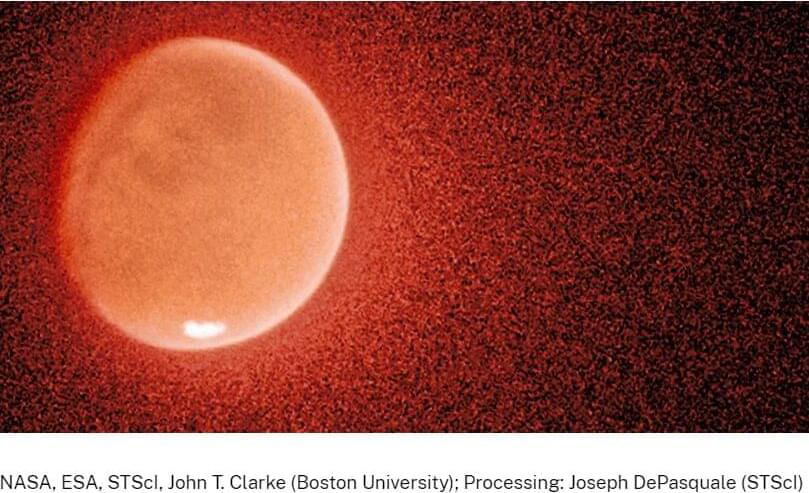
Mars was once a very wet planet, as is evident in its surface geological features. Scientists know that over the last 3 billion years, at least some water went deep underground, but what happened to the rest? Now, NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and MAVEN (Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution) missions are helping unlock that mystery.
“There are only two places water can go. It can freeze into the ground, or the water molecule can break into atoms, and the atoms can escape from the top of the atmosphere into space,” explained study leader John Clarke of the Center for Space Physics at Boston University in Massachusetts. “To understand how much water there was and what happened to it, we need to understand how the atoms escape into space.”
Clarke and his team combined data from Hubble and MAVEN to measure the number and current escape rate of the hydrogen atoms escaping into space. This information allowed them to extrapolate the escape rate backwards through time to understand the history of water on the red planet.