But not anytime soon.
The nation’s newest military branch doesn’t currently launch anyone to the final frontier. But that will change someday, if all goes according to plan.


CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. (AP) — NASA’s first new space potty in decades — a $23 million titanium toilet better suited for women — is getting a not-so-dry run at the International Space Station before eventually flying to the moon.
It’s packed inside a cargo ship that should have blasted off late Thursday from Wallops Island, Virginia. But the launch was aborted with just two minutes remaining in the countdown. Northrop Grumman said it would try again Friday night if engineers can figure out what went wrong.
Barely 100 pounds (45 kilograms) and just 28 inches (71 centimeters) tall, the new toilet is roughly half as big as the two Russian-built ones at the space station. It’s more camper-size to fit into the NASA Orion capsules that will carry astronauts to the moon in a few years.

ESA’s new exoplanet mission, Cheops, has found a nearby planetary system to contain one of the hottest and most extreme extra-solar planets known to date: WASP-189 b. The finding, the very first from the mission, demonstrates Cheops’ unique ability to shed light on the Universe around us by revealing the secrets of these alien worlds.
Launched in December 2019, Cheops (the Characterising Exoplanet Satellite) is designed to observe nearby stars known to host planets. By ultra-precisely measuring changes in the levels of light coming from these systems as the planets orbit their stars, Cheops can initially characterize these planets — and, in turn, increase our understanding of how they form and evolve.
The new finding concerns a so-called ‘ultra-hot Jupiter ’ named WASP-189 b. Hot Jupiters, as the name suggests, are giant gas planets a bit like Jupiter in our own Solar System; however, they orbit far, far closer to their host star, and so are heated to extreme temperatures.

There may be more rogue planets drifting through space in the Milky Way than there are actual stars. This is how they found one of them.
If a solar system is a family, then some planets leave home early. Whether they want to or not. Once they’ve left the gravitational embrace of their family, they’re pretty much destined to drift through interstellar space forever, unbound to any star.
Astronomers like to call these drifters “rogue planets,” and they’re getting better at finding them. A team of astronomers have found one of these drifting rogues that’s about the same mass as Mars or Earth.
Finding something in deep space that emits no light of its own is extremely challenging. But two organizations are doing just that. They’re the OGLE (Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment) collaboration and the KMTN (Korean Microlensing Telescope Network) collaboration.
There’s a reason our Perseverance rover and other missions left Earth for Mars recently: the two planets are close together right now. For those of us still on the ground, this also means Mars will be gorgeous in the sky this month. See more at: http://go.nasa.gov/34hp376

NASA just launched a new citizen science project — it wants the public’s help to find and identify brand new exoplanets.
Human Touch
This is the sort of work that technically could be automated with an algorithm trained to spot new worlds, Space.com reports. But it turns out that in this case, there’s no substitute for human judgment.
“Automated methods of processing TESS data sometimes fail to catch imposters that look like exoplanets,” Veselin Kostov, the NASA researcher leading the Planet Patrol project, said in a press release. “The human eye is extremely good at spotting such imposters, and we need citizen scientists to help us distinguish between the lookalikes and genuine planets.”
This video shows how holographic storage works, using green light to write data as a persistent hologram inside an optical crystal. The data can then be read…How does holographic storage work?
See a home you can live in, make a living out, and grow most of your food in too, the ultimate bug-in or bug-out location — on Mars — here on Earth, or just about anywhere! That is why I call it my Universal Habitat. This is a very low ecological footprint home that can be beautiful, almost no energy cost to maintain, could be built affordably, and be resistant to many natural and man-made disasters such as tornadoes, fire, radiation, and worse. This is the ultimate self-sufficient bunker/fortress.
You can support Galactic Gregs by supporting the sister channel Green Gregs by clicking the links below:
See the Special Deals at My Patriot Supply: www.PrepWithGreg.com
Awesome deals for long term food supplies!
For gardening in your Lunar habitat Galactic Gregs has teamed up with True Leaf Market to bring you a great selection of seed for your planting. Check it out: http://www.pntrac.com/t/TUJGRklGSkJGTU1IS0hCRkpIRk1K

