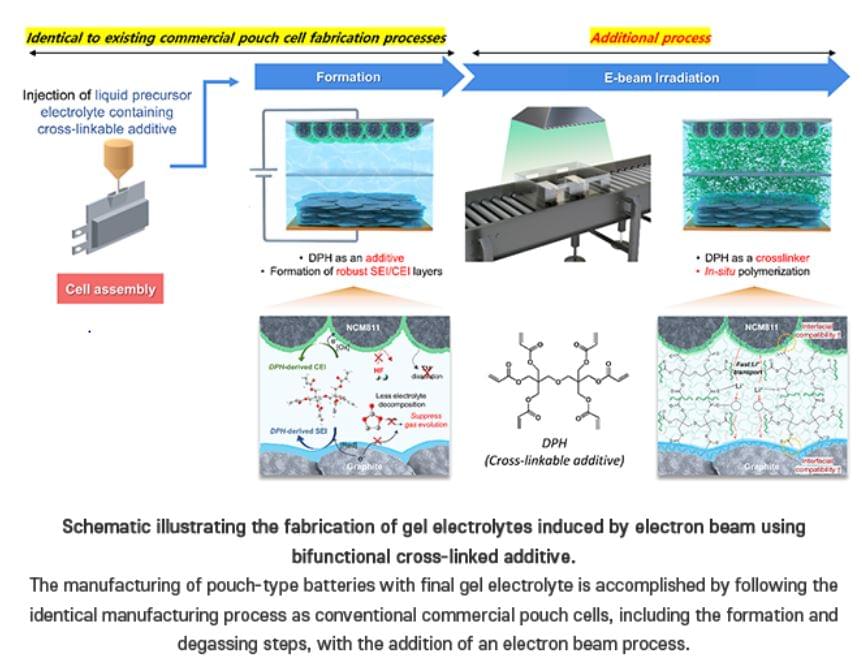
Whoever Controls #Electrolytes will Pave the way for #ElectricVehicles.
Team from the Dept of Chemistry at POSTECH have achieved a breakthrough in creating a gel electrolyte-based battery that is both stable and commercially viable…
Team develops a commercially viable and safe gel electrolyte for lithium batteries. Professor Soojin Park, Seoha Nam, a PhD candidate, and Dr. Hye Bin Son from the Department of Chemistry at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) have achieved a breakthrough in creating a gel electrolyte-based battery that is both stable and commercially viable. Their research was recently published in the international journal Small.
Lithium-ion batteries are extensively utilized in portable electronics and energy storage including electric vehicles. However, the liquid electrolytes used in these batteries pose a significant risk of fire and explosion, prompting ongoing research efforts to find safer alternatives. One alternative is the semi-solid-state battery which represents a middle ground between traditional lithium-ion batteries with liquid electrolytes and solid-state batteries. By using a gel-like electrolyte, these batteries offer enhanced stability, energy density, and a relatively longer lifespan.
Creating gel electrolytes typically involves a prolonged heat treatment at high temperatures, which can degrade the electrolyte, leading to diminished battery performance and increased production costs. Additionally, the interface resistance between the semi-solid electrolyte and the electrode poses a challenge in the fabrication process. Previous studies have encountered limitations in applying their findings directly to current commercial battery production lines due to complex fabrication methods and issues with large-scale applications.