Discovered last month by a telescope in Chile, the comet known as 3I-Atlas is only the third known interstellar object to pass our way.
Category: space – Page 54
Interstellar object Comet 3I/ATLAS: New image and more
On August 7, 2025, NASA shared a new image of Comet 3I/ATLAS and an updated estimate of its size. 3I/ATLAS, the 3rd-known interstellar object, was originally estimated to have a diameter of 20 km (12 miles). But with data from the Vera C. Rubin Observatory, astronomers re-estimated the size to be around 10 km (6 miles). And now the Hubble data puts the size of 3I/ATLAS’s nucleus at a diameter of 5.6 km (3.5 miles). But it could be as small as 320 meters (1,050 feet) across.


Jupiter-Venus conjunction: How to see our solar system’s 2 brightest planets in August
From meteor showers to visible nebulas, August is primed to be an action-packed month for stargazers in the United States.
And one of the highlights of the month? The impending meet-up of Jupiter and Venus.
The gas giant Jupiter, our solar system’s largest planet, is due to make a close approach in August with Venus, NASA said in an August skywatching guide. The rendezvous, known in astronomy terms as a conjunction, comes a few months after Venus underwent an inferior conjunction in March – meaning it appeared in the sky after sunset and again before sunrise.

Seismic activity on the moon could pose risk to long-term lunar infrastructure
A new paper reveals that ground acceleration from moonquakes, rather than meteor impacts, was responsible for shifting lunar landscapes at the moon’s Taurus-Littrow valley, where Apollo 17 astronauts landed in 1972. The study also pinpointed a possible cause for those surface changes and assessed damage risk using new models of the quakes—findings that may impact the safety of future lunar missions and the establishment of long-term bases on the moon.
The paper, authored by Smithsonian Senior Scientist Emeritus Thomas R. Watters and University of Maryland Associate Professor of Geology Nicholas Schmerr, is published in the journal Science Advances.
