Quantum computers developed to date have been one-of-a-kind devices that fill entire laboratories. Now, physicists at the University of Innsbruck have built a prototype of an ion trap quantum computer that can be used in industry. It fits into two 19-inch server racks like those found in data centers throughout the world. The compact, self-sustained device demonstrates how this technology will soon be more accessible.
Over the past three decades, fundamental groundwork for building quantum computers has been pioneered at the University of Innsbruck, Austria. As part of the EU Flagship Quantum Technologies, researchers at the Department of Experimental Physics in Innsbruck have now built a demonstrator for a compact ion trap quantum computer. “Our quantum computing experiments usually fill 30-to 50-square-meter laboratories,” says Thomas Monz of the University of Innsbruck. “We were now looking to fit the technologies developed here in Innsbruck into the smallest possible space while meeting standards commonly used in industry.” The new device aims to show that quantum computers will soon be ready for use in data centers. “We were able to show that compactness does not have to come at the expense of functionality,” adds Christian Marciniak from the Innsbruck team.
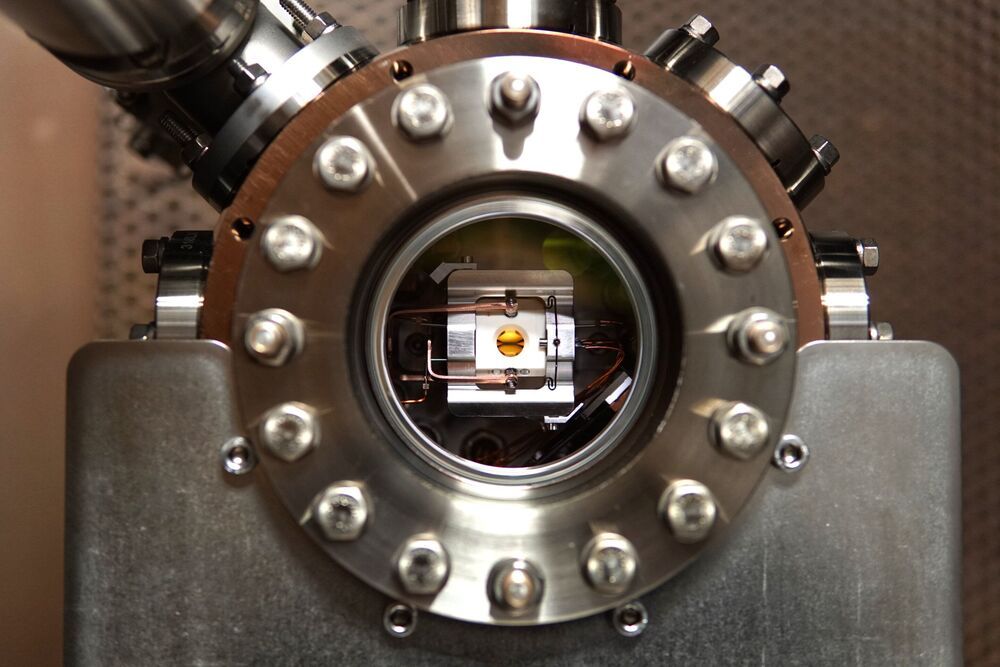
The individual building blocks of the world’s first compact quantum computer had to be significantly reduced in size. For example, the centerpiece of the quantum computer, the ion trap installed in a vacuum chamber, takes up only a fraction of the space previously required. It was provided to the researchers by Alpine Quantum Technologies (AQT), a spin-off of the University of Innsbruck and the Austrian Academy of Sciences which aims to build a commercial quantum computer. Other components were contributed by the Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Optics and Precision Engineering in Jena and laser specialist TOPTICA Photonics in Munich, Germany.