#spacex


See how we developed Hybrid rockets and launched them from high altitude balloon initially with the Huntsville Alabama L5 Society (HAL5)‘s High Altitude Lift-Off (HALO) Program and later with our High Altitude Research Corporation (HARC). See our Balloon Launch Return Vehicle (BLRV) and our HARC Cheap Access to Space (CATS) Prize rocket. Hear some of our war stories from these adventures. A balloon launched rocket is known as a rockoon.
Watch next week for a related interview, The Inside Scoop on Virgin Galactic with Tim Pickens.
You can support Galactic Gregs by supporting the sister channel Green Gregs by clicking the links below:
For your space habitat garden buy worms at greengregs.com!
See the Special Deals at My Patriot Supply (great space mission food): www.PrepWithGreg.com.
For gardening in your space habitat (or on Earth) Galactic Gregs has teamed up with True Leaf Market to bring you a great selection of seed for your planting. Check it out: http://www.pntrac.com/t/TUJGRklGSkJGTU1IS0hCRkpIRk1K
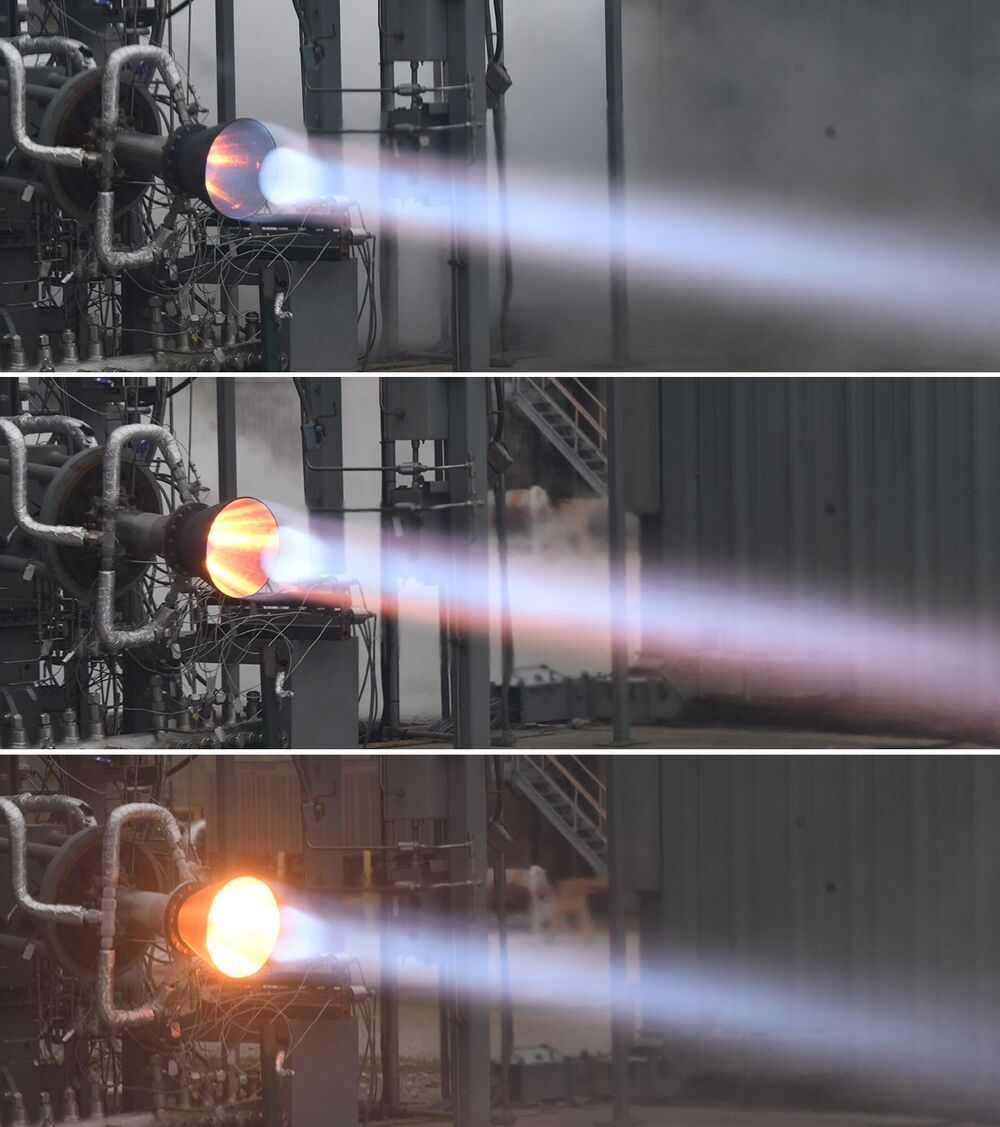
3D-printed parts can make rocket engines lighter, less expensive and more efficient.
At Marshall, we’re working with our industry partners to test the latest advances in additive manufacturing technologies:
NASA is partnering with Aerojet Rocketdyne to advance 3D printing technologies, known as metal additive manufacturing, and its capabilities for liquid rocket engines in landers and on-orbit stages/spacecraft.
WASHINGTON — A Japanese billionaire best known for buying a SpaceX Starship flight around the moon will go to space first on a Russian Soyuz spacecraft to the International Space Station, two months after a Russian actress and director visit the station.
Space tourism company Space Adventures and the Russian space agency Roscosmos announced May 13 that Yusaku Maezawa will fly to the ISS on the Soyuz MS-20 mission launching Dec. 8 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome. He will be accompanied by a production assistant, Yozo Hirano, on the 12-day flight, commanded by Russian cosmonaut Alexander Misurkin.
“We are excited for Maezawa-san, and we are honored to have enabled this opportunity for him to fly to space,” Eric Anderson, chairman and chief executive of Space Adventures, said in the statement.

O,.o! Woah
A never-ending detonation could be the key to hypersonic flight and space planes that can seamlessly fly from Earth into orbit. And now, researchers have recreated the explosive phenomenon in the lab that could make it possible.
Detonations are a particularly powerful kind of explosion that move outward faster than the speed of sound. The massive explosion that rocked the port of Beirut in Lebanon last August was a detonation, and the widespread destruction it caused demonstrates the huge amounts of energy they can produce.

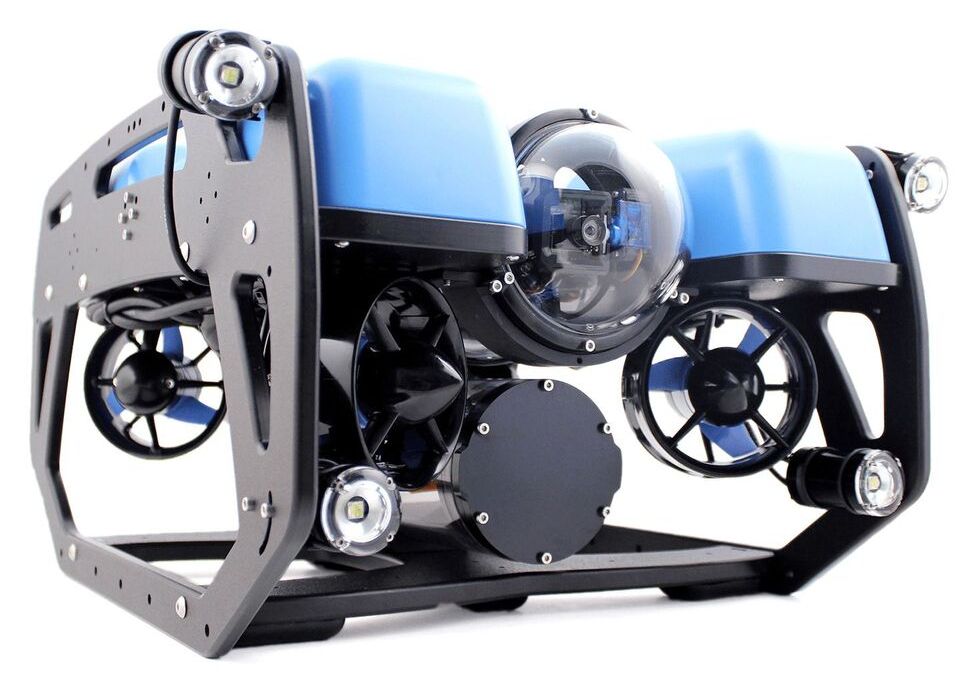
Blue Robotics, a leading developer of marine robotics systems and components, has partnered with Unmanned Systems Technology (“UST”) to demonstrate their expertise in this field. The ‘Silver’ profile highlights how their underwater ROVs (remotely operated vehicles), thrusters and accessories enable a wide range of missions for commercial, research and exploration applications.
The BlueROV2 is a high-performance, highly configurable ROV designed for underwater inspections, research and ocean exploring. With open-source hardware and software, the platform features an unprecedented level of flexibility and expandability, allowing users to easily make improvements and upgrades to take on a huge variety of missions down to depths of 100m (330 feet).
The ROV incorporates six Blue Robotics T200 thrusters in a vectored configuration, delivering excellent thrust-to-weight ratio and providing the ability to move precisely in any direction. The system can be expanded to eight thrusters via a Heavy Configuration Retrofit Kit, and features adjustable gain levels for precision control at extremely low speeds as well as high power to overcome currents and carry heavy loads. The BlueROV2 is provided with a Fathom ROV tether, with available length options from 25m (82 ft) up to 300 m (984 ft).

