It’ll be like that movie Passengers, but less creepy. #til
Category: space travel – Page 455
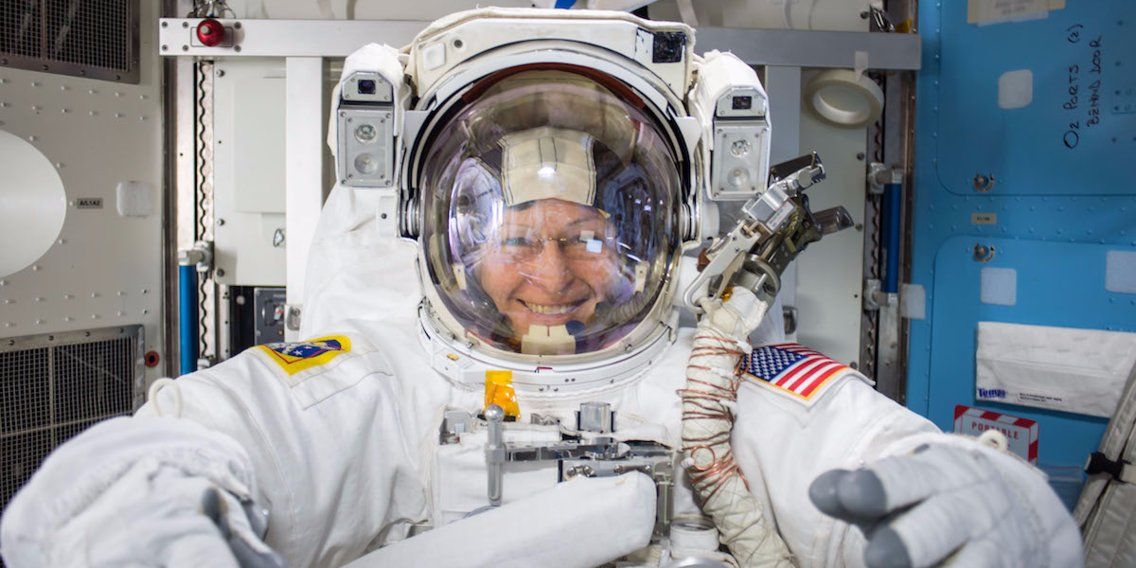

The incredible career of NASA’s Peggy Whitson, who applied to become an astronaut 10 times before she broke the American record for space travel
She retired from NASA on Friday after blazing a trail for countless female astronauts.
NASA astronaut Peggy Whitson, the 58-year-old from Iowa farm country who spent a record-breaking 665 days in space, retired from the space agency on Friday.
“I have hit my radiation limit,” Whitson told Business Insider during a recent interview. “So not going into space with NASA anymore.”
That realization is both melancholic and exciting for the biochemist, who only half-jokingly admits she’s still not sure what she’s going to do “when I grow up.”

A New Study Details Everything That Would Be Needed For An Interstellar Journey To Proxima Centauri
Scientists have determined the minimum amount of crew members needed for a 6,300-year journey to Proxima b.
A team of French scientists have recently published a new study detailing everything that would be needed if humans were to one day make the long interstellar journey to Proxima Centauri to start a new life and civilization. The research went to great lengths to determine the correct amount of people that would ensure a successful voyage to Proxima b.
The study was conducted by particle physicist Dr. Camille Beluffi and Dr. Frederic Marin from the Astronomical Observatory of Strasbourg and marks the second study conducted on such an interstellar journey to Proxima b, as ScienceAlert reported.
Smart Robots Are the Secret to Spaceflight’s Future
A spacecraft, spinning in Earth’s orbit, reaches inside itself. One of its four arms pulls out a length of polymer pipe that has been 3D-printed inside the body of the machines. All four of the spacecraft’s arms are securing pieces together as it builds a new space station right there in orbit.
This surreal project, called Archinaut, is the future vision of space manufacturing company Made In Space. The company promises a future of large imaging arrays, kilometer-scale communications tools, and big space stations all built off-planet by smart robots.
Space catapult startup gets $40 MILLION investment
A Silicon Valley startup has devised an ingenious way of sending rockets into space.
Dubbed SpinLaunch, the firm wants to blast tiny payloads into orbit atop miniature rockets.
But instead of using propellants like a typical launch would, SpinLaunch would slingshot them into space using a novel catapult technology.