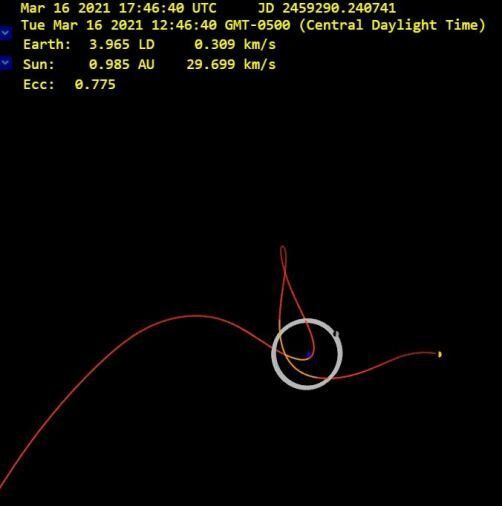
Is it a new asteroid mini–moon or a human-made mini-moon? That’s the question about a small object approaching Earth, called 2020 SO. NASA’s Small Body Database predicts the object will captured by Earth’s gravity in October 2020 and temporarily be trapped in orbit.
But a few unusual characteristics of 2020 SO suggest it might not be a small asteroid, like the two previously known temporary mini-moons that have briefly orbited our planet. Instead, this new object might in fact be an old object from Earth—an old second-stage rocket part from the Surveyor 2 lunar lander mission, launched in 1966.
Mini-moons, or TCOs (Temporarily Captured Objects) have probably occurred more over history than we know, but only two have ever been confirmed: 2006 RH120, which hung out in Earth orbit from 2006 to 2007, and the one discovered earlier this year, 2020 CD3, in Earth orbit from 2018 to 2020. Those objects were definitely small space rocks.
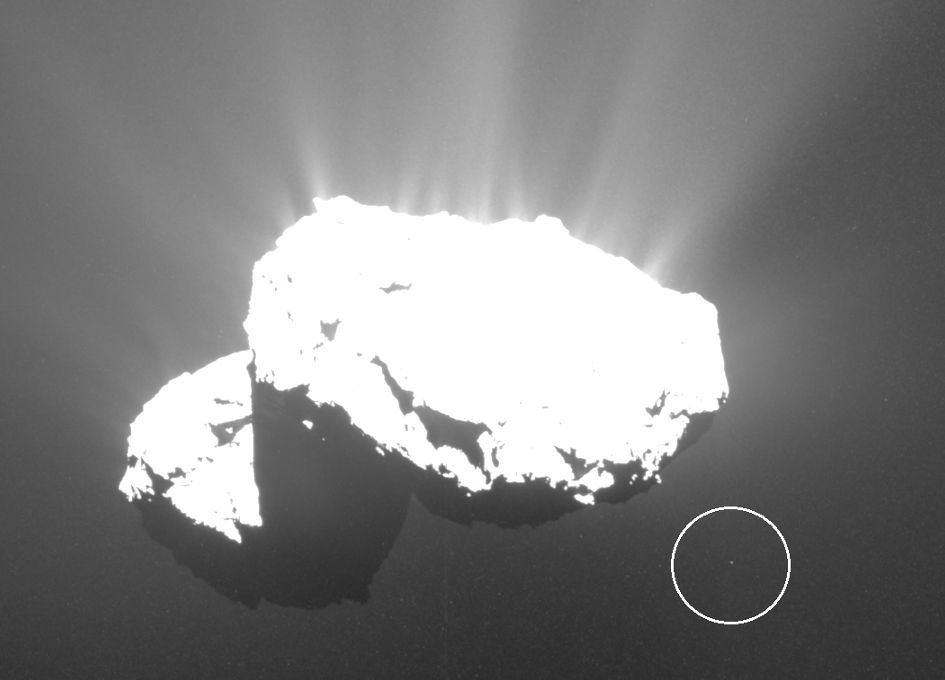

Comet 67P/C-G is a dusty object. As it neared its closest approach to the Sun in late July and August 2015, instruments on Rosetta recorded a huge amount of dust enshrouding the comet.
This is tied to the comet’s proximity to our parent star, its heat causing the comet’s nucleus to release gases into space, lifting the dust along. Spectacular jets were also observed, blasting more dust away from the comet. This disturbed, ejected material forms the ‘coma’, the gaseous envelope encasing the comet’s nucleus, and can create a beautiful and distinctive tail.
A single image from Rosetta’s OSIRIS instrument can contain hundreds of dust particles and grains surrounding the 4 km-wide comet nucleus. Sometimes, even larger chunks of material left the surface of 67P/C-G — as shown here.