The idea was first hypothesized about 70 years ago.


Our Universe is vast, ancient, and mysterious. It’s no surprise that in our quest to explore and explain it, many misconceptions have arisen.
The first 1,000 people to use the link will get a 1 month free trial of Skillshare https://skl.sh/isaacarthur05231
Join this channel to get access to perks:
/ @isaacarthursfia.
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Support us on Patreon: / isaacarthur.
Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a… Group: / 1,583,992,725,237,264 Reddit:
/ isaacarthur Twitter:
/ isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content. SFIA Discord Server:
/ discord Listen or Download the audio of this episode from Soundcloud: Episode’s Audio-only version:
/ misconceptions-about-space-time-the-universe Episode’s Narration-only version:
/ misconceptions-about-space-time-the-univer… ▬ Common Misconceptions ▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬ 0:00 Intro 2:34 Space is Huge 3:58 Space has no gravity 6:29 Space is not Dark 7:57 Space is Cold 12:14 Space is Empty 14:49 Explosive Decompression 16:31 No Noise in Space 17:48 Black Holes Suck 18:51 You can’t escape a Black Hole 22:37 Nothing goes faster than light 24:23 The Edge of The Universe is 13 Billion Light Years Away 27:23 The Universe has no Edge 29:31The Universe has no Center 30:13 We aren’t the Center of the Universe 32:48 Earth Orbits the Sun 35:34 The Sun is a fiery Yellow Dwarf 38:29 Time on Spaceships runs very slow 40:17 The Universe ends with the last stars Credits: Misconceptions About Space, Time & The Universe Science & Futurism with Isaac Arthur Episode 394, May 11, 2023 Written, Produced & Narrated by Isaac Arthur Editors: Briana Brownell David McFarlane Graphics: Jeremy Jozwik Music Courtesy of Epidemic Sound http://epidemicsound.com/creator.
Facebook Group: / 1583992725237264
Reddit: / isaacarthur.
Twitter: / isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: / discord.
Listen or Download the audio of this episode from Soundcloud: Episode’s Audio-only version: / misconceptions-about-space-time-the-universe.
