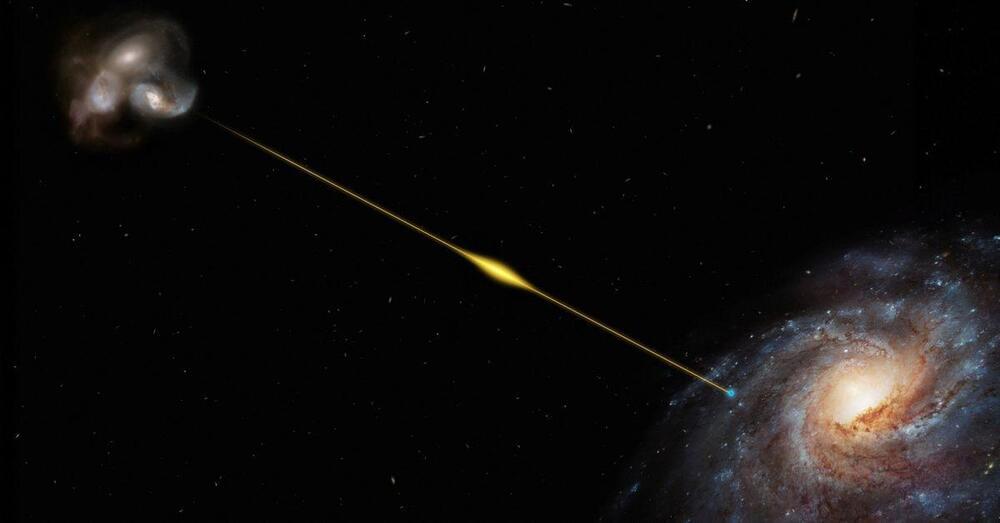
WASHINGTON, Oct 20 (Reuters) — Astronomers have detected an intense flash of radio waves coming from what looks like a merger of galaxies dating to about 8 billion years ago — the oldest-known instance of a phenomenon called a fast radio burst that continues to defy explanation.
This burst in less than a millisecond unleashed the amount of energy our sun emits in three decades, researchers said. It was detected using the Australian SKA Pathfinder, a radio telescope in the state of Western Australia. Its location was pinpointed by the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope in Chile, one of the most powerful optical telescopes.
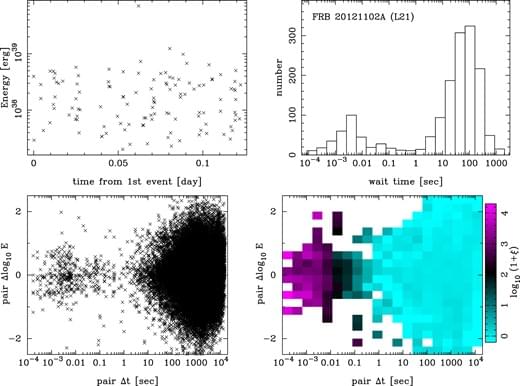
A fast radio burst, or FRB, is a pulse of radio-frequency electromagnetic radiation. It lasts a small fraction of a second but outshines most other sources of radio waves in the universe. Radio waves have the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum.