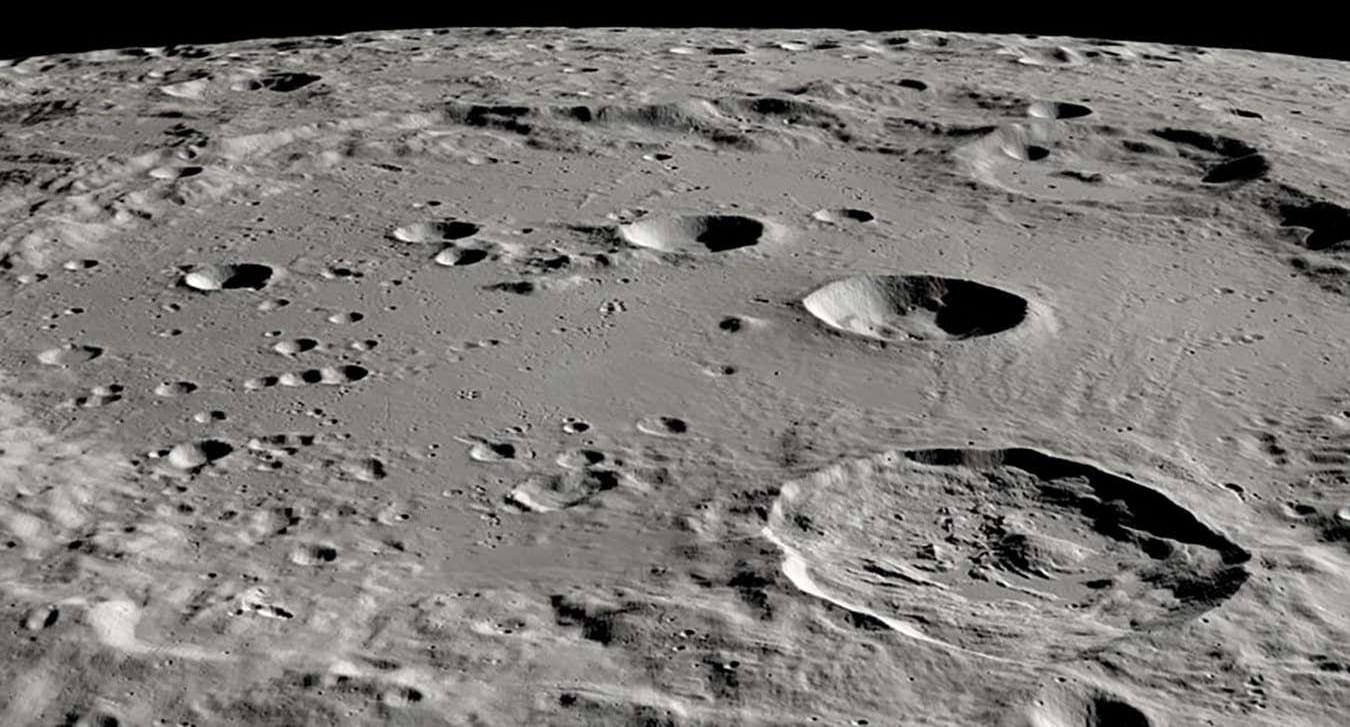
Craters on the moon could hold over a trillion dollars’ worth of platinum and other precious metals deposited there by asteroids. That means lunar prospecting may be more economically viable than travelling to asteroids individually to mine them – but the legality of doing this on the moon remains unclear.
Jayanth Chennamangalam, an independent researcher in Vancouver, Canada, and his colleagues looked at whether there may be commercial quantities of platinum group metals (platinum, palladium, rhodium, ruthenium, iridium and osmium) that were left behind by asteroids hitting the lunar surface.
Image: NASA’s Scientific Visualization Studio
Mining craters on the moon could be more practical than extracting precious metals from asteroids, but it might also introduce new legal difficulties.
By James Woodford