The setting of cookies on this website is set to “Allow Cookies”, in order to provide you with the best possible browsing experience. The site does not use visitor profiling cookies. If you continue to use the Website without changing your cookie settings or click “I Agree” below, you agree to this cookie policy. See also our privacy policy according to GDPR. … I AGREE.
Category: space – Page 52
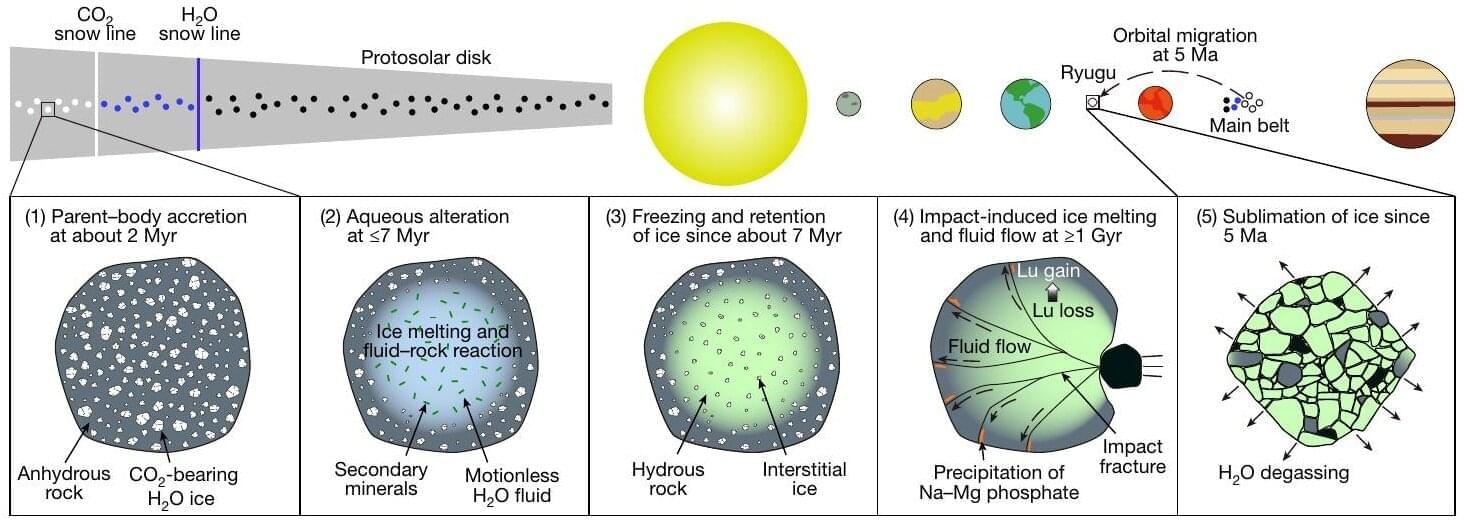
Isotopic analysis determines that water once flowed on asteroid Ryugu
A team of researchers, including those at the University of Tokyo, discovered that liquid water once flowed on the asteroid that spawned near-Earth asteroid Ryugu more than a billion years after it first formed. The finding, based on tiny rock fragments returned by the Hayabusa2 spacecraft of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), overturns long-held assumptions that water activity on asteroids only occurred in the earliest moments of solar system history. This could impact current models, including those describing the formation of Earth.
We have a relatively good understanding of how the solar system formed, but of course there are many gaps. One such gap in our knowledge is how Earth came to possess so much water. It’s long been known that so-called carbonaceous asteroids like Ryugu formed from ice and dust in the outer solar system supplied water to Earth.
Ryugu was famously visited by the Hayabusa2 spacecraft in 2018, the first visit of its kind, where not only were in-situ data collected, but small samples of material were brought back to Earth too. And it’s thanks to this endeavor that researchers can help fill in some missing details in the picture of our creation.