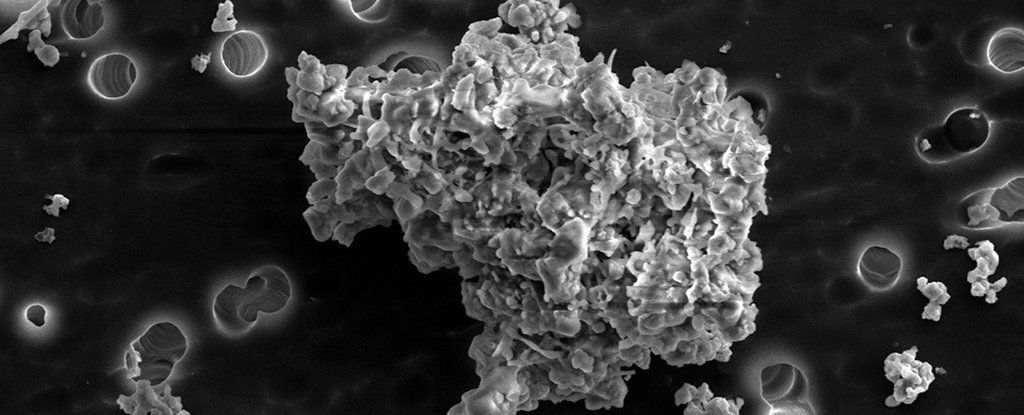
Scientists Have Found Interstellar Dust on Earth That’s Older Than Our Solar System
This ancient interstellar dust formed the Earth and the solar system.
Particles collected from Earth’s upper atmosphere, originally deposited by comets, are older than our Solar System, scientists say – and these fine bits of interstellar dust could teach us about how planets and stars form from the very beginning.
These cosmic particles have lived through at least 4.6 billion years and travelled across incredible distances, according to the new research into their chemical composition.
The international team of scientists behind this study are confident that we’re looking at the very basic materials making up the planetary bodies currently whizzing around our Sun. For anyone studying the origins of the Universe, it’s a fantastic finding.
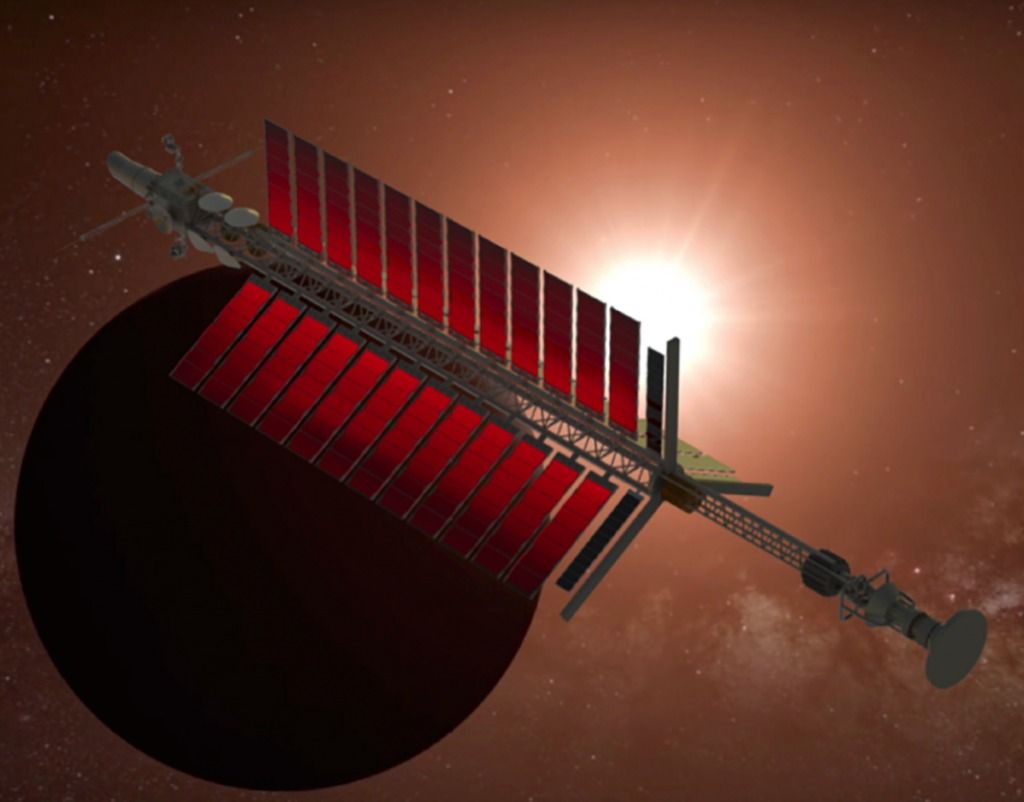



What would solar system travel be like with scaled Mach effect propellantless propulsion?
James Woodward and the Space Studies Institute has a Phase 2 NASA Innovative Advanced funded study. They are looking at the implementation of an innovative thrust producing technology for use in NASA missions involving in space main propulsion.
Dr. Heidi Fearn explained in a video made in 2017 how just scaling the power and size of the Mach effect propulsion causes problems. (heat, arcing and other problems). They currently believe they can scale the device to one newton of propulsion and then create large arrays of the devices for more thrust. The constant thrust could last for years or decades by using a nuclear power source.
For Mach effect propellantless propulsion it will be better to go to an array of smaller devices.