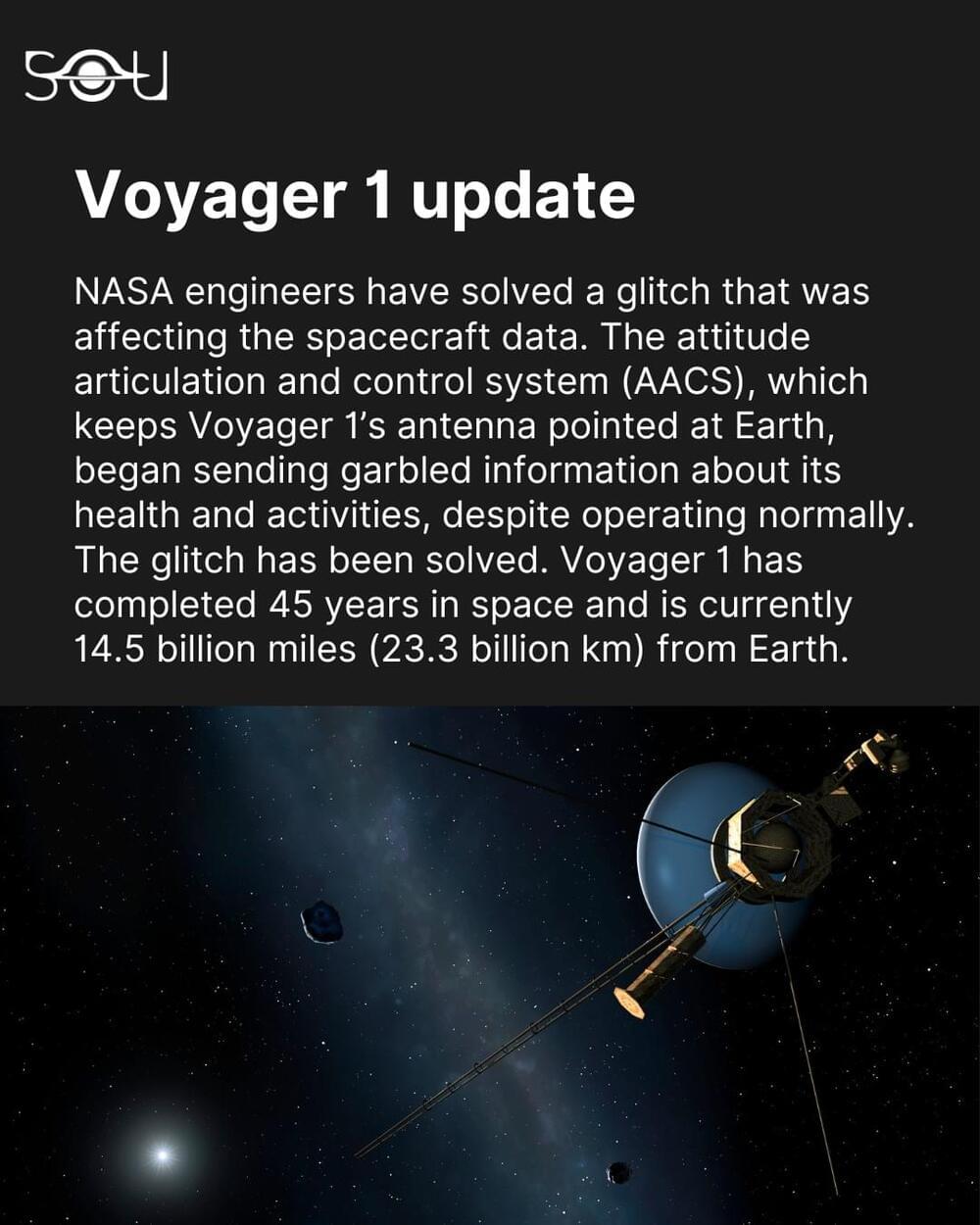
Despite the challenges of operating a 45-year-old spacecraft, NASA says the team is working to keep it operational and returning new science.