Episode’s Narration-only version: / misconceptions-about-space-time-the-univer…
▬ Common Misconceptions ▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬
0:00 Intro.
2:34 Space is Huge.
3:58 Space has no gravity.
6:29 Space is not Dark.
7:57 Space is Cold.
12:14 Space is Empty.
14:49 Explosive Decompression.
16:31 No Noise in Space.
17:48 Black Holes Suck.
18:51 You can’t escape a Black Hole.
22:37 Nothing goes faster than light.
24:23 The Edge of The Universe is 13 Billion Light Years Away.
27:23 The Universe has no Edge.
29:31The Universe has no Center.
30:13 We aren’t the Center of the Universe.
32:48 Earth Orbits the Sun.
35:34 The Sun is a fiery Yellow Dwarf.
38:29 Time on Spaceships runs very slow.
40:17 The Universe ends with the last stars.
Credits:
Misconceptions About Space, Time & The Universe.
Science & Futurism with Isaac Arthur.
Episode 394, May 11, 2023
Written, Produced & Narrated by Isaac Arthur.
Editors:
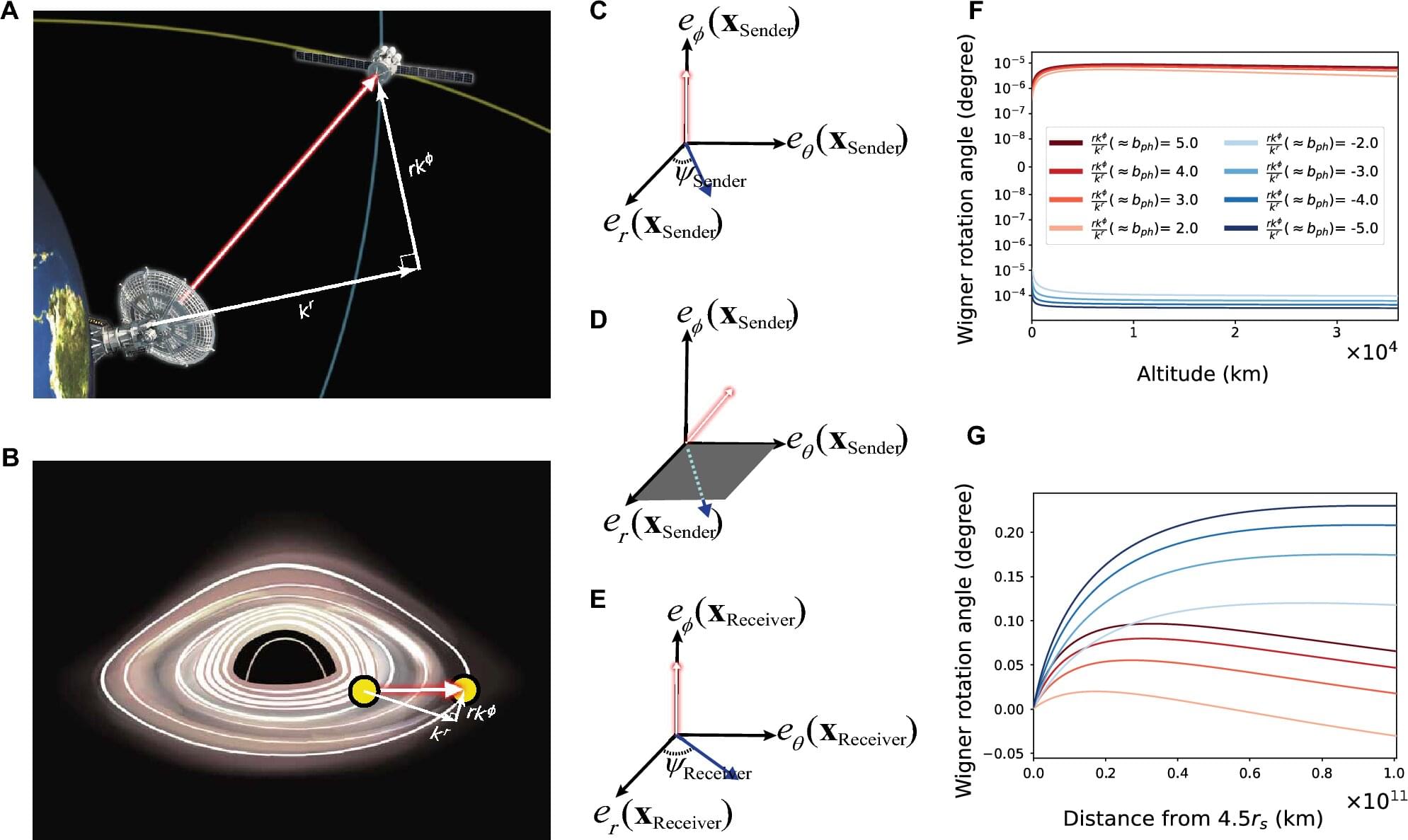
A team of physicists has uncovered a surprising new way to explore one of science’s greatest challenges: uniting the two fundamental theories that explain how our universe works—Einstein’s theory of gravity and quantum mechanics.
Despite decades of effort, no one has fully explained how gravity—which governs massive objects like planets and stars—fits with quantum mechanics, which describes the behavior of the tiniest particles in the universe. But now, scientists believe light may hold the key.
Warner A. Miller, Ph.D., co-author and a professor in the Department of Physics at Florida Atlantic University’s Charles E. Schmidt College of Science in collaboration with scientists at the University of Seoul and Seoul National University, South Korea, found that light’s polarization —the direction it vibrates as it travels—can behave in an unexpected way when passing through curved space. Normally, this polarization shifts slightly due to the warping of space by gravity, a well-known effect.
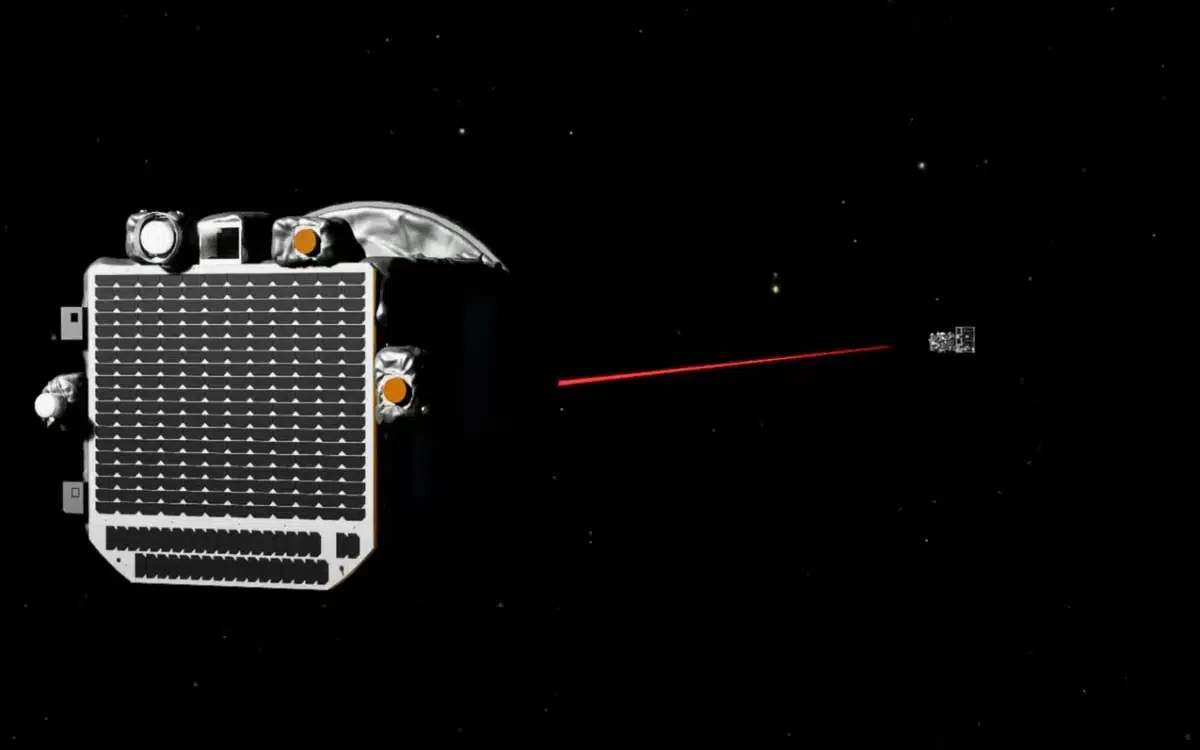

Space missions are often performed with lone spacecraft, but the Proba-3 spacecraft, built by the European Space Agency (ESA) has finally introduced some teamwork in the mix.
The ESA’s latest spacecraft made history by achieving the first spacecraft precision formation flying in orbit.
The mission was launched on an Indian rocket at the end of 2024, from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre on the east coast of India.
What happens when intelligence escapes the bounds of flesh and bone? In this episode, we explore post-biological civilizations—entities that may trade biology for digital minds, machine bodies, or stranger forms still—and ask what becomes of identity, purpose, and humanity when the body is no longer required.
Watch my exclusive video Antimatter Propulsion: Harnessing the Power of Annihilation — https://nebula.tv/videos/isaacarthur–… Nebula using my link for 40% off an annual subscription: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur Get a Lifetime Membership to Nebula for only $300: https://go.nebula.tv/lifetime?ref=isa… Use the link gift.nebula.tv/isaacarthur to give a year of Nebula to a friend for just $30. SFIA Discord Server: / discord Credits: Post-Biological Civilizations: Life Beyond Flesh and Bone Episode 498a; May 11, 2025 Written, Produced & Narrated by: Isaac Arthur Edited by: Ludwig Luska Select imagery/video supplied by Getty Images Music Courtesy of Epidemic Sound http://epidemicsound.com/creator Chris Zabriskie, “Unfoldment, Revealment” Phase Shift, “Forest Night” Lewis Gill, “The Phobos Diary” Stellardrone, “Red Giant” 0:00 Intro 1:24 The Physical Presence of Post-Biological Civilizations 3:38 Societal & Cultural Aspects of Post-Biological Life 5:08 The Scifi Path to Post-Biological Life 8:03 The Singularity and the Ultimate Transition 9:47 Many Paths to Post-Biological Life 17:50 The Fermi Paradox & Post-Biological Civilizations 27:39 Ethics & the Fate of Humanity 29:17 The Transition Process at a Civilizational Scale.
Get Nebula using my link for 40% off an annual subscription: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Get a Lifetime Membership to Nebula for only $300: https://go.nebula.tv/lifetime?ref=isa…
Use the link gift.nebula.tv/isaacarthur to give a year of Nebula to a friend for just $30.
SFIA Discord Server: / discord.
Credits:
Post-Biological Civilizations: Life Beyond Flesh and Bone.
Episode 498a; May 11, 2025
Written, Produced & Narrated by: Isaac Arthur.
Edited by: Ludwig Luska.
Select imagery/video supplied by Getty Images.
Music Courtesy of Epidemic Sound http://epidemicsound.com/creator.
Chris Zabriskie, \
Space habitation company, Vast, is now one year away from being able to stake its claim as the first commercial space station in history. The company based in Long Beach, California, aims to launch its single-module Haven-1 space station on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in May 2026. To that end, it completed both its primary structure and qualification article and is moving into manufacturing the flight version. More.

In tomorrow’s world, cities may rise into the clouds, dive beneath oceans, or float among the stars—join us as we journey through these radical urban frontiers.
Watch my exclusive video Antimatter Propulsion: Harnessing the Power of Annihilation — https://nebula.tv/videos/isaacarthur–…
Get Nebula using my link for 40% off an annual subscription: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Get a Lifetime Membership to Nebula for only $300: https://go.nebula.tv/lifetime?ref=isa…
Use the link gift.nebula.tv/isaacarthur to give a year of Nebula to a friend for just $30.
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Support us on Patreon: / isaacarthur.
Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a…
Facebook Group: / 1583992725237264
Reddit: / isaacarthur.
Twitter: / isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: / discord.
Credits:
Cities of the Future.
