Good news for whom? Producers or consumers? On a scale 1 to 10 is this healthier or not from traditional dark chocolate.
Cocoa fruit contains other valuable ingredients that have been underutilised until now, the researchers say.
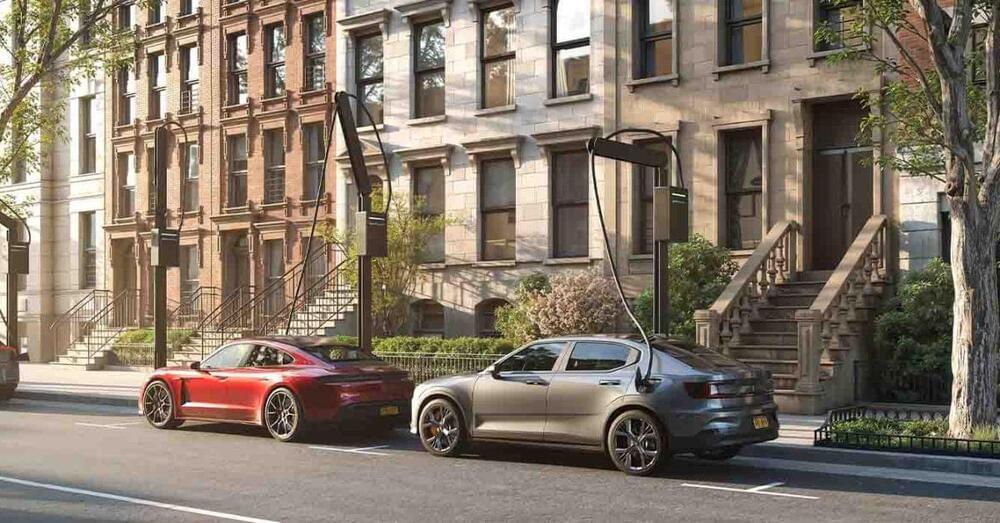


NY-based startup and EV infrastructure specialist Gravity has launched a new line of universal EV charger “trees” it hopes will bring convenient charging sessions curbside on city streets. The deployment will start modestly, but Gravity is targeting a street charging network that is” more expansive than Tesla’s current Supercharger network.”
Gravity Inc. is a startup focused on sustainable fleets and the infrastructure required to operate them efficiently. In 2021, Gravity began rolling out a fleet of all-electric Mustang Mach-E yellow cabs around New York City while partnering with building owners and parking operators to implement electric vehicle charging infrastructure to support individual drivers and large EV fleets.
At that time, Gravity was already teasing plans to open the “only true fast-charging site in Manhattan” to support the taxis and local EV owners. In October 2023, Gravity released a full suite of 500kW EV chargers, some of the fastest we’ve seen.
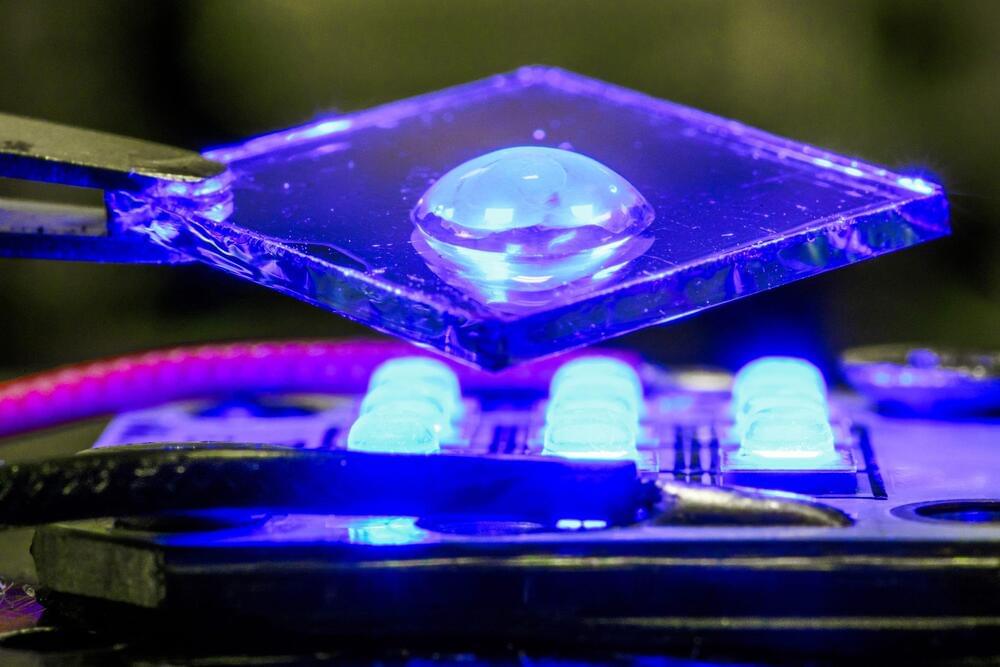


