As the name suggests, most electronic devices today work through the movement of electrons. But materials that can efficiently conduct protons—the nucleus of the hydrogen atom—could be key to a number of important technologies for combating global climate change.
Most proton-conducting inorganic materials available now require undesirably high temperatures to achieve sufficiently high conductivity. However, lower-temperature alternatives could enable a variety of technologies, such as more efficient and durable fuel cells to produce clean electricity from hydrogen, electrolyzers to make clean fuels such as hydrogen for transportation, solid-state proton batteries, and even new kinds of computing devices based on iono-electronic effects.
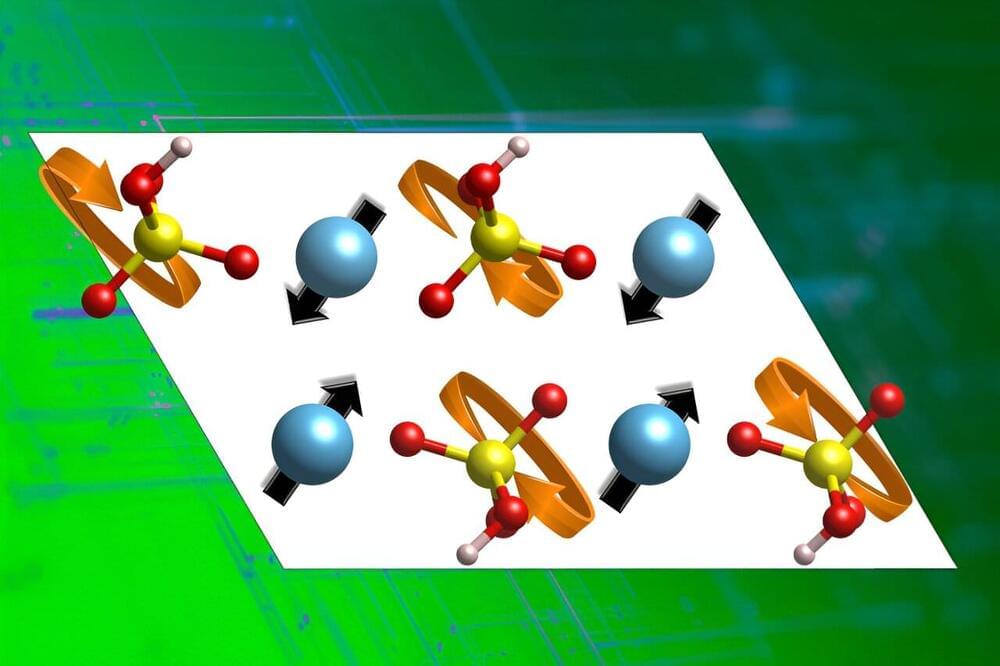
In order to advance the development of proton conductors, MIT engineers have identified certain traits of materials that give rise to fast proton conduction. Using those traits quantitatively, the team identified a half-dozen new candidates that show promise as fast proton conductors. Simulations suggest these candidates will perform far better than existing materials, although they still need to be conformed experimentally. In addition to uncovering potential new materials, the research also provides a deeper understanding at the atomic level of how such materials work.