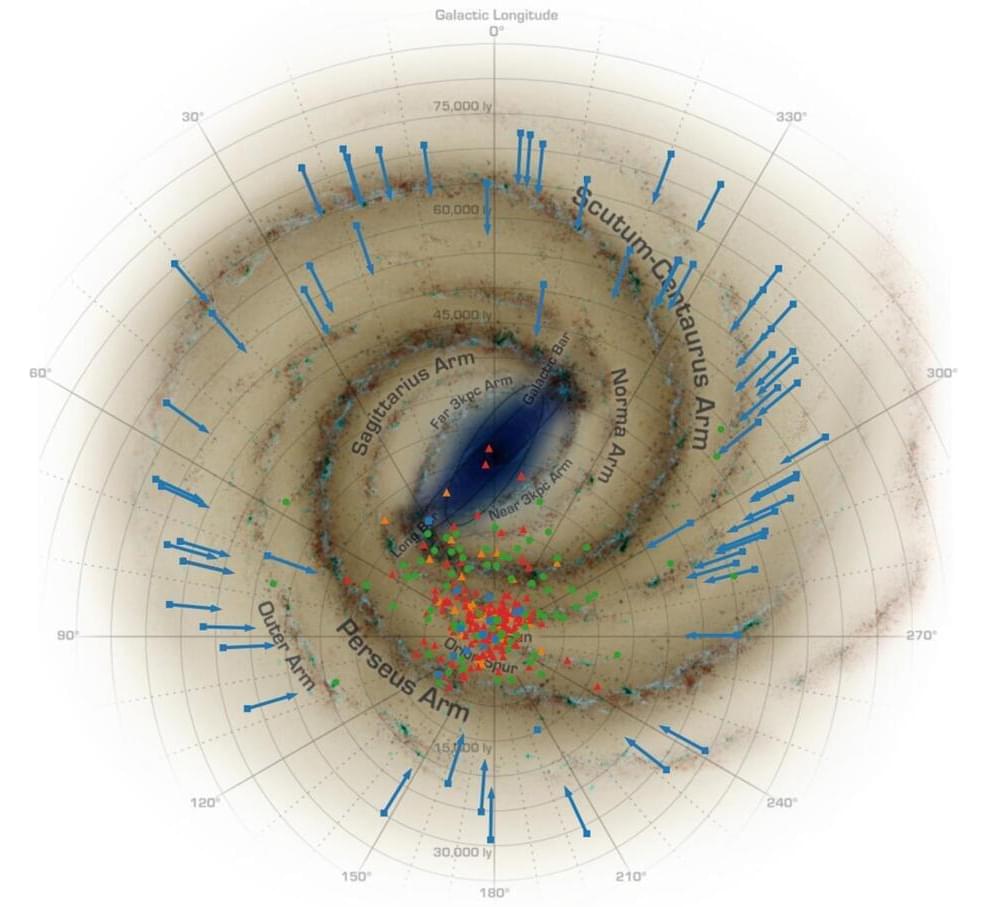
The U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL), in conjunction with the international Fermi Large Area Telescope Collaboration, announce the discovery of nearly 300 gamma ray pulsars in the publication of their Third Catalog of Gamma Ray Pulsars. This milestone comes 15 years after the launch of Fermi in 2008 when there were fewer than ten known gamma-ray pulsars.
“Work on this important catalog has been going on in our group for years,” said Paul Ray, Ph.D., head of the High Energy Astrophysics and Applications Section at NRL. “Our scientists and postdocs have been able to both discover and analyze the timing behavior and spectra of many of these newfound pulsars as part of our quest to further our understanding of these exotic stars that we are able to use as cosmic clocks.”
Pulsars are formed when massive stars have burned through their fuel supply and become unable to resist the inward pull of their own gravity. This results in the star collapsing into a dense, spinning, magnetized neutron star. Their spinning magnetic fields send out beams of gamma rays, the most energetic form of light. As these beams sweep across the Earth, the highly sensitive Fermi gamma-ray telescope can observe their periodic energy pulses. With more than 15 years of data, Fermi has transformed the field of pulsar research.