In recent years, engineers and material scientists have been trying to create increasingly advanced battery technologies that are charged faster, last longer, and can store more energy. These batteries will ultimately play a crucial role in the advancement of the electronics and energy sector, powering the wide range of portable devices on the market, as well as electric vehicles.
Lithium-ion batteries (LiBs) are currently the most widespread batteries worldwide, powering most electronics we use every day. Identifying scalable methods to increase the speed at which these batteries charge is thus one of the primary goals in the energy field, as it would not require switching to entirely new battery compositions.
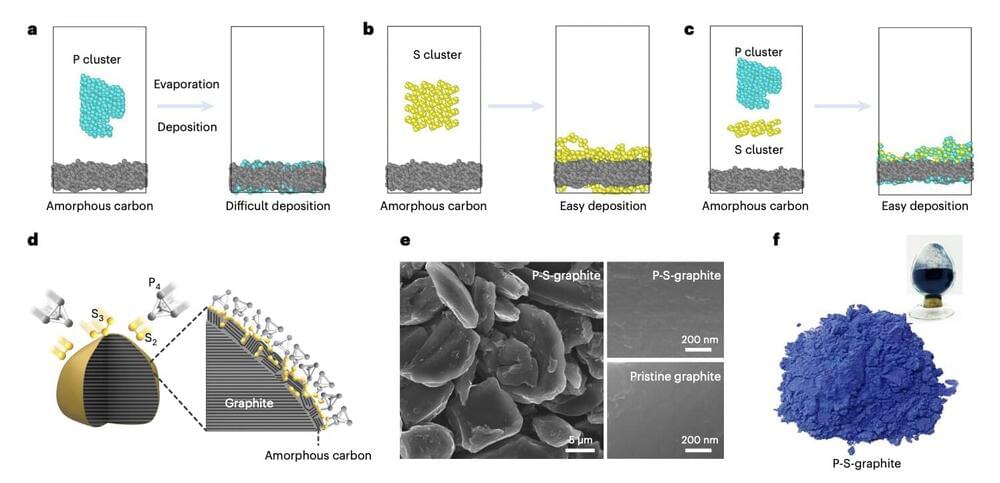
Researchers at Huazhong University of Technology in China recently introduced a new strategy to develop fast-charging LiBs containing a graphite-based material. Their proposed battery design, outlined in a paper published in Nature Energy, was found to successfully speed up the charging time of LiBs, while also allowing them to retain much of their capacity even after they are charged thousands of times.