NASA Says Mars Rover Discovered Potential Biosignature Last Year
A sample collected by NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover from an ancient dry riverbed in Jezero Crater could preserve evidence of ancient microbial life. Taken
Redox-driven mineral and organic associations in Jezero Crater, Mars
A geological, petrographic and geochemical survey of distinctive mudstone and conglomerate outcrops of the Bright Angel formation on Mars reveals textures, chemical and mineral characteristics, and organic signatures that warrant consideration as potential biosignatures.
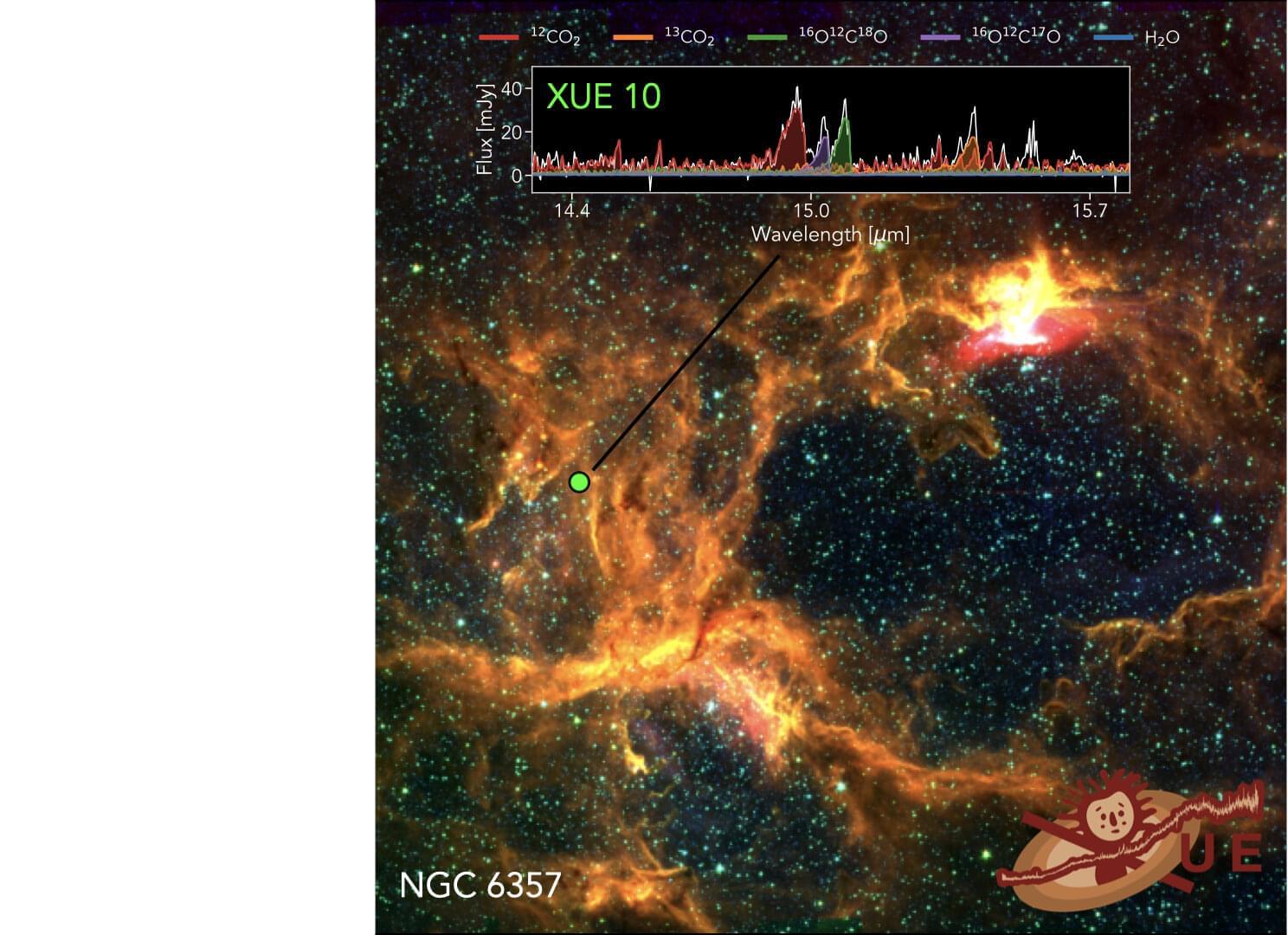
Unusual CO₂-rich disk detected around young star challenges planet formation models
A study led by Jenny Frediani at Stockholm University has revealed a planet-forming disk with a strikingly unusual chemical composition: an unexpectedly high abundance of carbon dioxide (CO2) in regions where Earth-like planets may one day form.
