The AstroAccess initiative is working to advance disability inclusion in space.
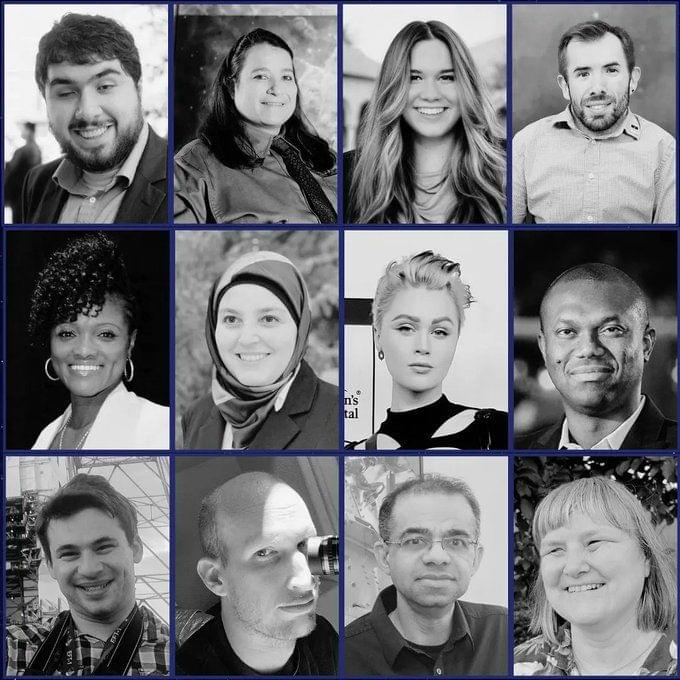
Twelve disability ambassadors will fly weightlessly on Sunday (Oct. 17) as part of an initiative to advance disability inclusion in space.
AstroAccess, the latest mission from the SciAccess Initiative, which aims to make STEM (science, technology, engineering and mathematics) more accessible, will fly a crew of 12 disability ambassadors on a weightless parabolic flight. The flight will take off on Sunday from Long Beach, California, aboard Zero Gravity Corporation’s (Zero-G) “G-Force One” plane, which flies in a parabolic arc pattern that creates short periods of weightlessness in its cabin.