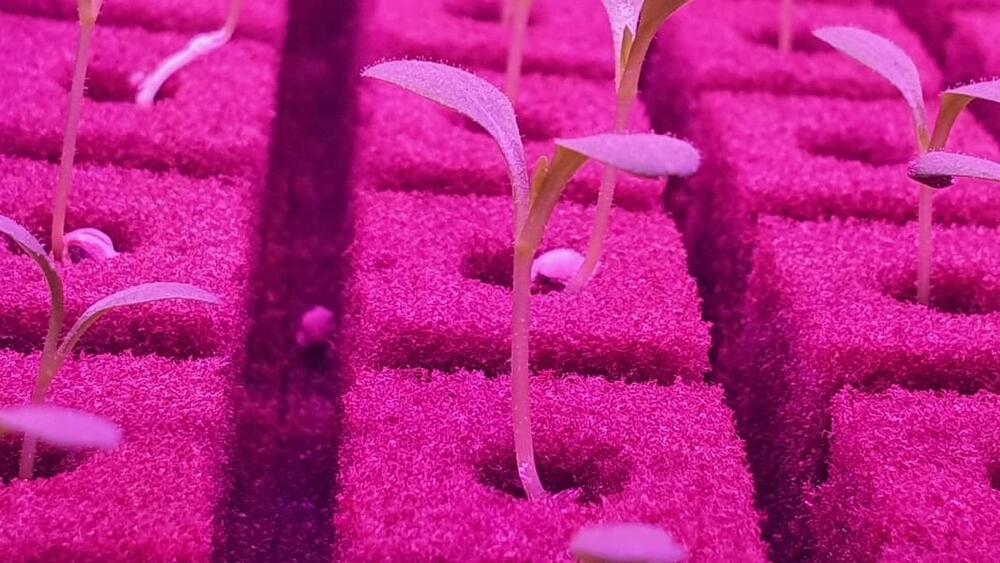
The Dubai facility has the capacity to produce over two million pounds of leafy greens annually, and will grow lettuces, arugula, mixed salad greens, and spinach.
ECO stands for Emirates Crop One; the vertical farm is a joint venture between Crop One Holdings (a Massachusetts-based vertical farming company) and Emirates Flight Catering (the catering business that serves Emirates Airlines). Greens from the vertical farm will be served onboard Emirates flights, and will also be sold in grocery stores in the UAE. Since they’re grown in a sterile environment without pesticides, herbicides, or chemicals, the greens come ready-to-eat and don’t need to be washed.
The UAE is in many ways an ideal location for vertical farming, if not a place where the technology may soon become essential. It gets an abundance of sunlight but doesn’t have much water to speak of (it was, fittingly, the field testing site for a nanoparticle technology that helps sandy soil retain water and nutrients); that means vertical farms could use energy from solar panels to grow food indoors using 95 percent less water than traditional agriculture.