There’s still a long way to go before beaming power from space becomes a profitable venture.
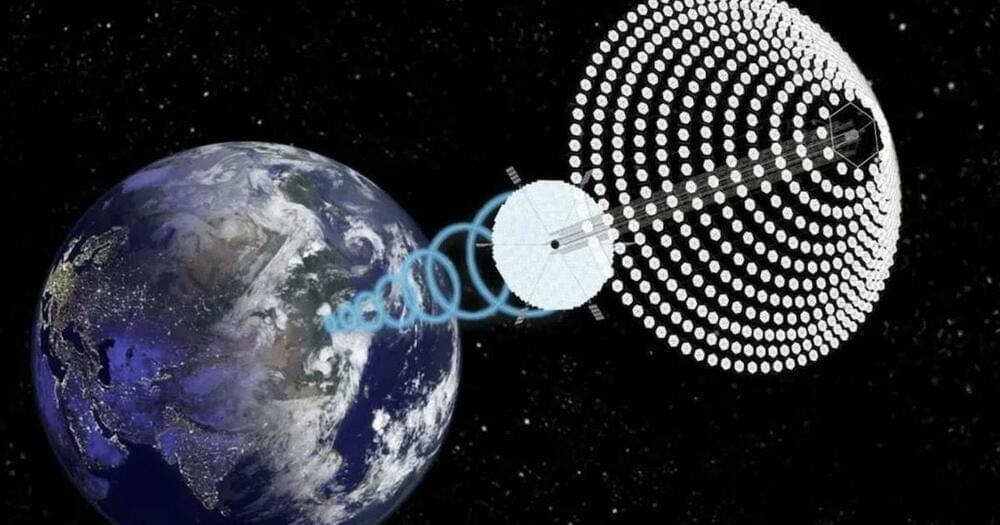
Space-based solar power satellites could eventually power remote mines, but at the moment they face a major challenge.



EPFL
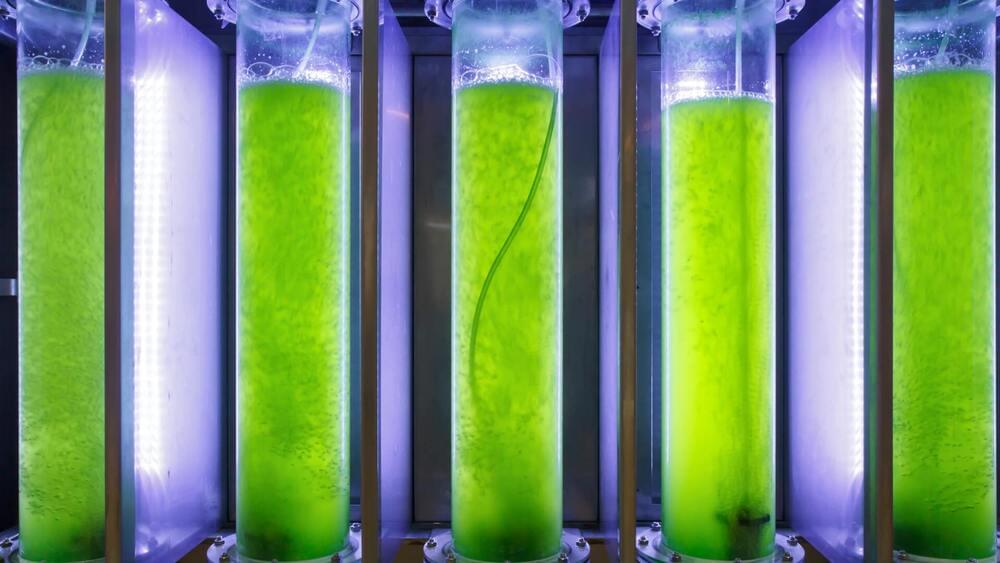
According to a report by Euronews, researchers at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) have discovered a way to create transparent photosensitizers, molecules that can be activated by light and adsorb light across the entire visible light spectrum. Previous versions of DSCs were largely dependent on direct sunlight.
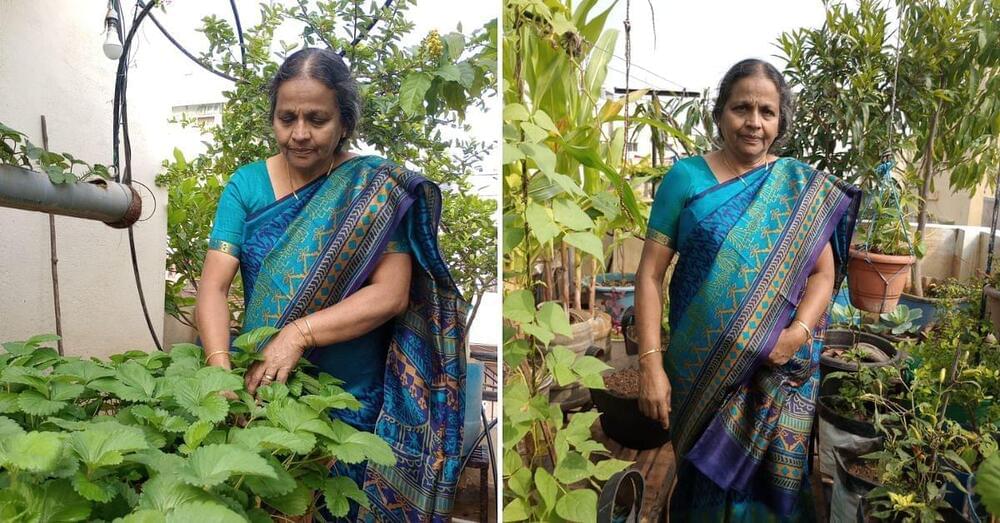

For 70-year-old Lizy John from Bengaluru, Karnataka, nurturing a lush vegetable and fruit garden on her terrace has been highly rewarding and satisfying. Without a second thought, she credits her passion for farming to be the sole reason for staying healthy and energetic even at this age.
After running a snacks business for over 25 years, she decided to retire and focus on expanding her farming venture. Though there wasn’t enough space, she says that it wasn’t a challenge at all.
“Though we have a 1,200 sqft terrace, I grow my veggies in less than 1,000 sqft, as the solar panels and water tanks consume the rest of the space. But it was more than enough for me. I admit that I am happier and at peace ever since I started growing my own food at home,” Lizy tells The Better India.
Solar energy is reaching new heights faster than ever.
A tandem solar cell developed by researchers at the Helmholtz Zentrum Berlin (HZB) has converted 32.5 percent of incident solar radiation into electrical energy, a world record. The achievement was certified by the European Solar Test Installation (ESTI) in Italy, a university press release said.
As the demand for renewable energy grows, researchers are looking at ways of increasing the efficiency of solar cells. This enables more energy to be harvested from the same area of land deployed to generate power. There has been significant success when halide perovskites have been used to make solar cells.

Technology developed at Argonne can help narrow the field of candidates for molten salts, a new study demonstrates.
Scientists are searching for new materials to advance the next generation of nuclear power plants. In a recent study, researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory showed how artificial intelligence could help pinpoint the right types of molten salts, a key component for advanced nuclear reactors.
The ability to absorb and store heat makes molten salt important to clean energy and national climate goals. Molten salts can serve as both coolant and fuel in nuclear power reactors that generate electricity without emitting greenhouse gases. They can also store large amounts of energy, which is increasingly needed on an electric grid with fluctuating sources such as wind and solar power.
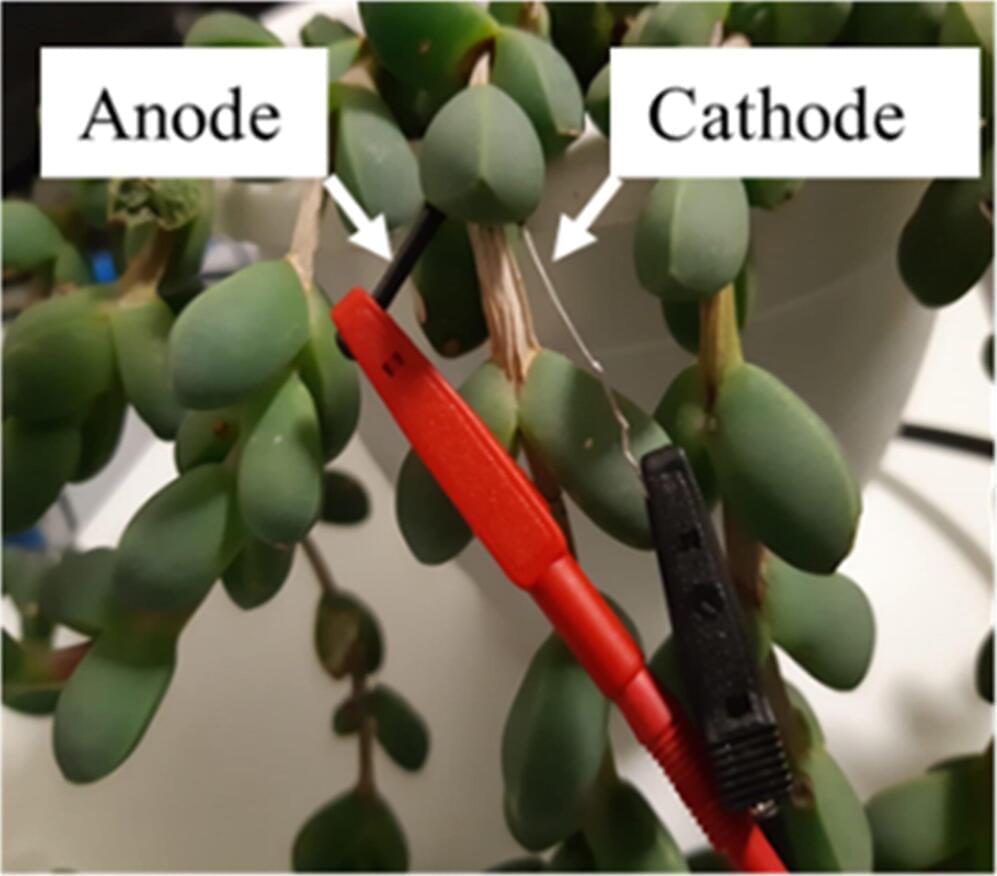
Though plants can serve as a source of food, oxygen and décor, they’re not often considered to be a good source of electricity. But by collecting electrons naturally transported within plant cells, scientists can generate electricity as part of a “green,” biological solar cell.
