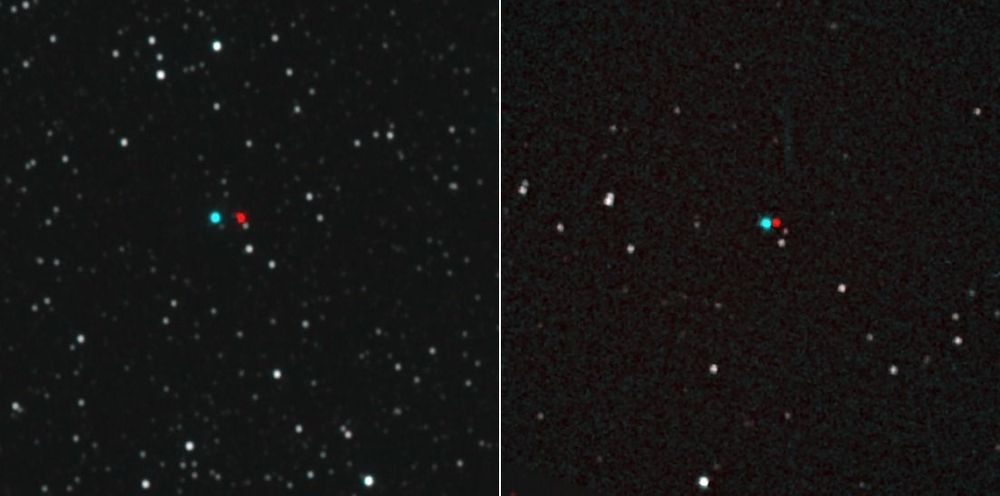
Quantum key distribution (QKD)1,2,3 is a theoretically secure way of sharing secret keys between remote users. It has been demonstrated in a laboratory over a coiled optical fibre up to 404 kilometres long4,5,6,7. In the field, point-to-point QKD has been achieved from a satellite to a ground station up to 1,200 kilometres away8,9,10. However, real-world QKD-based cryptography targets physically separated users on the Earth, for which the maximum distance has been about 100 kilometres11,12. The use of trusted relays can extend these distances from across a typical metropolitan area13,14,15,16 to intercity17 and even intercontinental distances18. However, relays pose security risks, which can be avoided by using entanglement-based QKD, which has inherent source-independent security19,20. Long-distance entanglement distribution can be realized using quantum repeaters21, but the related technology is still immature for practical implementations22. The obvious alternative for extending the range of quantum communication without compromising its security is satellite-based QKD, but so far satellite-based entanglement distribution has not been efficient23 enough to support QKD. Here we demonstrate entanglement-based QKD between two ground stations separated by 1,120 kilometres at a finite secret-key rate of 0.12 bits per second, without the need for trusted relays. Entangled photon pairs were distributed via two bidirectional downlinks from the Micius satellite to two ground observatories in Delingha and Nanshan in China. The development of a high-efficiency telescope and follow-up optics crucially improved the link efficiency. The generated keys are secure for realistic devices, because our ground receivers were carefully designed to guarantee fair sampling and immunity to all known side channels24,25. Our method not only increases the secure distance on the ground tenfold but also increases the practical security of QKD to an unprecedented level.