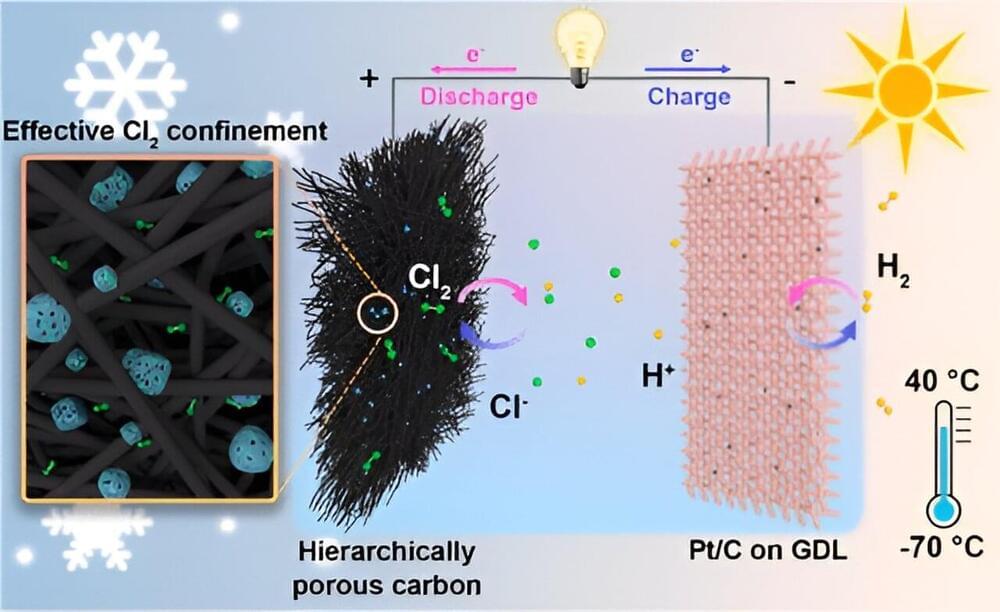
A research team led by Prof. Chen Wei from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) designed a rechargeable hydrogen-chlorine (H2-Cl2) battery that can operate in temperatures ranging from −70°C to 40°C. The study was published in Journal of the American Chemical Society as the cover article.
Hydrogen fuel cells are a promising technology valuable for their sustainability and the abundance of hydrogen, among which H2-Cl2 fuel cells stand out due to fast electrochemical kinetics, high redox potential and high specific capacity of Cl2/Cl- redox couple. However, the volatile chlorine gas cannot be retained during the charging process, resulting in poor Coulombic efficiency (CE) and reversibility. There is an urgent need to develop aqueous chlorine batteries with high performance and applicability at different temperatures.
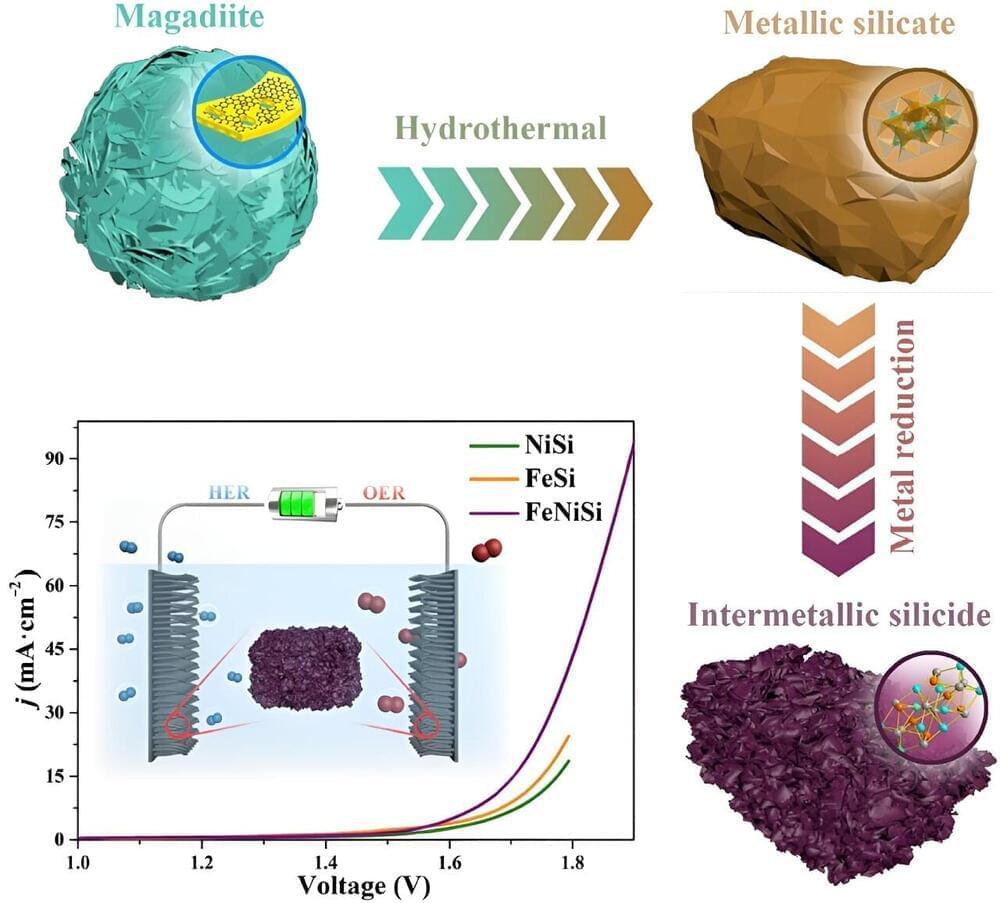
The research team first discovered that due to the lack of binding sites with strong affinity to Cl2, traditional adsorptive cathodes have difficulty immobilizing Cl2, causing low reversibility. To tackle this problem, the team designed a hierarchically porous carbon cathode composed of highly micro-/mesoporous carbon (HPC) and macroporous carbon felt (CF), effectively confining the Cl2 on the cathode and improving the reversibility.