Even had the same name.
https://tmp2.fandom.com/wiki/Modular_Unmanned_Orbital_Laboratory_-_MUOL
https://tmp2.fandom.com/wiki/Telerobotic_Outpost.
Originally
Developed as part of the Modular Unmanned Orbital Laboratory — MUOL program early in the Asgard phase, Inchworm telerobots are likely to become the most common form of workhorse utility robot throughout TMP. Deriving from the simple robotic arms employed by later generation space agency spacecraft and orbital outposts, employ a very simple architecture to the utmost in multi-purpose flexibility. An Inchworm is a simple robot consisting of a single mechanical arm equipped with at least three two-axis electric-powered joints; two at end-effector units and others at intervals in-between. Unlike simpler arm robots, the end-effector units at both ends of the Inchworm feature small stereo cameras, LED lights, and a modular quick-connect interface including bus interfaces for power and communication. The Inchworm needs no internal power supplies, relying entirely on power through its end-effector bus connectors and plug-in anchor point grid, though out would be able to carry independent power sources in mobile anchor units. These end effector units are intended to serve alternately as tool-heads and anchor points, thus allowing the robot to traverse a grid of anchor sockets by traveling end-over-end while simultaneously carrying a pallet of modular tools. In addition, sections of the Inchworm arms may optionally include telescoping linear actuators allowing them to expand or contract in length –though the use of this would often depend on load bearing capacities of such mechanisms. would also be able to link end-to-end to create composite robots of greater length, their joints optionally including a lock-pin system to rigidize them in a given position. Originally intended for simple remote control or teleoperation, would also be easily employed with fully automated control based on centralized computers, allowing them to be used in coordinated groups and task/production lines or to off-load certain amounts of their control to overcome limitations in manual communications latency. This would afford them increasing autonomous capability in proportion to this centralized and networked computer intelligence but still allow for direct manual control on demand.

The seedlings reached up to 30 cm.
Chinese astronauts have successfully grown rice seedlings onboard the Tiangong space station. Experts said on Monday that this experiment could provide important information about how astronauts can grow food to support extended space journeys, according to China Daily.
Even though prior rice experiments have been conducted in space, the one carried out aboard Tiangong is the first of its type to attempt to produce the entire life cycle of the plant, which starts with a seed and ends with a full plant generating new seeds.
On July 24, China launched the Wentian space laboratory into orbit to dock it with the Tianhe core module of the Chinese space station.
Chinese astronauts have successfully grown rice seedlings onboard the Tiangong space station and this experiment that may yield key insights into how astronauts can cultivate food to support long-term space missions, experts said on Monday.
While there have been other rice experiments in space, the one being conducted on Tiangong is the first of its kind that aims to produce the complete life cycle of the plant, which begins with a seed and ends with a mature plant producing new seeds.
Why was NASA’s Artemis launch date rescheduled for 3 Sep 22? Get the real skinny here.
Why was NASA’s Artemis Iaunch date rescheduled for 3 Sep 22? Get the real skinny here.
Worm-hole generators by the pound mass: https://greengregs.com/
For gardening in your Lunar habitat Galactic Gregs has teamed up with True Leaf Market to bring you a great selection of seed for your planting. Check it out: http://www.pntrac.com/t/TUJGRklGSkJGTU1IS0hCRkpIRk1K
Awesome deals for long term food supplies for those long missions to deep space (or prepping in case your spaceship crashes: See the Special Deals at My Patriot Supply: www.PrepWithGreg.com.
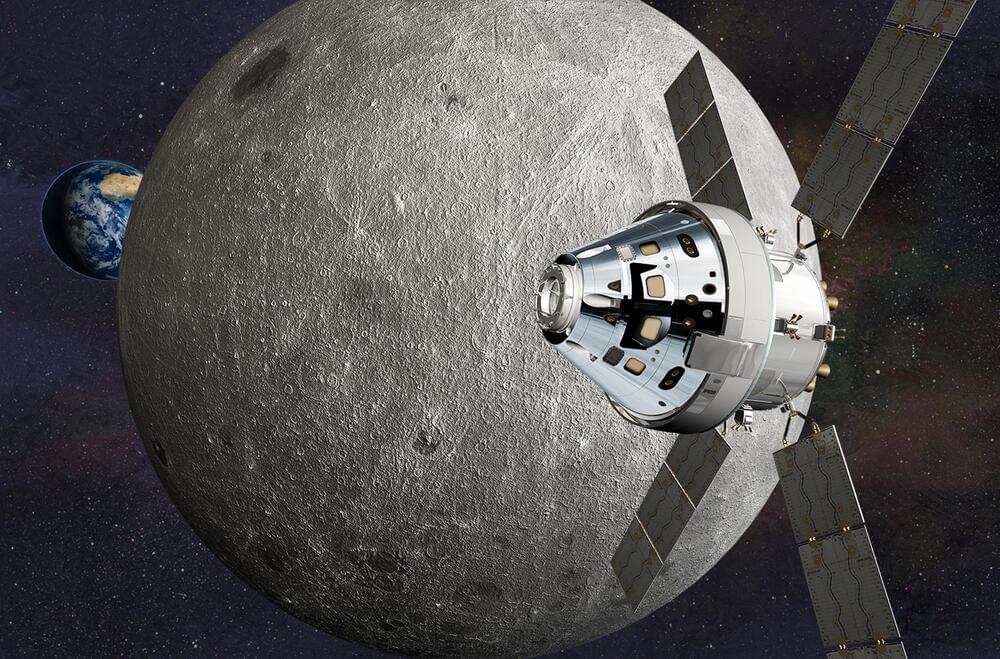
The Lockheed Martin Orion is the latest arrival of a human-rated spacecraft slated to take humans beyond the bounds of Low Earth Orbit and close to the surface of another heavenly body. But for all its grace, sophistication, and dedicated design team, there are undoubtedly public misconceptions surrounding the ship.
What is the real reason the NASA Artemis I Launch got scrubbed on 29 Aug 21? NASA made a valiant attempt to launch the SLS Artemis I Moon Rocket this morning, but it was not to be. The launch was scrubbed. Get the real skinny here.
Worm-hole generators by the pound mass: https://greengregs.com/
For gardening in your Lunar habitat Galactic Gregs has teamed up with True Leaf Market to bring you a great selection of seed for your planting. Check it out: http://www.pntrac.com/t/TUJGRklGSkJGTU1IS0hCRkpIRk1K
Awesome deals for long term food supplies for those long missions to deep space (or prepping in case your spaceship crashes: See the Special Deals at My Patriot Supply: www.PrepWithGreg.com.

