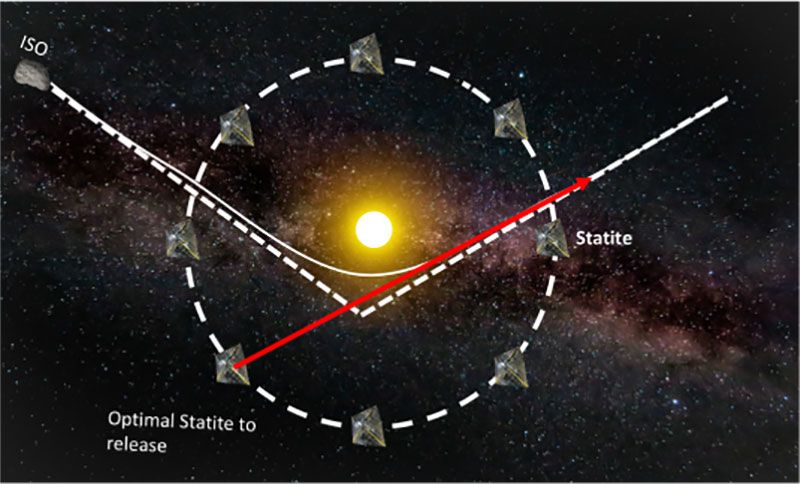
An MIT research proposal outlines a new method for rendezvousing with interstellar objects (ISOs) like ‘Oumuamua using a solar slingshot technique. By using solar sails to position deep-space probes on the edge of the solar system, the idea is to use the gravitational pull of the Sun to accelerate the spacecraft and set it on an intercept course with an interstellar visitor.
When ‘Oumuamua passed by in 2017, it was a truly historic event. For the first time, an object from interstellar space was detected entering the solar system. Traveling on a hyperbolic trajectory, it flew through the inner system before returning to the outer darkness, never to return. As it did so, observatories around the world focused on the object, giving scientists their first close-up glimpse at something that didn’t originate in our system.
However, a glimpse was all they had time for. Ideally, a long, leisurely look would have been preferable, but there wasn’t any time to even plan a mission to send a spacecraft to visit ‘Oumuamua – much less launch one. Worse, such a mission would have faced major technical challenges. Not the least of which being the requirement of a massive rocket to reach the needed velocity to overtake the object.