Will the wagers of a few entrepreneurs yield a golden age in space exploration?
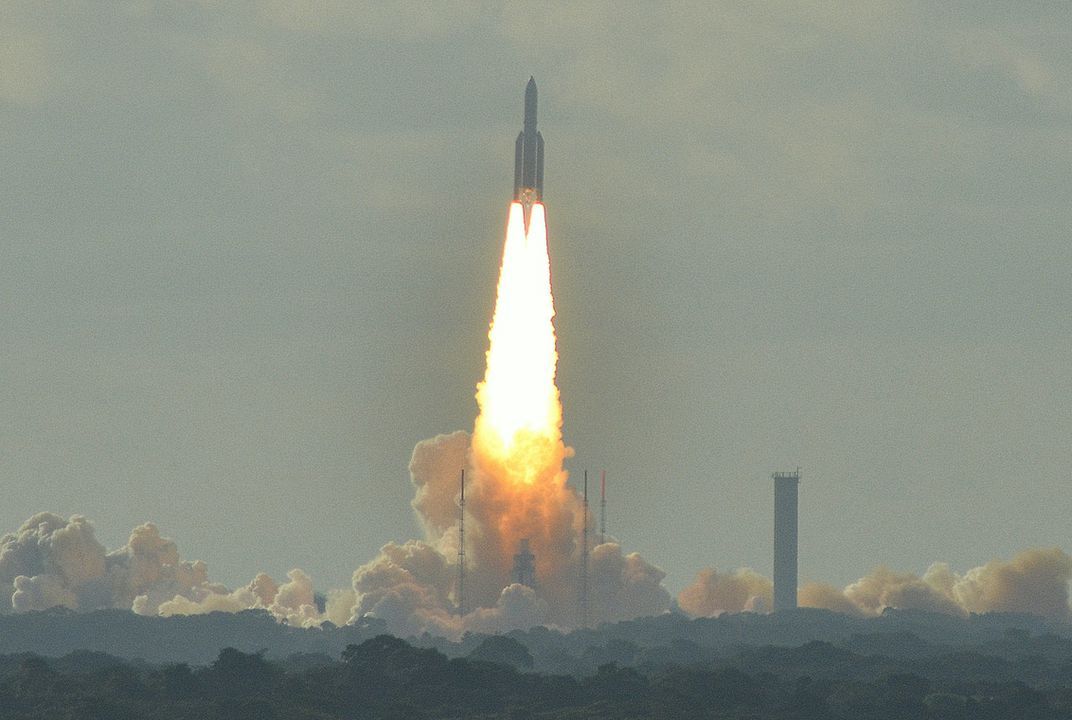




The U.S. and Russia each sent astronauts to the International Space Station with a Wednesday, March 21 launch from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan.
NASA sent two astronauts to the space station while Russian space agency Roscosmos sent one. The three crew members were launched aboard the Soyuz spacecraft, and are expected to dock with the space station’s module sometime Friday afternoon. NASA will have a stream of this docking starting 3 p.m. Friday on NASA TV and its website.