The discovery, made using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), challenges long-standing assumptions about the chemistry of planetary birthplaces. The study is published in Astronomy & Astrophysics.
“Unlike most nearby planet-forming disks, where water vapor dominates the inner regions, this disk is surprisingly rich in carbon dioxide,” says Jenny Frediani, Ph.D. student at the Department of Astronomy, Stockholm University.
Envisioning a Neutrino Laser
A Bose-Einstein condensate of radioactive atoms could turn into a source of intense, coherent, and directional neutrino beams, according to a theoretical proposal.
Neutrinos are the most abundant massive particles in the Universe, yet they are the ones about which we know the least. What makes these elusive particles hard to study is their feeble interaction with matter—trillions of neutrinos pass through our bodies every second without leaving a trace. However, neutrinos may hold deep secrets about the Universe—understanding their properties could hint at new particles and forces beyond the standard model of particle physics or shed light on why matter came to dominate over antimatter. Despite these tantalizing prospects, some of the most basic questions about neutrinos remain unanswered. To address such questions experimentally, Benjamin Jones of the University of Texas at Arlington and Joseph Formaggio of MIT suggest that a Bose-Einstein condensate (BEC) of radioactive atoms could offer a platform for building a “neutrino laser” [1].
BREAKING: Tesla Megablock Revolution | Fast Power, Grid Stability & AI Ready Solutions
Tesla megablock revolution | fast power, grid stability & AI ready solutions.
## Tesla’s Megablock is a revolutionary energy storage solution that enables fast power, grid stability, and scalability to support widespread renewable energy adoption, AI data centers, and energy independence.
## Questions to inspire discussion.
🚀 Q: How quickly can Tesla’s Megablock be deployed? A: Tesla’s Megablock can deliver 1 GWh of power in just 20 days, capable of powering 40,000 homes in less than a month.
⚡ Q: What makes the Megablock’s deployment so efficient? A: The Megablock’s modular, plug-and-play design allows for rapid scalability and deployment, with integrated transformers and switchgear reducing complexity.
Grid Stability and Performance.
