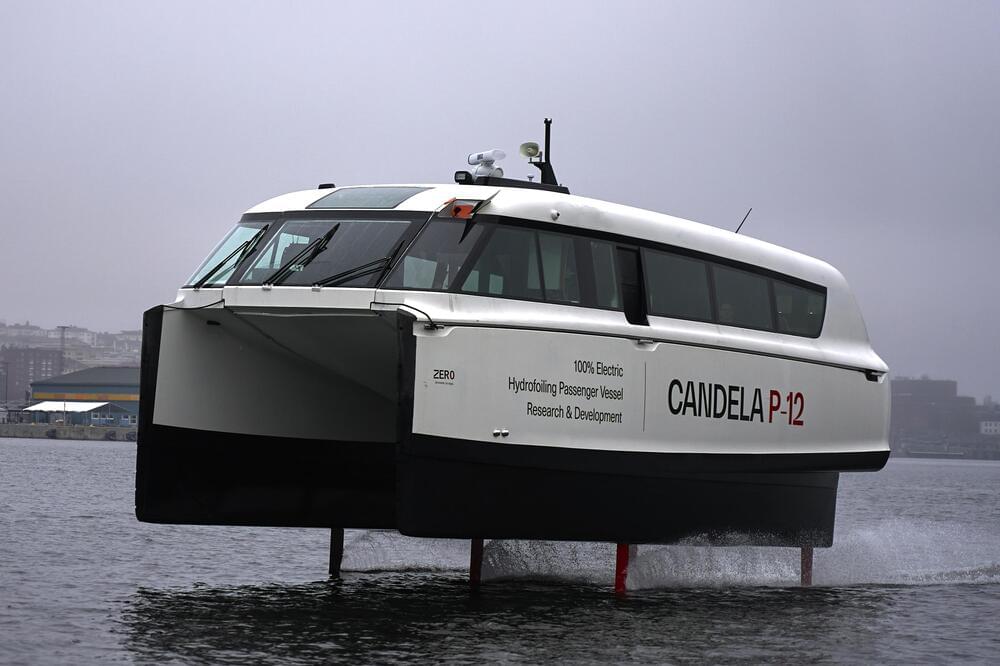
STOCKHOLM (AP) — Many cities around the world see clean and efficient public transport as a crucial way to lower their carbon emissions. For cities with waterways, a high-tech ferry in Sweden could soon set a new standard.
Speeding through Stockholm’s archipelago, electric boat maker Candela’s new P-12 vessel barely makes a sound as it glides over a meter (3 feet) above the water. Its developers hope the ferry, which was unveiled this week, will yield a new era of waterborne public transport.
“This is a real leap forward,” said Erik Eklund, who is in charge of the commercial vessel division at Candela. “The energy savings we get by going airborne on the foils give us the speed and range we need to make this work on batteries.”