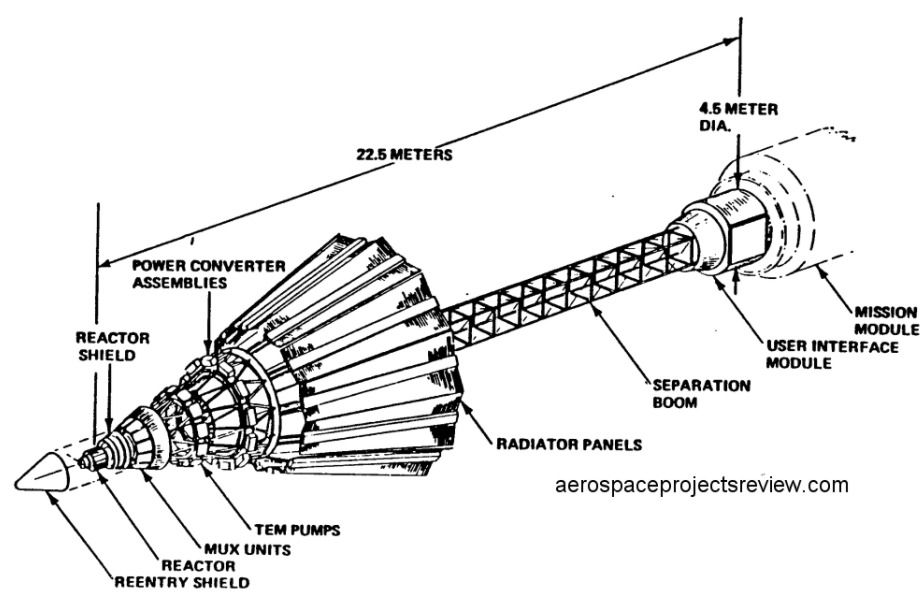
Neutral-particle beams, a concept first tried in the 1980s, may get a fresh look under Michael Griffin.
“Directed energy is more than just big lasers, Griffin said. ”That’s important. High-powered microwave approaches can effect an electronics kill. The same with the neutral particle beam systems we explored briefly in the 1990s” for use in space-based anti-missile systems. Such weapons can be ”useful in a variety of environments” and have the ”advantage of being non-attributable,” meaning that it can be hard to pin an attack with a particle weapon on any particular culprit since it leaves no evidence behind of who or even what did the damage.
Like lasers, neutral-particle beams focus beams of energy that travel in straight lines, unaffected by electromagnetic fields. But instead of light, neutral-particle beams use composed of accelerated subatomic particles traveling at near-light speed, making them easier to work with (though the folks that run CERNs hadron collider may disagree). When its particles touche the surface of a target, they takes on a charge that allows them to penetrate the target’s shell or exterior more deeply.

Recent headlines have contained lots of asteroid-nuking talk. There’s a team of Russian scientists zapping mini asteroids in their lab, and supposedly NASA is thinking about a plan that would hypothetically involve nuking Bennushould it threaten Earth in 2135.
It’s true that NASA is drafting up ideas on how one might nuke an incoming asteroid, a theoretical plan called HAMMER, or the Hypervelocity Asteroid Mitigation Mission for Emergency Response, as we’ve reported. But scientists probably won’t need to use such a response on the “Empire State Building-sized” asteroid 101955 Bennu, which is set to pass close to Earth in 2135. Diverting such a threat could be much, much easier.
“Even just painting the surface a different color on one half would change the thermal properties and change its orbit,” Michael Moreau, NASA’s OSIRIS-REx Flight Dynamics System Manager, told Gizmodo. That would involve literally sending a spacecraft to somehow change the color of some of the asteroid.
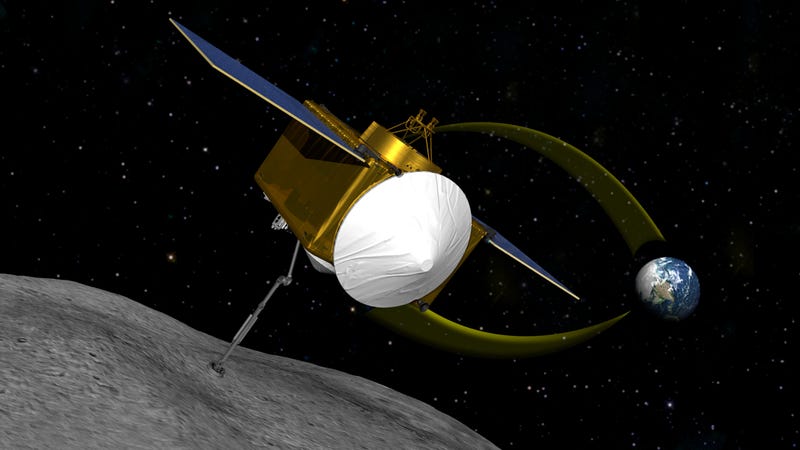
There’s lots we don’t know about asteroids just yet, which is why NASA has sent the probe OSIRIS-REx toward Bennu. This mission aims to scoop up and return a sample of the rock in 2023.
