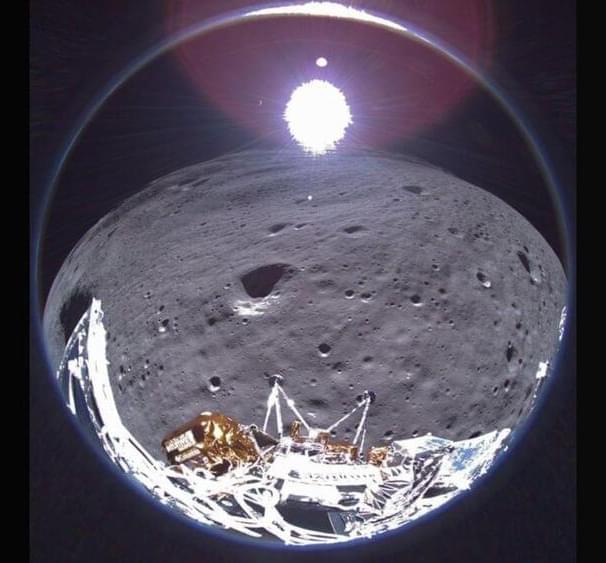
Odysseus, which was built by Houston-based company Intuitive Machines, powered down one week after landing as lunar night began for 14 days. Flight controllers ordered the spacecraft to snooze for three weeks, while the moon’s south pole faced away from the sun, but they hoped Odie would reawaken once sunlight hit its solar panels again.
“Intuitive Machines started listening for Odie’s wake-up signal on March 20, when we projected enough sunlight would potentially charge the lander’s power system and turn on its radio,” representatives of the company wrote on X, formerly called Twitter.