Now, researchers reporting in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces have, for the first time, used a succulent plant to create a living “bio-solar cell” that runs on photosynthesis.
In all living cells, from bacteria and fungi to plants and animals, electrons are shuttled around as part of natural, biochemical processes. But if electrodes are present, the cells can actually generate electricity that can be used externally. Previous researchers have created fuel cells in this way with bacteria, but the microbes had to be constantly fed. Instead, scientists, including Noam Adir’s team, have turned to photosynthesis to generate current.
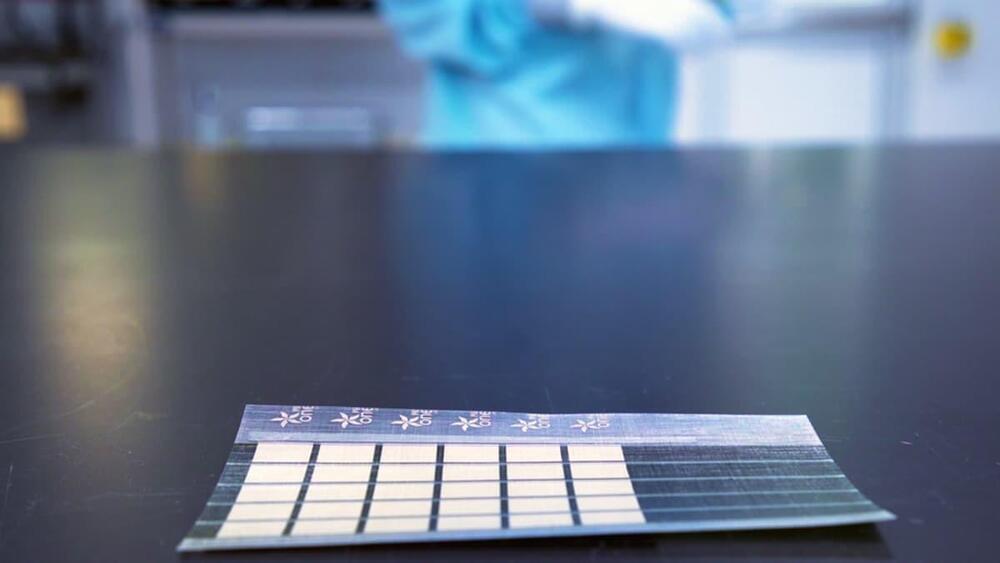

Solar cell technology is a seen as a key pillar in our transition to cleaner forms of energy, but within this field there is all kinds of room for experimentation. Solar cells that are thin and flexible hold unique promise in the area, as they could be applied to all kinds of irregular, curvy or otherwise unsuitable surfaces. Thinner than a human hair, a new lightweight solar cell from MIT scientists continues to push the envelope in this space.
The MIT team behind the technology sought to build on its previous advances in material science, which in 2016 culminated in ultra-thin solar cells light enough to sit atop a soap bubble without breaking it. As is the case with other thin, light and flexible solar cells we’ve looked at over the years, this pointed to all kinds of possibilities, from paper-based electronics to lightweight wearables that harvest energy throughout your day.
Despite the potential, the team still had some problems to solve, with the fabrication technique for the solar cells requiring vacuum chambers and expensive vapor deposition methods. In order to scale the technology up, the scientists have now turned to ink-based printable materials to streamline the process.
The ultralight solar cells are made of semiconducting inks using printing processes that can be scaled in the future to large-area manufacturing.
A group of engineers at MIT have developed a rather interesting solution to be deployed in remote locations or for assistance in emergencies: solar cells made of ultralight fabric that can turn any surface into a power source.
The research is published in Small Methods.
Melanie Gonick, MIT
Thinner than human hair, the durable, flexible solar cells are stuck on a strong, lightweight fabric that makes them very easy to affix to a surface, just like a sticker.
It features cutting-edge solar panels and wind turbines.
Do you have a high-rise building that needs renewable power? PowerNEST is the only rooftop renewable energy system that can fully power a medium-to a high-rise building, according to its official website.
It all began while CEO Dr. Alexander Suma was studying for his Ph.D. at the University of Miami, and he was stunned by the number of A/C units running all day in his neighborhood. With 6 million people living in sunny Miami-Dade, all running their wasteful air conditioning nonstop, Dr. Suma knew it was time for a better solution: that’s how he conceived of PowerNEST.