There is a minuscule chance, around 1 in 2,700 odds, that Bennu will strike Earth in 2135, reports the Washington Post. The rock isn’t big enough to end humanity, but it could cause some major damage. The OSIRIS-REx spacecraft will study the rock more, and NASA will continue to collect data to either rule out the chance of an impact or increase the odds.
But don’t worry about Bennu yet. Should the odds of a Bennu strike grow too high, the laws of physics will allow for a much easier solution than nuking. We could just splash it with some paint.
The sun pelts everything in the solar system with a slew of tiny particles, for example. This imparts a little bit of pressure. These particles are of no consequence to our own orbit, since Earth is incredibly massive, but Bennu weighs only around 13 times the mass of the Great Pyramid of Giza. That’s very light, comparatively. Given the 120 years or so we’ve got and the amount of distance Bennu has left to travel before its nearby approach, if scientists could make some of it more susceptible to the solar radiation, that would slightly alter its path enough that it would miss us. Doing so would require changing part of its surface so it absorbs more radiation—for example, by covering one side of it with paint. Scientists first need to better study its orbit around the sun to determine the best course of action.
All that is to say, as usual, we’re not about to be hit by the giant asteroid in the headlines.
There are asteroids we need to worry about, of course. But as we’ve reported before, we’re not tracking them. The government has only required that NASA track asteroids larger than a football field or so. Something smaller could go under the radar and cause significant local damage without the 120 years of warning Bennu has afforded us.
The thought of nuking asteroids makes for great science fiction. But instead, you should spend more time upset that we don’t know what smaller asteroids are threatening us, rather than worry about the ones scientists are tracking that could be diverted more easily.
Elon Musk has a reputation for pushing the envelop and making bold declarations. In 2002, he founded SpaceX with the intention of making spaceflight affordable through entirely reusable rockets. In April of 2014, his company achieved success with the first successful recovery of a Falcon 9 first stage. And in February of this year, his company successfully launched its Falcon Heavy and managed to recover two of the three boosters.
But above and beyond Musk’s commitment to reusability, there is also his longer-term plans to use his proposed Big Falcon Rocket (BFR) to explore and colonize Mars. The topic of when this rocket will be ready to conduct launches was the subject of a recent interview between Musk and famed director Jonathon Nolan, which took place at the 2018 South by Southwest Conference (SXSW) in Austin, Texas.
During the interview, Musk reiterated his earlier statements that test flights would begin in 2019 and an orbital launch of the full BFR and Big Falcon Spaceship (BFS) would take place by 2020. And while this might seem like a very optimistic prediction (something Musk is famous for), this timeline does not seem entirely implausible given his company’s work on the necessary components and their success with reusability.

I recently got a private tour of a NASA space shuttle’s cockpit, a quirky mosaic-covered LA home, and a peaceful chapel with light streaming through ornate stained-glass windows—all without leaving my chair.
That chair was in an office at Google’s Silicon Valley headquarters, and I was wearing an HTC Vive virtual-reality headset on my face. But because these places were filmed with a high-resolution prototype camera that reproduces some of the key cues we use to understand depth in the real world, it felt more like actually being there than anything I’ve experienced with any other live-action VR. Which is to say it was pretty damn cool.
I could peer around the seats in the space shuttle Discovery, revealing buttons and switches on the walls of the cockpit that were previously obscured. As I looked closely at mirrored bits of tile on the outside of the mosaic house, I glimpsed reflections of other tiles in the background and saw a dizzying display of shapes and patterns. In the chapel, I gazed at the floor, and the colorful sunbeams moved as I did.

