Heavy instrument platform falls before engineers can perform controlled demolition.





Shockingly, Carroll notes that if our own Earth had formed just one percent farther away from the Sun, it would have suffered a runaway glaciation. By contrast, one percent further in and Earth would have suffered a runaway greenhouse and the fate that befell present-day Venus. “The habitable zone is a planetary tightrope,” writes Carroll.
However, the book does cover the possibility that super-earths and/or gas giant planets that lie in their parent stars’ habitable zones might also harbor planet-sized moons. As the book notes, it’s an idea that Hollywood director James Cameron’s embraced in his ground-breaking movie “Avatar.”
“Envisioning Exoplanets” also offers the reader capsule summaries of the various detection techniques that astronomers have used through the years to remotely explore and characterize these far-flung worlds.
Welcome back to our series on Martian colonization! In Part I, we looked at the challenges and benefits of colonization. In Part II, we looked at what it would take to transport people to and from Mars. In Part III, we looked at how people could live there. Today, we will address the question of how people could establish an industrial base there.
If we intend to “go interplanetary” and establish a colony on Mars, we need to know how to address the long-term needs of the colonists. In addition to shelter, air, water, food security, and radiation shielding, the people will need to create an economy of sorts. The question is, what kind of industry would Mars support?
There’s Gold in Them Thar’ Hills!
One of the main reasons why Mars is considered an attractive location for a colony is the similarities it has to Earth. Like Earth, it’s a terrestrial (aka. rocky) planet that’s composed primarily of metals and silicate minerals, which are differentiated between a metallic core and a silicate mantle and crust.
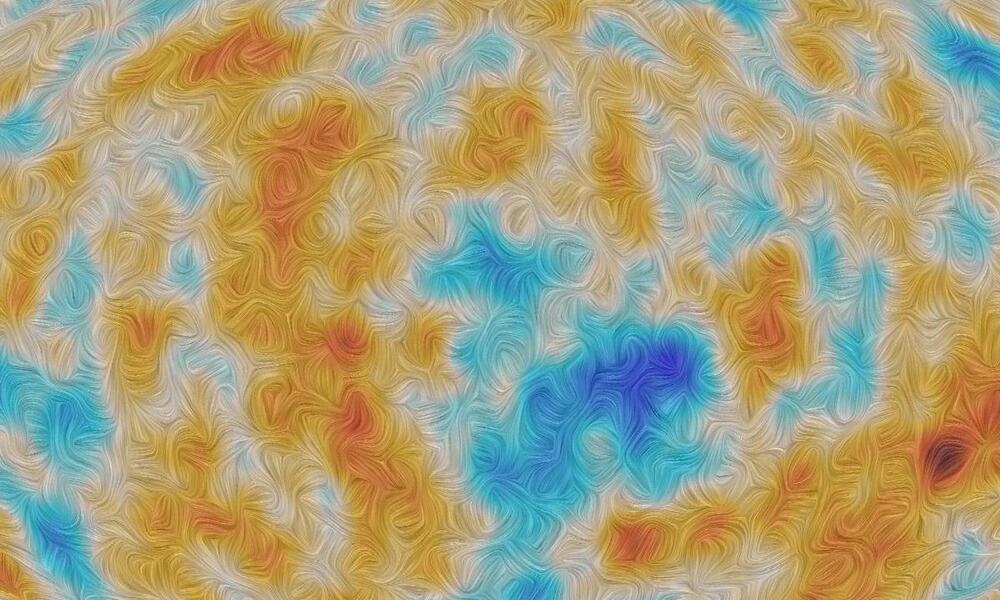
Distant light from the big bang is twisted as it travels to us. This could mean dark matter is more exotic than we thought.
The oldest light in the universe is that of the cosmic microwave background (CMB). This remnant glow from the big bang has traveled for more than 13 billion years. Along the way, it has picked up a few tales about the history and evolution of the cosmos. We just need to listen to what it has to say.
One of the ways the CMB tells a story is through its polarization. If you think of light as an oscillating wave, then this wave motion can have different orientations, the orientation of a light wave’s oscillation is known as its polarization. Often, light is a random jumble of orientations, making it unpolarized, but the light from the CMB is light that has scattered off the hot gas of the early universe and has an orientation known as E-mode polarization.
If there were nothing but empty, flat space between us and the cosmic microwave background, then all the light from the CMB would be E-mode polarized. But deep space isn’t empty. It’s filled not only with diffuse gas and dust, but also dark matter and dark energy. As the light from the big bang travels through this, its polarization changes slightly, twisting through an angle,? This shifts the orientation of CMB light toward B-mode polarization.

Here, he became an authority on the aurora, and after that the director of the Geophysical Institute at the University of Alaska Fairbanks. He later used his reputation and connections to establish the International Arctic Research Center. His look-away-from-the-crowd nature once made a writer describe him as Alaska’s climate-change skeptic.
