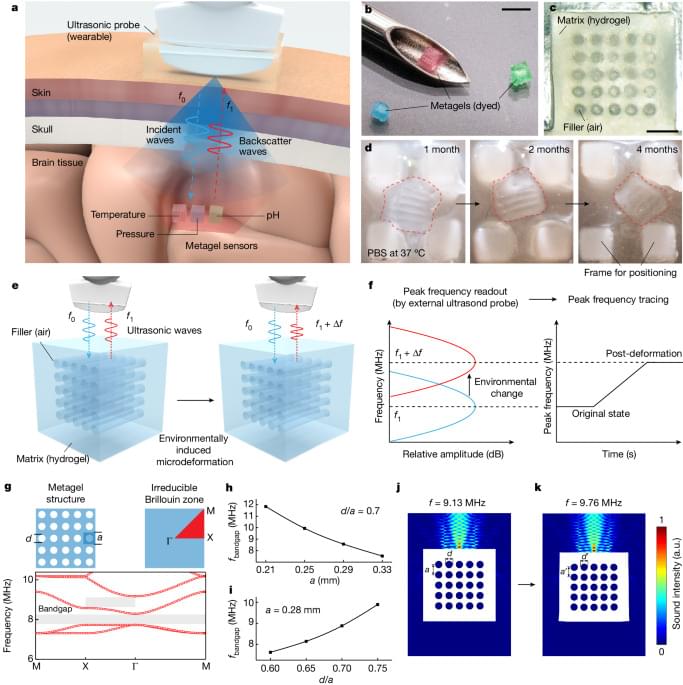
Most distant spacecraft, #Voyager1, is now returning data from all four science instruments for the first time following a technical issue last November.
NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft is conducting normal science operations for the first time following a technical issue that arose in November 2023.
The team partially resolved the issue in April when they prompted the spacecraft to begin returning engineering data, which includes information about the health and status of the spacecraft. On May 19, the mission team executed the second step of that repair process and beamed a command to the spacecraft to begin returning science data. Two of the four science instruments returned to their normal operating modes immediately. Two other instruments required some additional work, but now, all four are returning usable science data.
The four instruments study plasma waves, magnetic fields, and particles. Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 are the only spacecraft to directly sample interstellar space, which is the region outside the heliosphere — the protective bubble of magnetic fields and solar wind created by the Sun.