Spending an extended period of time in outer space takes a toll on the human body. And while NASA was aware of some physical changes that astronauts needed to be prepared for upon coming back to Earth, they were curious to learn further about how extended space time would affect a human body on a molecular level. After one astronaut spent a year in space, NASA was able to determine that the prolonged spaceflight actually altered his DNA.
Astronaut Scott Kelly and his twin brother Mark Kelly took part in NASA’s twin study, a means to compare the human body on Earth to its counterpart following a year in space. While Scott spent a year in space, Mark stayed behind, and upon Scott’s return, NASA was able to track and monitor the ways that spaceflight had altered Scott’s body.
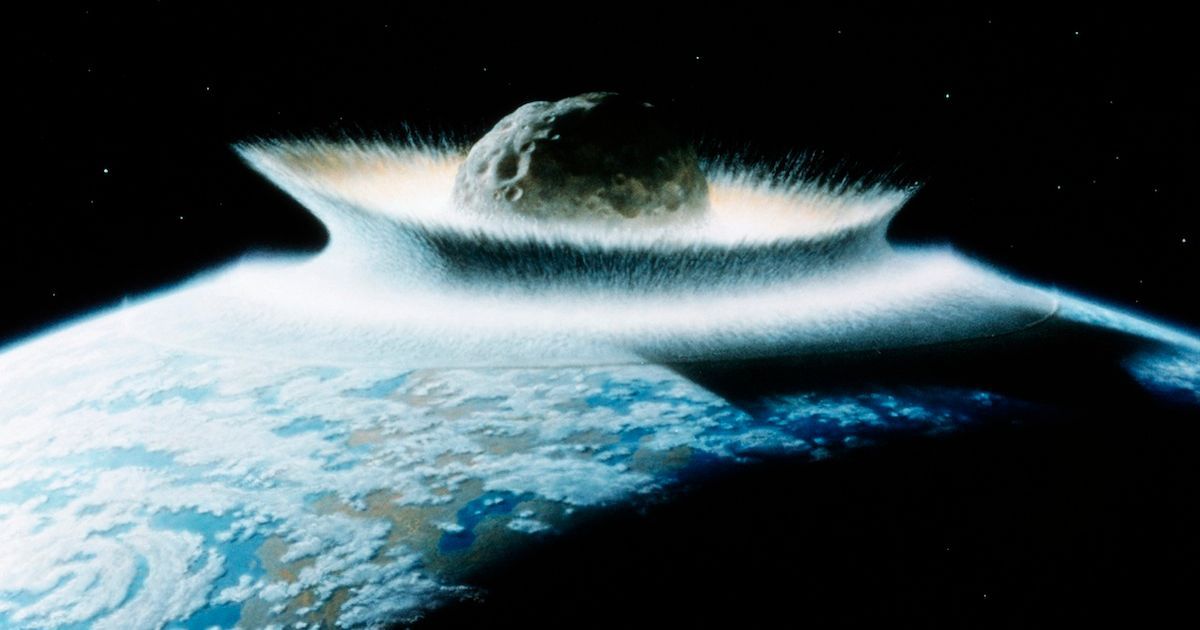

NASA has a plan to deal with potential asteroid impacts that sounds like it’s been taken straight from a science fiction film.
The space agency is building a spacecraft named HAMMER — which stands for Hypervelocity Asteroid Mitigation Mission for Emergency Response.
The plan is to blow any harmful looking asteroids out of the sky before they have a chance to hit out planet.

Buzz Aldrin, the second man on the Moon, once said, “Mars is there, waiting to be reached.”
If Elon Musk has his way, he’ll be the one to reach it, even if it’s likely to be a dangerous journey that could result in the loss of human life.
Speaking at the South by South West festival in Austin, Texas, SpaceX and Tesla CEO Musk said he envisions test flights of his Mars spacecraft next year, though he cautioned early trips could end in death.