Electrifying transportation is an essential step towards mitigating climate change. To improve the power, efficiency and safety of electric vehicles, researchers must continue to develop better batteries.
All-solid-state lithium batteries (SSBs), which have a solid electrolyte instead of a liquid, are safer than traditional lithium-ion batteries because they are less flammable and more stable at higher temperatures. They could also have higher energy densities than lithium-ion batteries, allowing for longer lasting batteries in smaller sizes for portable electronics and other applications.
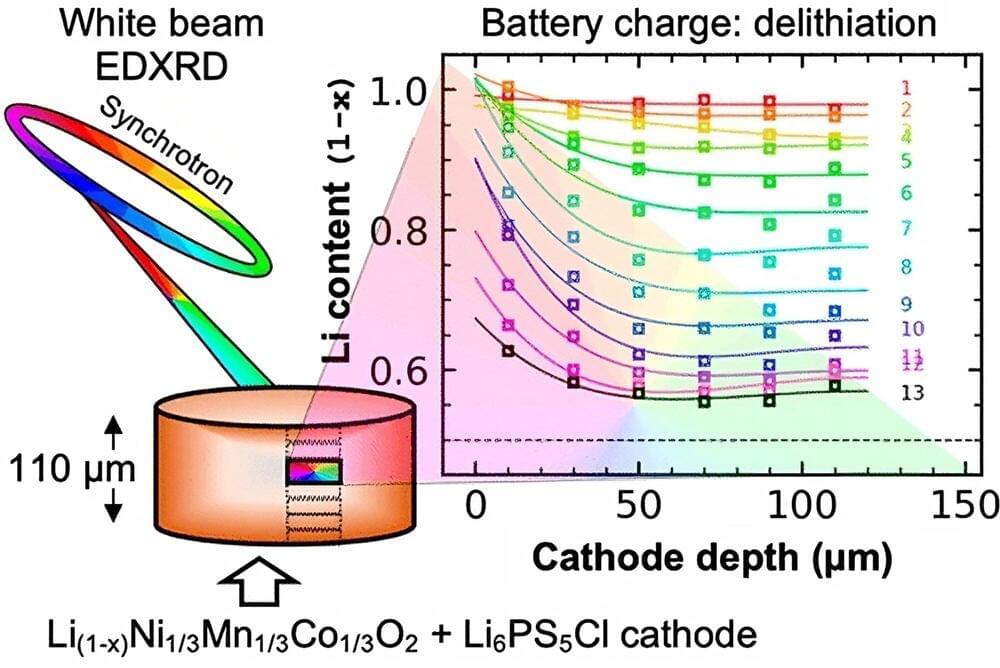
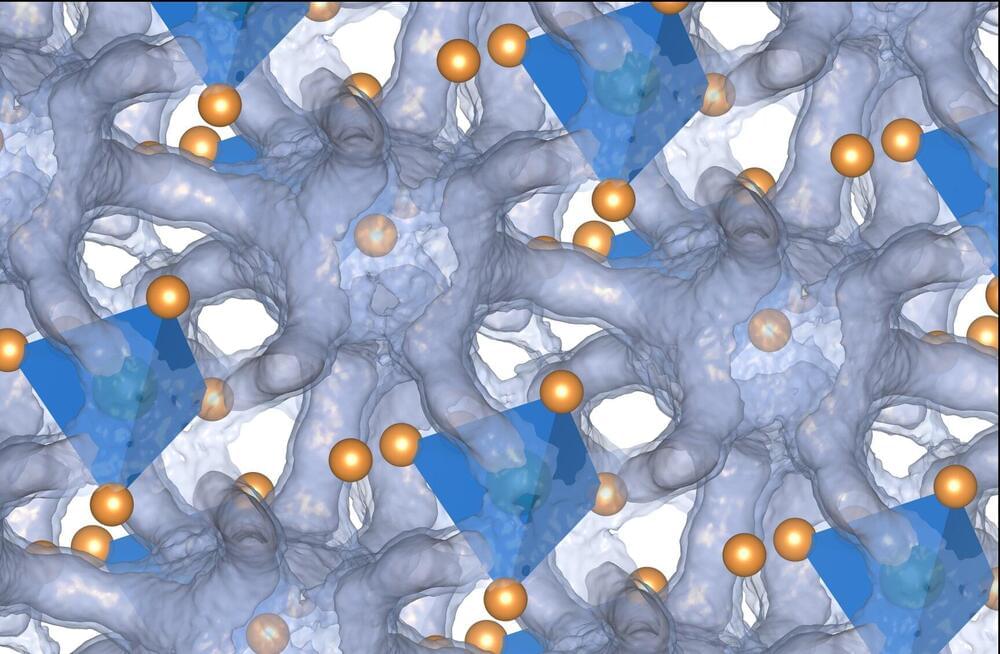
A research team led by Joshua Gallaway of Northeastern University in Boston and scientists at the Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory recently tested how the composition of thick cathodes affected electrochemical reactions in SSBs. The team used the resources of the Advanced Photon Source (APS), a DOE Office of Science user facility at Argonne. Their discoveries were published in the journal ACS Energy Letters.