Semiconductors are the foundation of all modern electronics. Now, researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, have developed a new method where organic semiconductors can become more conductive with the help of air as a dopant. The study, published on May 15 in the journal Nature, is a significant step toward future cheap and sustainable organic semiconductors.
“We believe this method could significantly influence the way we dope organic semiconductors. All components are affordable, easily accessible, and potentially environmentally friendly, which is a prerequisite for future sustainable electronics,” says Simone Fabiano, associate professor at Linköping University.
Semiconductors based on conductive plastics instead of silicon have many potential applications. Among other things, organic semiconductors can be used in digital displays, solar cells, LEDs, sensors, implants, and for energy storage.
Innovation For A Sustainable Global Energy Transformation — Dr. Roland Roesch, Ph.D. — Director, Innovation and Technology Centre, International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA)
Dr. Roland Roesch, Ph.D. is Director, Innovation and Technology Centre (IITC), of the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA — https://www.irena.org/) where he oversees the Agency’s work on advising member countries in the area of technology status and roadmaps, energy planning, cost and markets and innovation policy frameworks.
The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) is a leading global intergovernmental agency for energy transformation that serves as the principal platform for international cooperation, supports countries in their energy transitions, and provides state of the art data and analyses on technology, innovation, policy, finance and investment. IRENA drives the widespread adoption and sustainable use of all forms of renewable energy, including bioenergy, geothermal, hydropower, ocean, solar and wind energy in the pursuit of sustainable development, energy access, and energy security, for economic and social resilience and prosperity and a climate-proof future.
Dr. Roesch currently leads IRENA´s work on RE Innovation, Grids-Assessments and the Strategies Teams for the Power Sector Transformation and for the Gas Sector Transformation. He actively leads the development of IRENA´s work in the fields of ocean energy, blue economy and decarbonizing the shipping sector.
Before becoming Director, Dr. Roesch served as IITC Deputy Director from 2018.
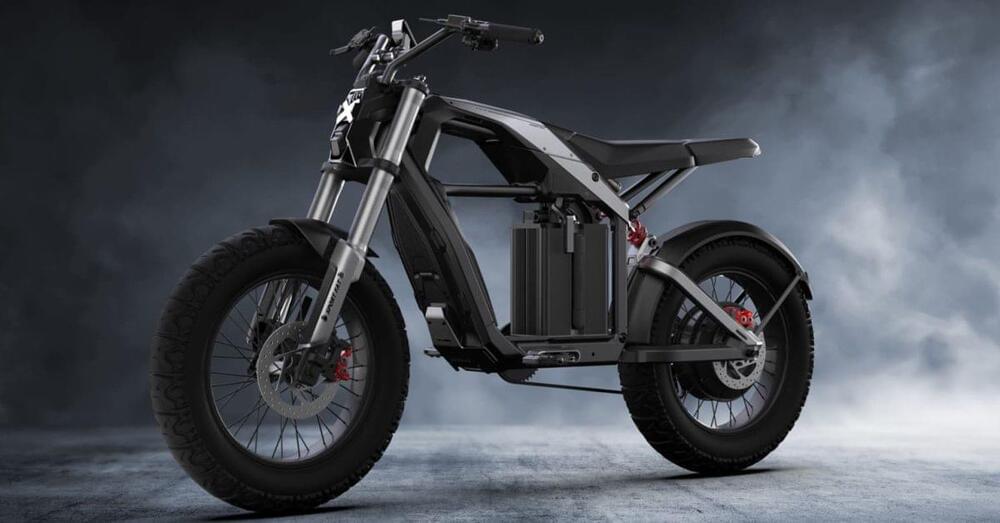


