Would you consent to a surveillance system that watches without video and listens without sound?
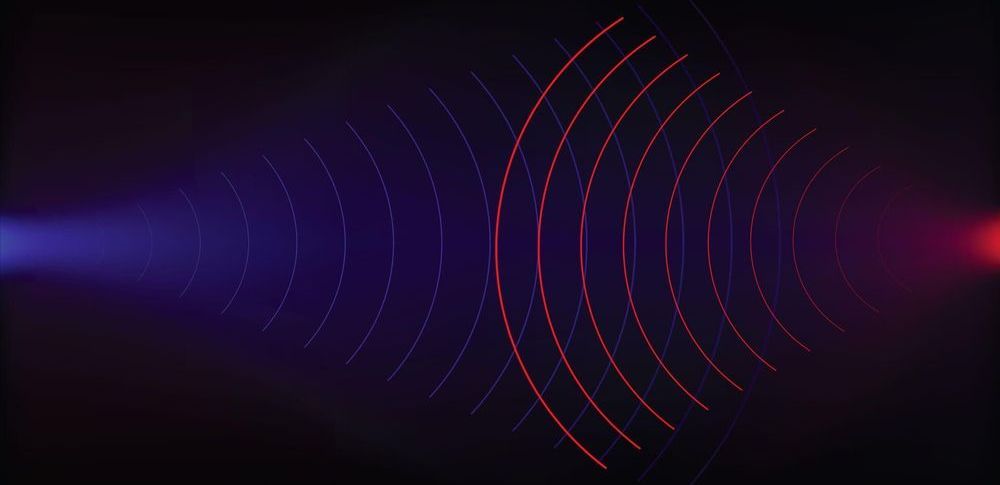
If your knee-jerk reaction is “no!”, then “huh?” I’m with you. In a new paper in Applied Physics Letters, a Chinese team is wading into the complicated balance between privacy and safety with computers that can echolocate. By training AI to sift through signals from arrays of acoustic sensors, the system can gradually learn to parse your movements—standing, sitting, falling—using only ultrasonic sound.
To study author Dr. Xinhua Guo at the Wuhan University of Technology, the system may be more palatable to privacy advocates than security cameras. Because it relies on ultrasonic waves—the type that bats use to navigate dark spaces—it doesn’t capture video or audio. It’ll track your body position, but not you per se.