Wearing suspenders and a button-up dress shirt, Akasofu would — every weekday until the 2020 pandemic — drive 3 miles into the university for a few hours. His workspace is a cubicle in the Akasofu Building. That sun-catching, metal-and-glass structure on the highest part of the Fairbanks campus houses a science institute — the International Arctic Research Center — that would not exist without him.
Akasofu’s Alaska journey began when he wrote a letter to Sydney Chapman, a British space physicist who lived a reverse-snowbird existence, living in Fairbanks in the winter and Boulder, Colorado, in the summer.
The technology doesn’t seem to be here yet; obviously, the ice on Mars will be harvested to provide drinking and irrigation water.
If we ever intend to send crewed missions to deep-space locations, then we need to come up with solutions for keeping the crews supplied. For astronauts aboard the International Space Station (ISS), who regularly receive resupply missions from Earth, this is not an issue. But for missions traveling to destinations like Mars and beyond, self-sufficiency is the name of the game.
This is the idea behind projects like BIOWYSE and TIME SCALE, which are being developed by the Centre for Interdisciplinary Research in Space (CIRiS) in Norway. These two systems are all about providing astronauts with a sustainable and renewable supply of drinking water and plant food. In so doing, they address two of the most important needs of humans performing long-duration missions that will take them far from home.
Even though the ISS can be resupplied in as little as six hours (the time between launch and the time a supply capsule will dock with the station), astronauts still rely on conservation measures while in orbit. In fact, roughly 80% of the water aboard the ISS comes from airborne water vapor generated by breathing and sweat, as well as recycled shower water and urine—all of which is treated with chemicals to make it safe for drinking.
Excerpts from the Red Folder.
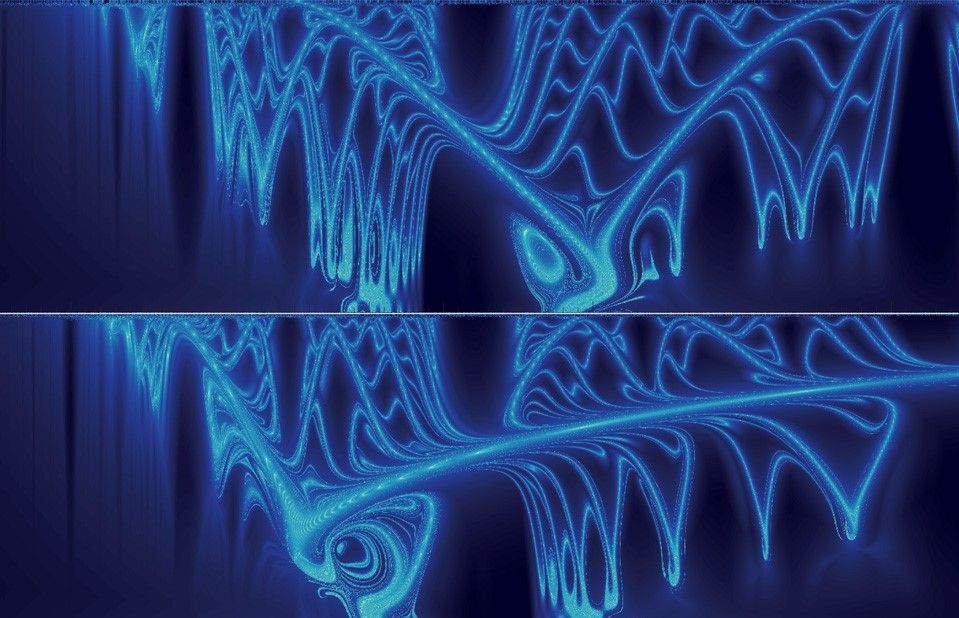
If we had a “Physics paper title of the year award”, the 2020 winner would surely have to be “The arches of chaos in the solar system”, which was published this week in Science Advances by Nataša Todorović, Di Wu and Aaron Rosengren. In their paper, the trio “reveal a notable and hitherto undetected ornamental structure of manifolds, connected in a series of arches that spread from the asteroid belt to Uranus and beyond”. These manifolds are structures that arise from the gravitational interactions between the Sun and planets. They play an important role in spacecraft navigation and also explain the erratic nature of comets.
The paper is beautifully written, describing the manifolds as “a true celestial autobahn,” and going on to say that they “enable ‘Le Petit Prince’ grand tour of the solar system”. And if that has not piqued your curiosity, the figures are wonderful as well – with the above image being “Jovian-minimum-distance maps for the Greek and Trojan orbital configurations”.
The luxury watchmaker Bremont has released the Hawking Limited Edition watch that contains bits of a wooden desk once used by the late Stephen Hawking. The “exquisite chromometer” also contains pieces of a meteorite and is etched with a view of the night sky as seen from Oxford on 8 January 1942, Hawking’s place and date of birth. What is more, the serial number of the watch is printed on paper from a 1979 paper by Hawking that was cowritten by Gary Gibbons.