Episode 498; May 8, 2025
Written, Produced & Narrated by: Isaac Arthur.
Edited by: Briana Brownell & Thomas Owens.
Graphics: Bryan Versteeg, Ervin Oprea, Ken York YD Visual, Sergio Botero.
Select imagery/video supplied by Getty Images.
Music Courtesy of Epidemic Sound http://epidemicsound.com/creator.
Chris Zabriskie, \
What is time? Speaking time travel, black holes and the remits of science. In this podcast conversation, we speak with Professor David Wilkinson — physicist and author of popular science books on Stephen Hawking to explore the question: can we ever fully understand time through science, or does it open up more mystery?
Owl in space at https://owlinspace.com
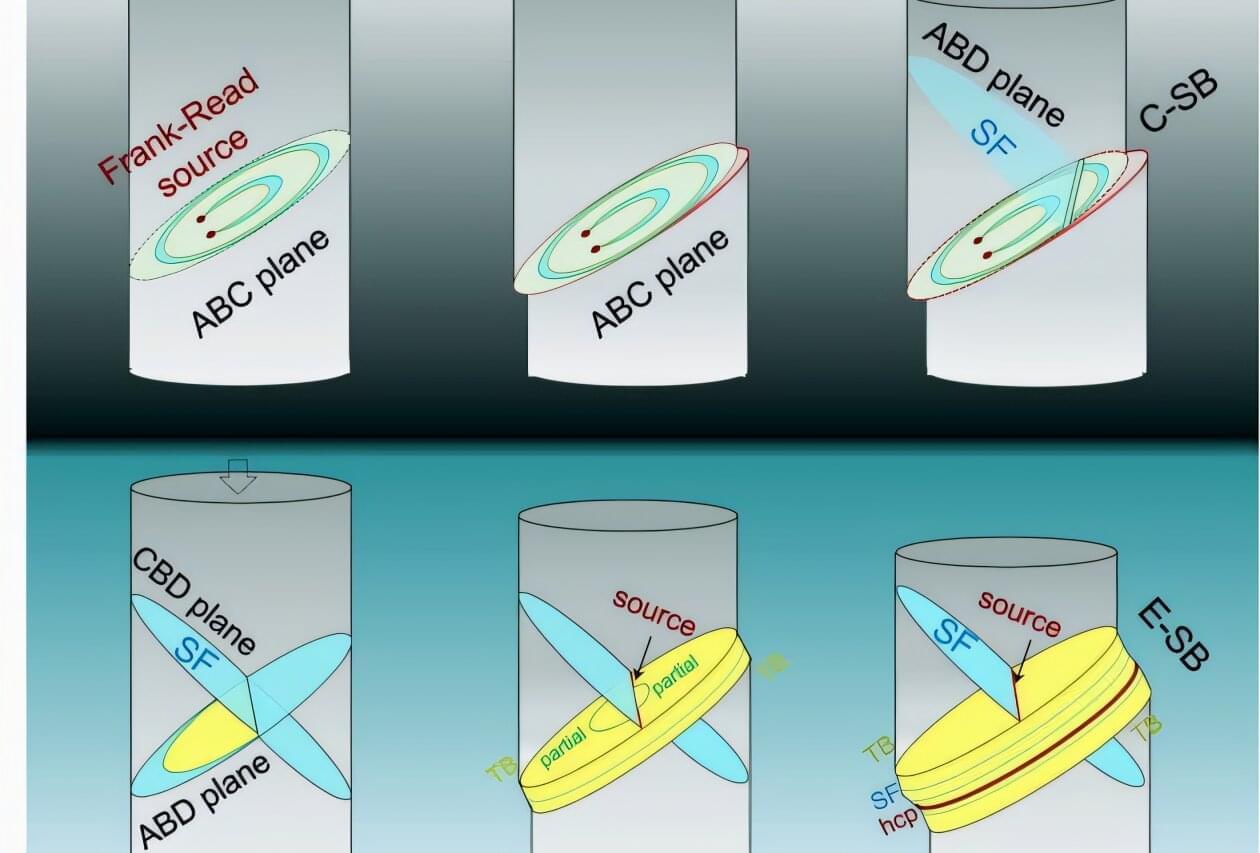
University of California, Irvine scientists have expanded on a longstanding model governing the mechanics behind slip banding, a process that produces strain marks in metals under compression, gaining a new understanding of the behavior of advanced materials critical to energy systems, space exploration and nuclear applications.
In a paper published recently in Nature Communications, researchers in UC Irvine’s Samueli School of Engineering report the discovery of extended slip bands—a finding that challenges the classic model developed in the 1950s by physicists Charles Frank and Thornton Read.
While the Frank–Read theory attributes slip band formation to continuous dislocation multiplication at active sources, the UC Irvine team found that extended slip bands emerge from source deactivation followed by the dynamic activation of new dislocation sources.