Jared Isaacman’s privately funded trip to Earth’s orbit will raise money for St. Jude’s.
Inspiration4 will be motivated in part by Isaacman’s effort to raise more than $200 million for St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, a pediatric cancer research hospital that does not charge the families of children for their treatment. Isaacman pledged $100 million out of his own pocket.
“I’ve been very lucky in life; you really don’t get to a position that I’m fortunate enough to be in without the ball bouncing your way a couple times,” said Isaacman in an interview with Space.com. “These families [at St. Jude] were dealt horrible hands. They’re going through what no one should ever have to go through. It’s immense heartache, and the sad part is many of those kids will not grow up to have any of the experiences that I’ve been lucky enough to have in life. We’ve just got to do something about that.”
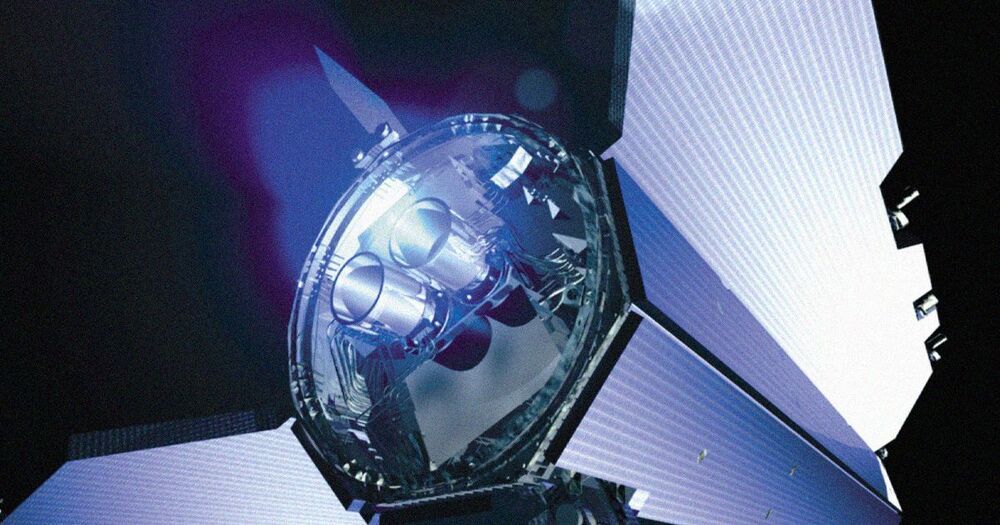

An international team of researchers have come up with a fusion-based spacecraft thruster that uses a hydrogen isotope called deuterium as a fuel source, as Popular Mechanics reports.
Their “direct fusion drive,” (DFD) — as detailed in a yet-to-be-peer-reviewed preprint — is theoretically able to speed up a spacecraft to a blistering 44 kilometers per second, covering the distance from here to Neptune and beyond in less than a decade.
While electric propulsion systems powered by the rays of the Sun have allowed us to explore the inner reaches of our solar system, venturing beyond Jupiter would require gigantic solar arrays, the team argues in its paper.
NASA astronauts Michael Hopkins, Victor Glover, and Shannon Walker, along with Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Soichi Noguchi, participated in the first media event following their mission and splashdown, where they answered questions about their historic mission on the International Space Station and return to Earth.
SpaceX ’s Crew Dragon, named Resilience, carrying Hopkins, Glover, Walker, and Noguchi, splashed down at 2:56 a.m. May 2 under parachutes in the Gulf of Mexico, off the coast of Panama City, Florida, and was successfully recovered by SpaceX. After returning to shore, the astronauts immediately flew back to Houston, where they were greeted by their families and colleagues.
NASA’s SpaceX Crew-1 astronauts answer questions about their historic mission on the International Space Station and their return to Earth. At around 14:15 Victor Glover discusses how it feels to be subjected to 4.5 Gs for over a minute on reentry after experiencing weightlessness for 167 days: “I felt really heavy!”