Segway has taken to the Consumer Electronics Expo (CES) in Las Vegas to unveil a pair of new electric two-wheelers. The first is an electric bicycle called the Xafari, while the latter is a borderline electric motorcycle known as the Xyber.
Both bikes are ostensibly categorized as electric bicycles in the US, fitting within the legal definition of the category. The Xafari even feels like it fits nicely under the e-bike classification, though the Xyber seems to carry a bit more Sur Ron vibes than Schwinn vibes, if you get the idea.
Any way you slice them, both bikes mark a major push deeper into the industry for Segway as the company continues to expand in the micromobility category.

A recent United Nations report found that the world generated 137 billion pounds of electronic waste in 2022, an 82% increase from 2010. Yet less than a quarter of 2022’s e-waste was recycled. While many things impede a sustainable afterlife for electronics, one is that we don’t have systems at scale to recycle the printed circuit boards (PCBs) found in nearly all electronic devices.
PCBs — which house and interconnect chips, transistors and other components — typically consist of layers of thin glass fiber sheets coated in hard plastic and laminated together with copper. That plastic can’t easily be separated from the glass, so PCBs often pile up in landfills, where their chemicals can seep into the environment. Or they’re burned to extract their electronics’ valuable metals like gold and copper. This burning, often undertaken in developing nations, is wasteful and can be toxic — especially for those doing the work without proper protections.
A team led by researchers at the University of Washington developed a new PCB that performs on par with traditional materials and can be recycled repeatedly with negligible material loss. Researchers used a solvent that transforms a type of vitrimer — a cutting-edge class of sustainable polymers — to a jelly-like substance without damaging it, allowing the solid components to be plucked out for reuse or recycling.
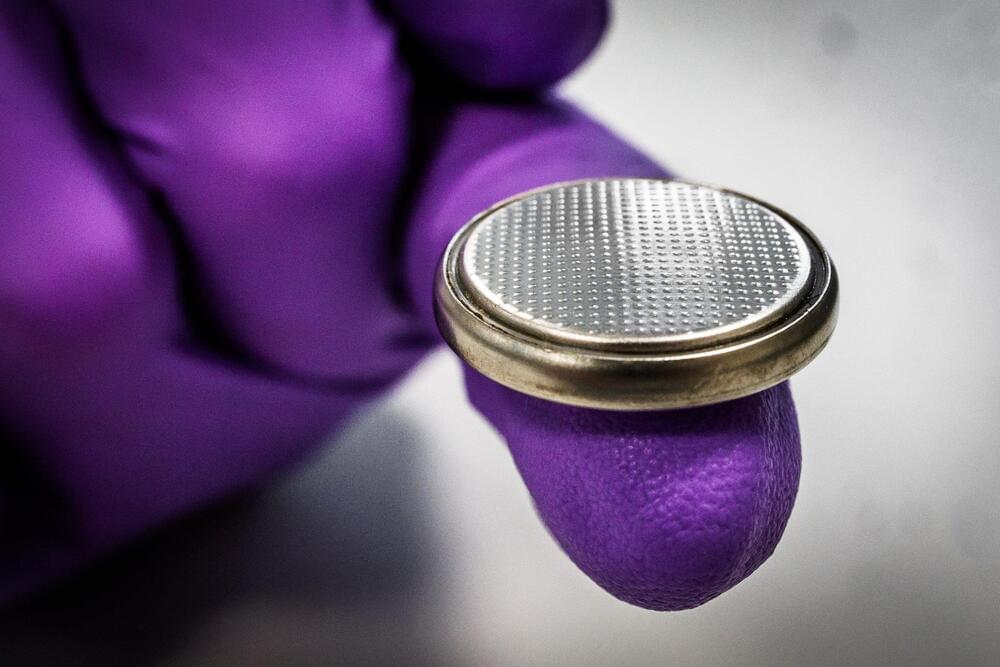

A battery made from zinc and lignin that can be used over 8,000 times has been developed by researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, with a vision to provide a cheap and sustainable battery solution for countries where access to electricity is limited. The study has been published in the journal Energy & Environmental Materials.