The scientists analyzed evidence from the Apollo 17 landing site, where NASA astronauts collected samples from boulder falls and landslides that were likely triggered by moonquakes. By studying the geological evidence left behind, the researchers were able to estimate the strength of these ancient moonquakes and identify their most probable source.
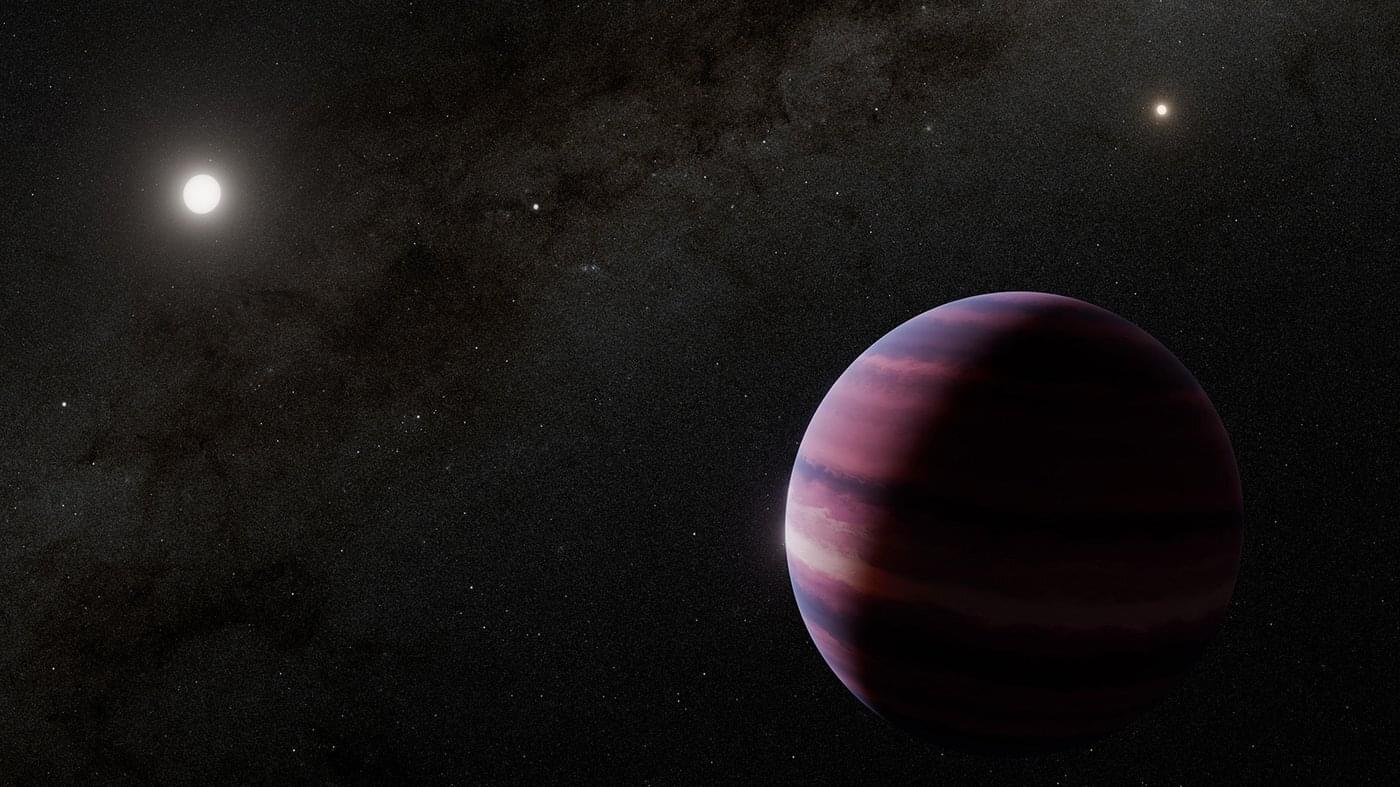

Evidence found for planet around closest sun-like star
Astronomers have used NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope to find strong evidence for a planet orbiting a star in the triple system closest to our own sun. At just 4 light-years away from Earth, the Alpha Centauri star system has long been a compelling target in the search for worlds beyond our solar system called exoplanets.
The system is made up of a close pair of orbiting stars, Alpha Centauri A and Alpha Centauri B, the two closest sun-like stars to Earth, as well as the faint red dwarf star Proxima Centauri. While there are three confirmed planets orbiting Proxima Centauri, the presence of other worlds surrounding the sun-like twins of Alpha Centauri A and Alpha Centauri B has proved challenging to confirm.
Now, Webb’s observations from its Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) are providing the strongest evidence to date of a gas giant planet orbiting in the habitable zone of Alpha Centauri A. (The MIRI instrument was developed in part by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory [JPL], which is managed by Caltech for NASA). The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures could be right for liquid water to pool on a planet’s surface.

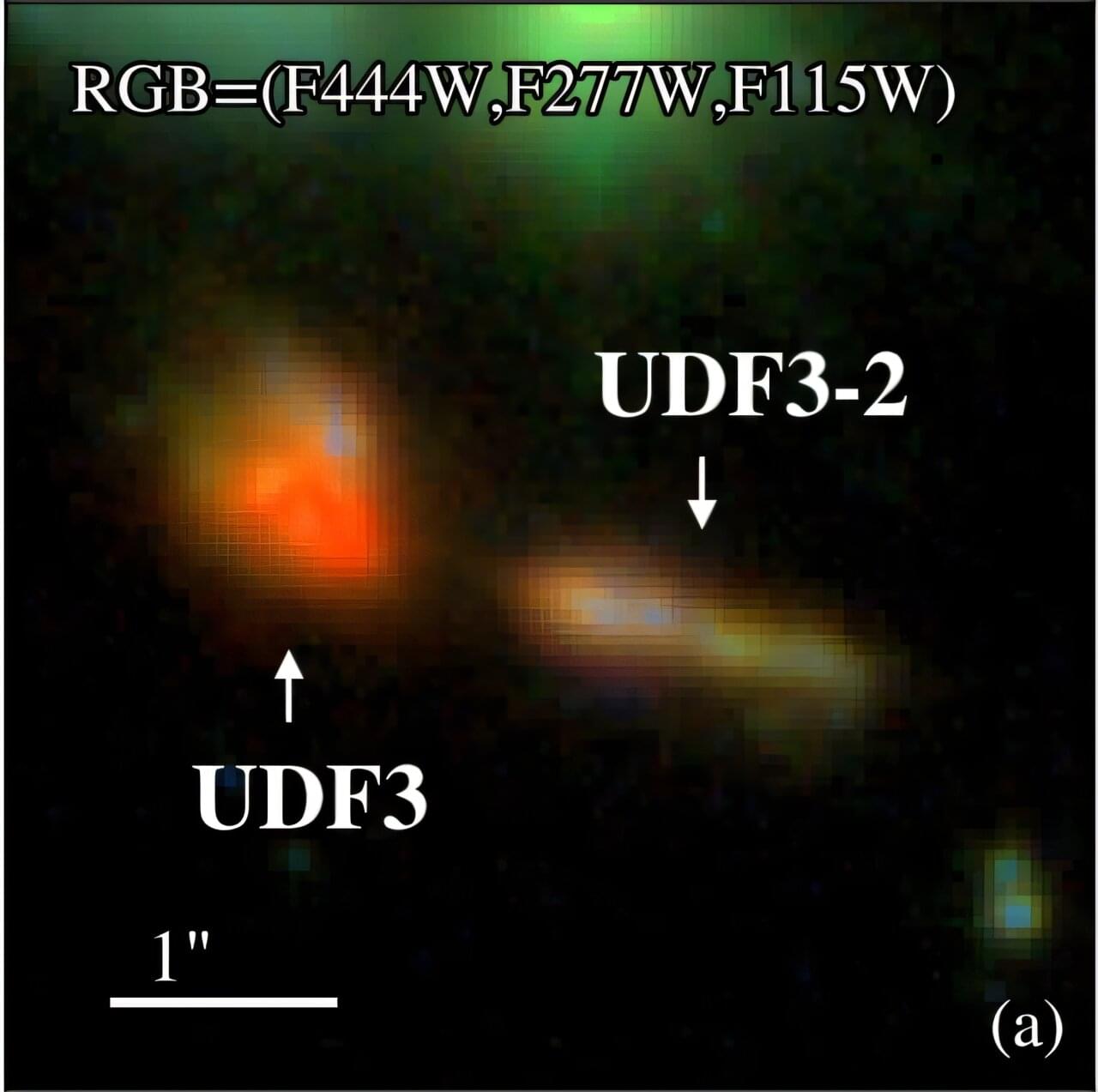
Deep-sky survey detects an X-ray emitting pair of galaxies
By conducting multiwavelength observations with various telescopes and space observatories, astronomers from Tsinghua University and Steward Observatory have detected a galaxy pair exhibiting significant X-ray emission. The finding was reported in a research paper published July 31 on the pre-print server arXiv.
The Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey (GOODS) is a deep-sky survey conducted by multiple observatories to study the formation and evolution of galaxies. It combines multiwavelength data from space observatories like the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), Chandra X-ray Observatory, Spitzer spacecraft, XMM-Newton satellite, and the largest ground-based facilities, such as the Very Large Telescope (VLT), Keck telescopes, Gemini Observatory or the Very Large Array (VLA).
Recently, a team of astronomers led by Tsinghua University’s Sijia Cai conducted a search for Chandra X-ray detected star-forming galaxies in the Southern field of the GOODS survey (GOODS-S). For this purpose, they combined observations from VLA and the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), spectroscopic data from the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and VLT, as well as photometry from HST and JWST.
Ocean sediments might support theory that comet impact triggered Younger Dryas cool-off
Analysis of ocean sediments has surfaced geochemical clues in line with the possibility that an encounter with a disintegrating comet 12,800 years ago in the Northern Hemisphere triggered rapid cooling of Earth’s air and ocean. Christopher Moore of the University of South Carolina, U.S., and colleagues present these findings in the journal PLOS One on August 6, 2025.
During the abrupt cool-off—the Younger Dryas event—temperatures dropped about 10 degrees Celsius in a year or less, with cooler temperatures lasting about 1,200 years. Many researchers believe that no comet was involved, and that glacial meltwater caused freshening of the Atlantic Ocean, significantly weakening currents that transport warm, tropical water northward.
In contrast, the Younger Dryas Impact Hypothesis posits that Earth passed through debris from a disintegrating comet, with numerous impacts and shockwaves destabilizing ice sheets and causing massive meltwater flooding that shut down key ocean currents.