Category: space – Page 658
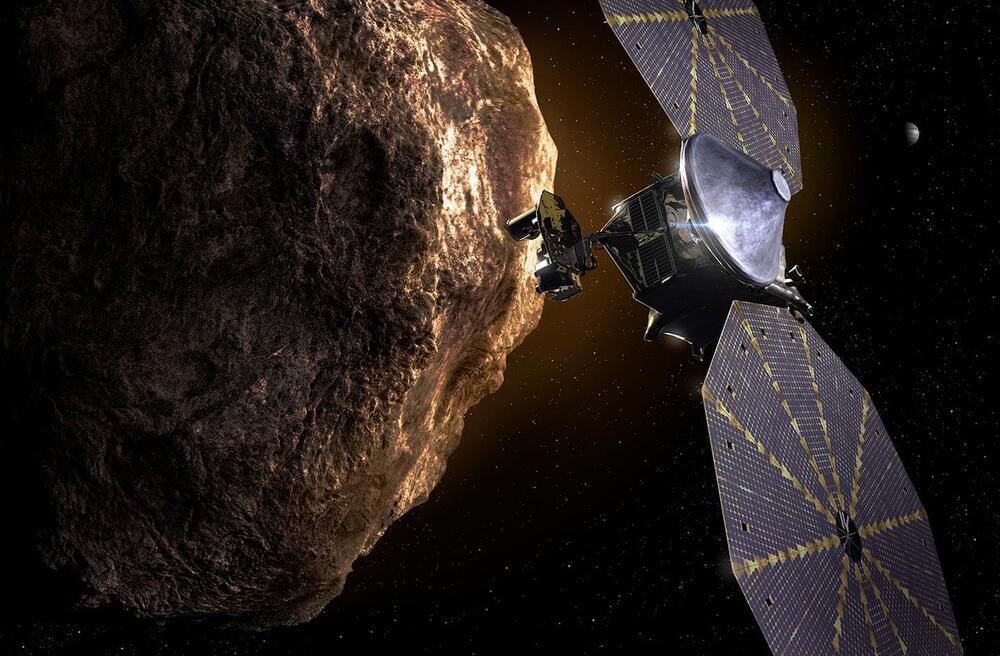

Lucy Is Going to Space — To Explore Time Capsules From the Birth of Our Solar System
Time capsules from the birth of our Solar System more than 4 billion years ago, the swarms of Trojan asteroids associated with Jupiter.
Jupiter is the largest planet in the solar system and the fifth planet from the sun. It is a gas giant with a mass greater then all of the other planets combined. Its name comes from the Roman god Jupiter.

Foundation — Why Asimov’s vision is more relevant than ever
A new video upload. Why the story of Asimov’s Foundation is relevant today.
Can our civilization collapse?
Apple TV has released a new TV series, Foundation, based on Asimov’s book series by the same name.
The story tell about civilization collapse and how scientists who’d predicted the fall can help to soften the fall.
In this video we will review how this story can be relevant to our civilization right here Earth. And what some foundations and organization are doing about it.
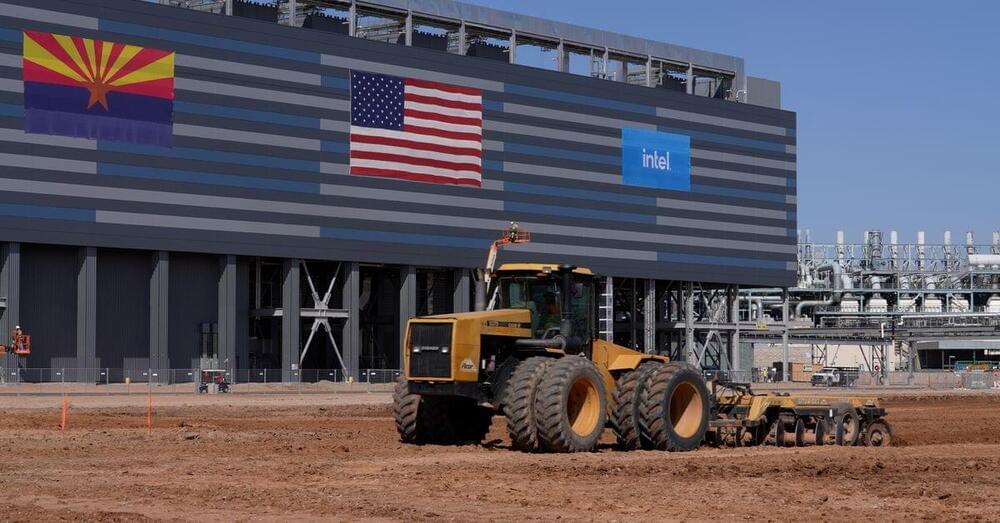


