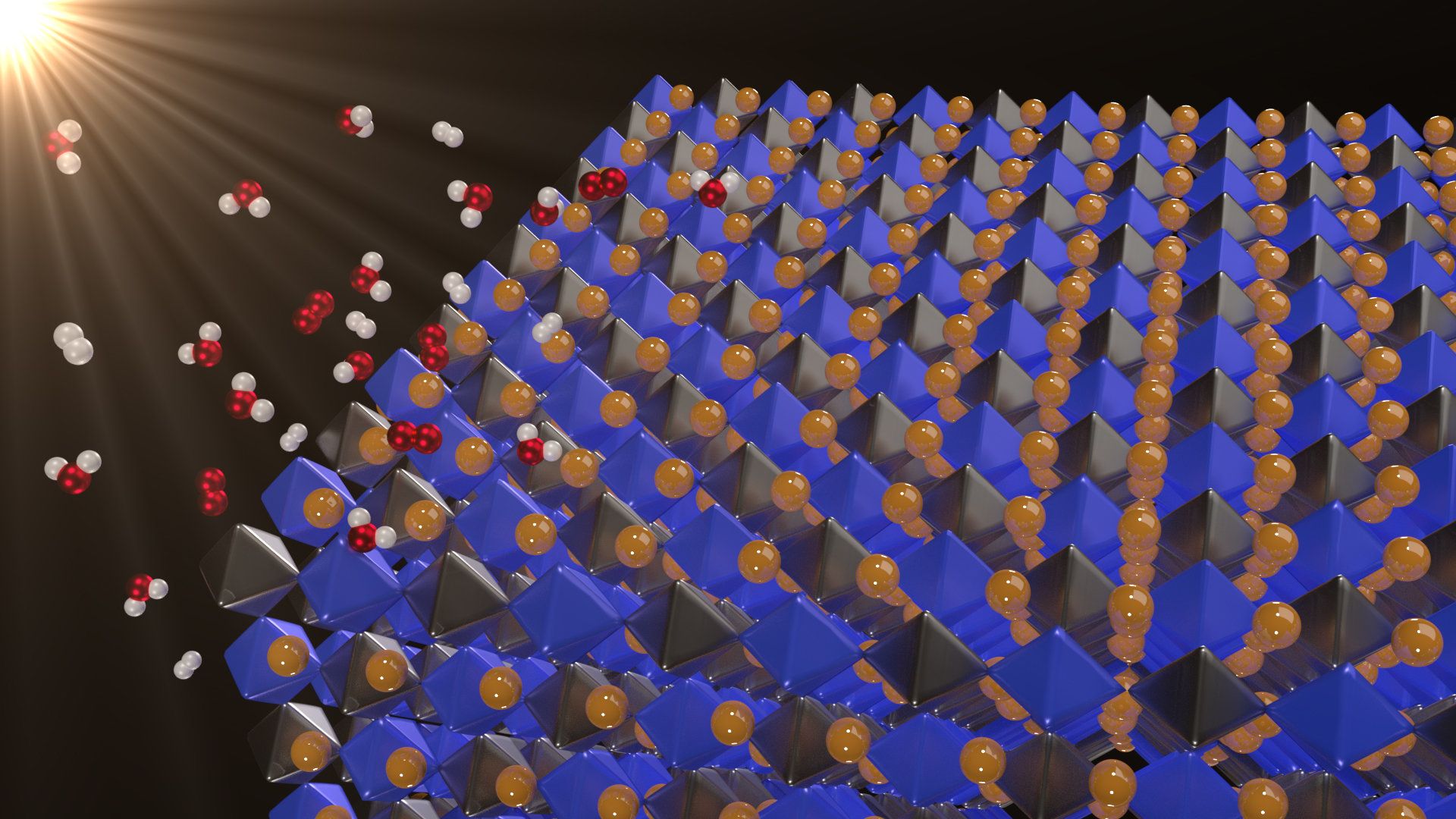
Solar energy is clean and abundant. But when the sun isn’t shining, you must store the energy in batteries or through a process called photocatalysis—in which solar energy is used to make fuels. In photocatalytic water splitting, sunlight separates water into hydrogen and oxygen. The hydrogen and oxygen can then be recombined in a fuel cell to release energy.
Now, a new class of materials—halide double perovskites—may have just the right properties to split water, according to a newly published paper in Applied Physics Letters.
“If we can come up with a material that can be useful as a water-splitting photocatalyst, then it would be an enormous breakthrough,” said Feliciano Giustino, a co-author on the paper.