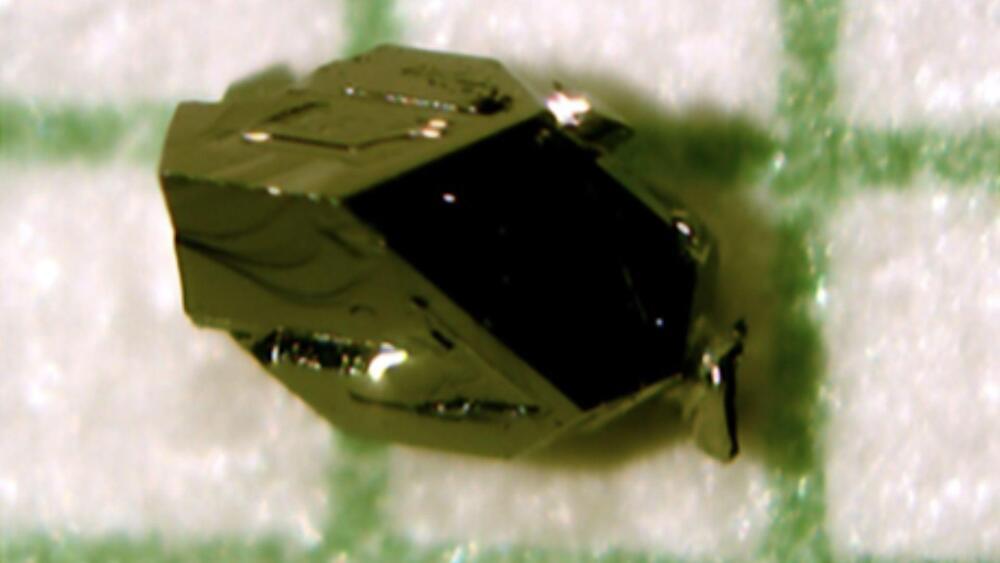
Oregon State University scientists studying ways to filter greenhouse gases from the air recently discovered that when molecules of the metal vanadium are bound with oxygen molecules as peroxide, they can pull carbon dioxide from the air. The carbon molecules can be siphoned off using a small amount of energy that’s then funneled into other uses, like making limestone for buildings or enhancing the atmospheric carbon in greenhouses, accelerating plant growth.
The process could help improve nascent technologies in capturing carbon dioxide from the air to slow the impacts of global climate change. The discovery was published in the journal of the Royal Society of Chemistry in December.
Carbon dioxide is responsible for about two-thirds of the atmospheric heating causing global climate change, and it is primarily released in the burning of fossil fuels for energy, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.