Intel breaks ground on $20 bln Arizona plants as U.S. chip factory race heats up
Sept 24 (Reuters) — Intel Corp (INTC.O) on Friday broke ground on two new factories in Arizona as part of its turnaround plan to become a major manufacturer of chips for outside customers.
The $20 billion plants — dubbed Fab 52 and Fab 62 — will bring the total number of Intel factories at its campus in Chandler, Arizona, to six. They will house Intel’s most advanced chipmaking technology and play a central role in the Santa Clara, California-based company’s effort to regain its lead in making the smallest, fastest chips by 2,025 after having fallen behind rival Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co Ltd (2330.TW).
The new Arizona plants will also be the first Intel has built from the ground up with space reserved for outside customers. Intel has long made its own chips, but its turnaround plan calls for taking on work for outsiders such as Qualcomm Inc (QCOM.O) Amazon.com’s (AMZN.O) cloud unit, as well as deepening its manufacturing relationship with the U.S. military.
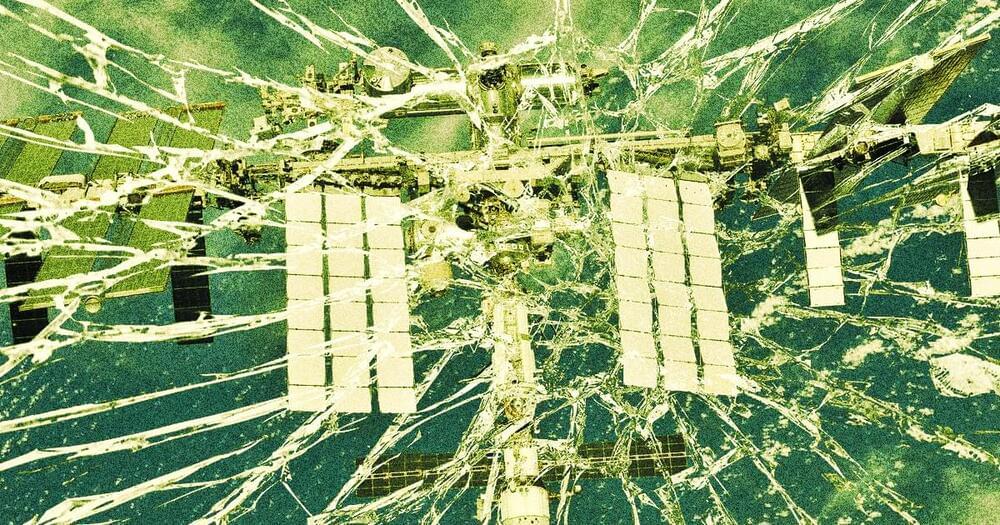

Astronaut Who Helped Build Space Station Says Damage Is “Serious”
The space station has been showing its age, with new damage and other signs of wear being found in various modules. Most recently, Russian cosmonauts spotted about half a dozen new cracks in their Zarya module. And while both NASA and Roscosmos say the cracks don’t pose a threat to crewmembers, Insider reports that Shepherd spoke to a House of Representatives committee on Tuesday, telling the lawmakers that they need to pay attention to the possible hazard, which he called a “serious problem.”
NASA is currently trying to secure another four years’ worth of funding for the ISS, which would allow it to keep the orbital outpost running until 2,028 according to Insider. But Shepherd says NASA would be unwise to do so before actually investigating these cracks to determine not only how bad they are today but whether they’ll continue to get worse, as Russian officials have warned they might.
“Getting to the bottom of this is a fairly serious issue,” Shepherd told Congress. “I don’t think the station’s in any immediate danger. But before we clear the station for another so many years of operational use, we should better understand this.”

