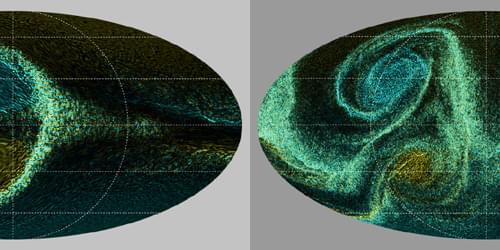
Supercomputer simulations of the weather on a hot Jupiter reveal a previously unseen storm pattern in which cyclones are repeatedly generated and destroyed.

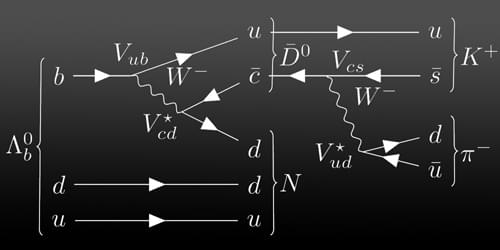
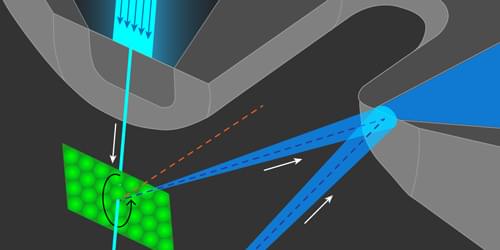
Researchers have developed an atom-diffraction imaging method with micrometer spatial resolution, which may allow new applications in material characterization.
Microscopy with atoms offers new possibilities in the study of surfaces and two-dimensional (2D) materials [1]. Atom beams satisfy the most important requirements for microscopic probing: they can achieve high contrast and surface-specificity while doing little damage to the sample. A subtype of atomic microscopy—atomic-diffraction imaging—obtains measurements in reciprocal, or momentum, space, which is ideal for studying the surfaces of large and uniform crystalline samples. However, scientists developing this technique face challenges in achieving micrometer-scale spatial resolutions that would allow the study of polycrystalline materials, nonuniform 2D materials, and other surfaces without long-range order.

As someone who never lived in the extreme northern latitudes of Earth, I always found it exciting when I heard auroras might be visible farther south. I would always crane my eyes skyward, hoping I could see those ghostly dancing lights, almost trying to wish them into existence. Alas, I was never that lucky. Though as we approach solar maximum in 2025, we ought not to only get excited about seeing auroras, but perhaps also ask: What could a powerful geomagnetic storm do to our technological infrastructure?
Geomagnetic storms can be triggered by either coronal mass ejections, giant bubbles of plasma erupting from the surface of the sun, or very powerful solar flares. It’s because these events can accelerate particles to extremely fast speeds. And when some of those particles hit the Earth’s magnetic field, this generates what we see as brilliant auroras — however, those particles can also damage satellite equipment and even harm astronauts in orbit.
A truly gigantic magnetic storm has not affected the Earth in well over one hundred years — and since then, technology has changed quite significantly. Satellite communications, air travel and the power grid have been brought into existence, and they all can be impacted by these events. Yet, scientists aren’t quite sure what, exactly, would happen to the integral technological components of society if a major solar storm shrouded Earth with charged particle showers.
Two teams of astronomers led by scientists at Caltech, have discovered the largest reservoir of water ever detected in the universe. And it’s 30 billion trillion miles away.
Yep, you read that correctly. The largest reservoir has been found in the cosmos, more specifically in a quasar, which is one of the brightest and most violent objects in the cosmos.
The mass of water vapour is at least 140 trillion times more than all of the water in the world’s oceans combined.
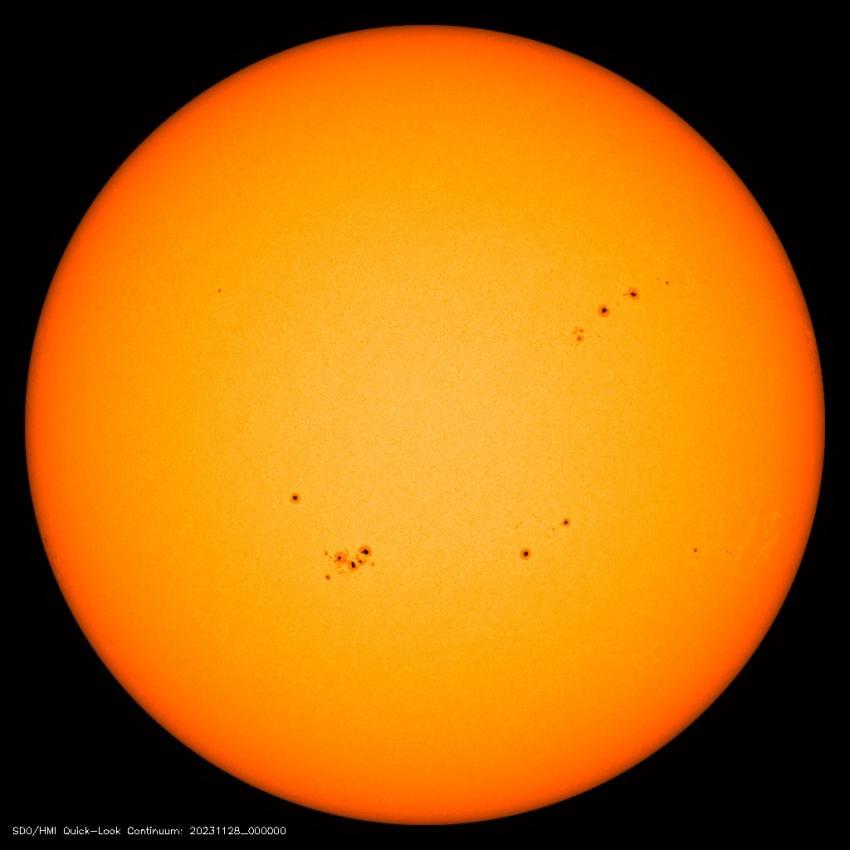


Researchers at the Center of Excellence in Space Sciences India at IISER Kolkata have discovered a new relationship between the Sun’s magnetic field and its sunspot cycle, that can help predict when the peak in solar activity will occur. Their work indicates that the maximum intensity of solar cycle 25, the ongoing sunspot cycle, is imminent and likely to occur within a year. The new research appears in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters.
Our star, the Sun, is made up of hot ionized gas known as plasma.
Huge plasma flows and convection conspire together to form magnetic fields inside the Sun which manifest on the surface as dark spots.


X.AI, Elon Musk’s artificial intelligence startup, has filed with the SEC to raise up to $1 billion in an equity offering. The company has raised nearly $135 million from four investors, with the first sale occurring on Nov. 29, according to the filing. The AI startup, which Musk announced in July,…
X.AI, an artificial intelligence startup founded by Elon Musk, has filed with the SEC to raise up to $1 billion in an equity offering.
The company has already brought in nearly $135 million from four investors, with the first sale occurring on Nov. 29, and has a “binding and enforceable agreement” for the purchase of the remaining shares, the filing says.
The AI startup, which Musk announced in July, seeks to “understand the true nature of the universe,” according to its website. Last month, X.AI released a chatbot called Grok, which the company says is modeled after “The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy.” The chatbot debuted with two months of training and has real-time knowledge of the internet, the company claims.