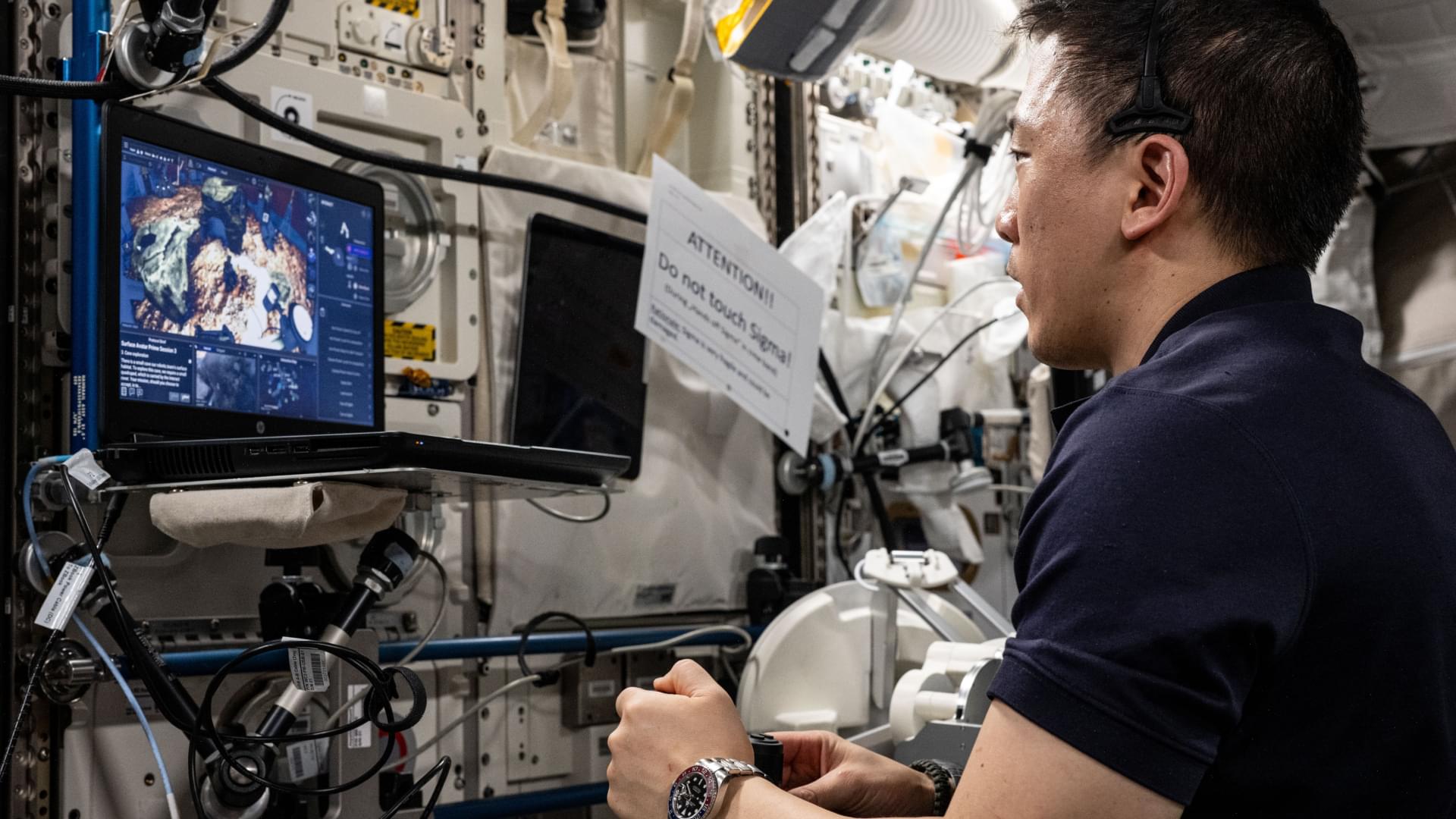
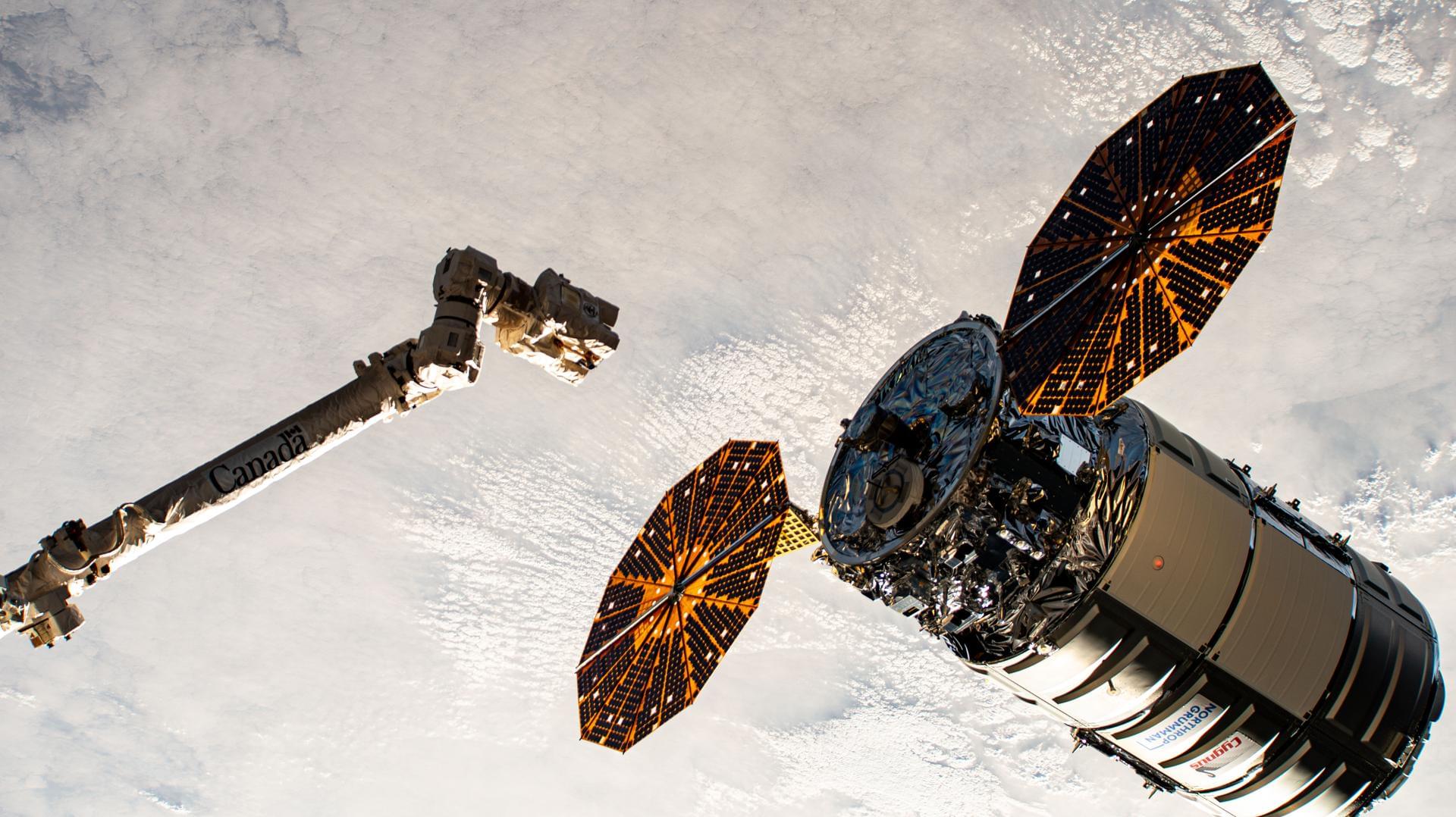


NASA Sets Coverage for Northrop Grumman CRS-23, SpaceX Falcon 9 Launch
NASA, Northrop Grumman, and SpaceX are targeting no earlier than 6:11 p.m. EDT, Sunday, Sept. 14, for the next launch to deliver science investigations, supplies, and equipment to the International Space Station. The mission is known as NASA’s Northrop Grumman Commercial Resupply Services 23, or Northrop Grumman CRS-23.
Watch the agency’s launch and arrival coverage on NASA+, Amazon Prime, and more. Learn how to watch NASA content through a variety of platforms, including social media.
Filled with more than 11,000 pounds of supplies, the Northrop Grumman Cygnus XL spacecraft, carried on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, will launch from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. This mission will be the first flight of the Cygnus XL, the larger, more cargo-capable version of the company’s solar-powered spacecraft.
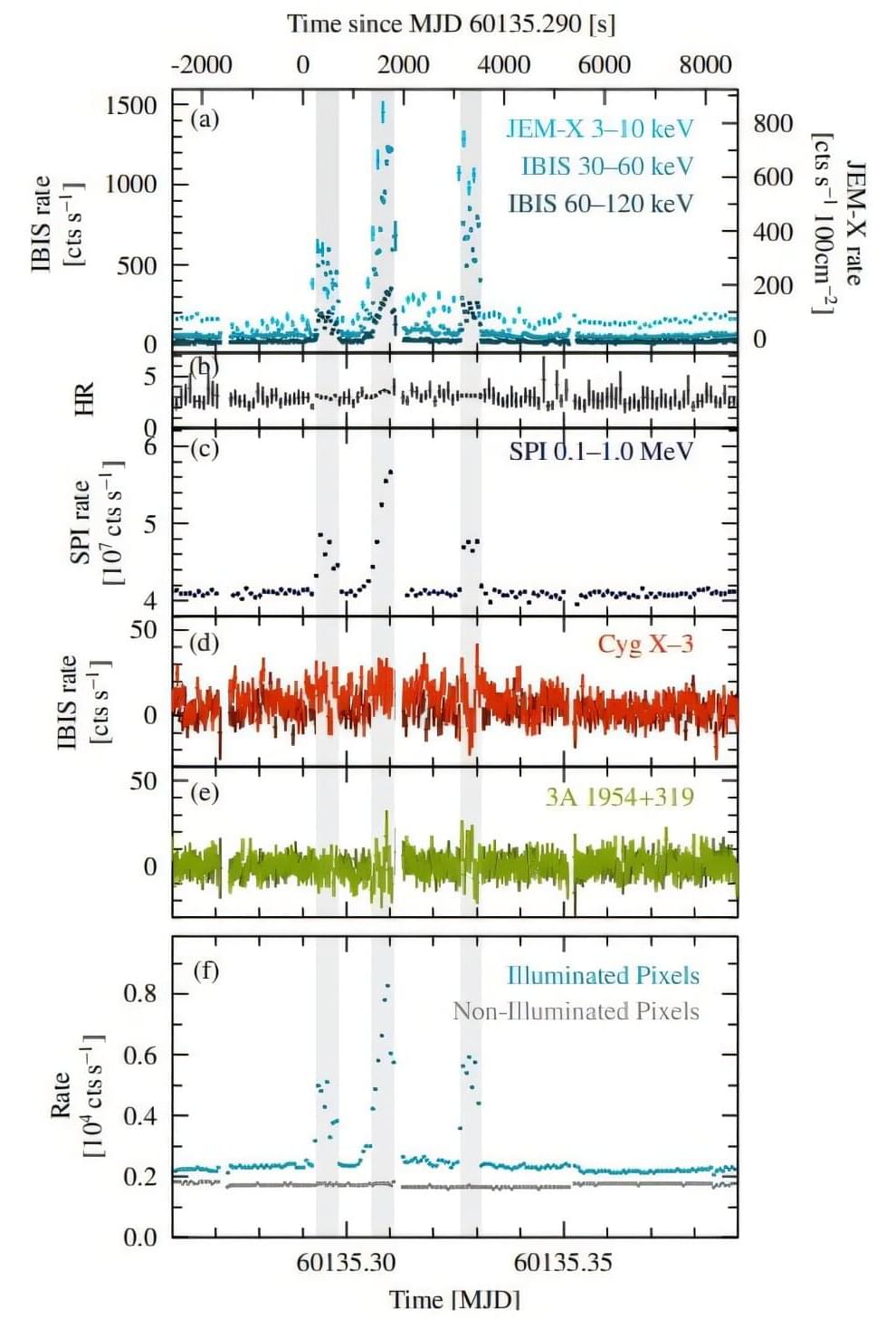
INTEGRAL observes exceptionally bright X-ray flares from Cygnus X-1
Using ESA’s INTEGRAL spacecraft, astronomers have detected exceptionally bright X-ray flares from the Cygnus X-1 X-ray binary system. This is the first time that such strong flaring activity has been observed in this system although it has been monitored for decades. The new findings were detailed in a paper published August 28 on the pre-print server arXiv.