargers in the U.S.—not to mention the 150000 gas stations running more than a million nozzles. Yet Ample’s founders Khaled Hassounah and John de Souza are convinced that it’s only a matter of time before the U.S. discovers that swapping is a necessary part of the transition to electric vehicles.