Artemis is the name of NASA’s program to return astronauts to the lunar surface. We are going forward to the Moon to stay.
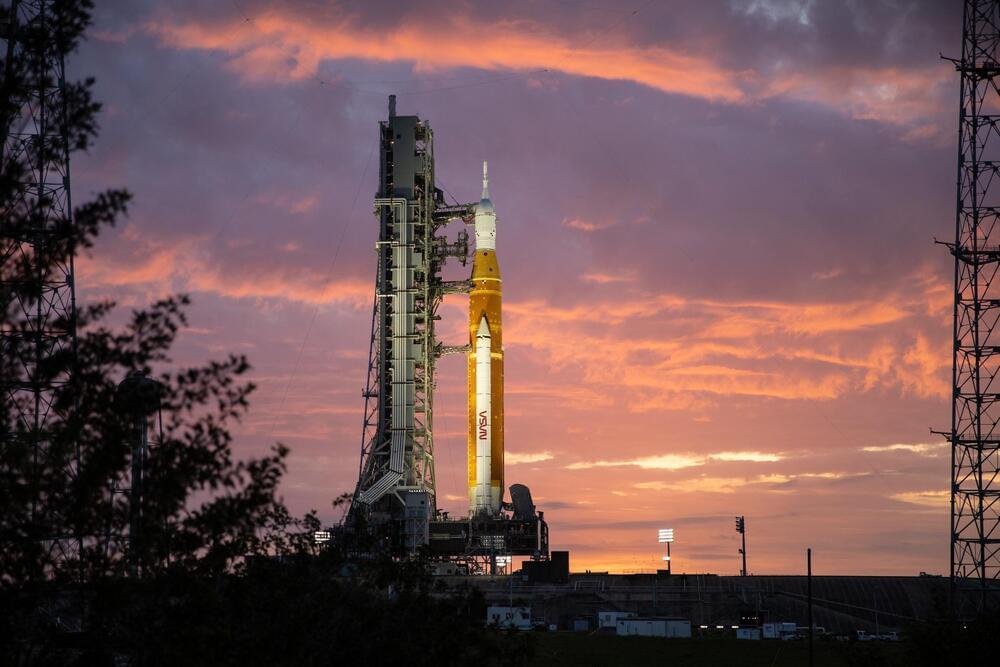

Have you heard about the biggest rocket launch in human history? It’s getting almost zero press coverage, but before breakfast on Monday, August 29, 2022, NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket will make its maiden voyage.
It’s now on the launchpad in Florida.
Everything you need to know about timings and live coverage of NASA’s most impressive rocket launch since 1973 as the Artemis-1 mission sees the Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft go to the Moon.

Billionaire Elon Musk is known for being frugal. In June of 2021, he tweeted about living in a tiny house, stating: “My primary home is literally a ~$50k house in Boca Chica / Starbase that I rent from SpaceX. It’s kinda awesome though.”
That home is so small that it does not even have space for his mom when she visits. As such, the matriarch has to sleep in the garage.
@MattWallace888 My primary home is literally a ~$50k house in Boca Chica / Starbase that I rent from SpaceX. It’s kinda awesome though.
Only house I own is the events house in the Bay Area. If I sold it, the house would see less use, unless bought by a big family, which might happen some day.