In recent decades, computer scientists have been developing increasingly advanced machine learning techniques that can learn to predict specific patterns or effectively complete tasks by analyzing large amounts of data. Yet some studies have highlighted the vulnerabilities of some AI-based tools, demonstrating that the sensitive information they are fed could be potentially accessed by malicious third parties.
A machine learning approach that could provide greater data privacy is federated learning, which entails the collaborative training of a shared neural network by various users or parties that are not required to exchange any raw data with each other. This technique could be particularly advantageous when applied in sectors that can benefit from AI but that are known to store highly sensitive user data, such as health care and finance.
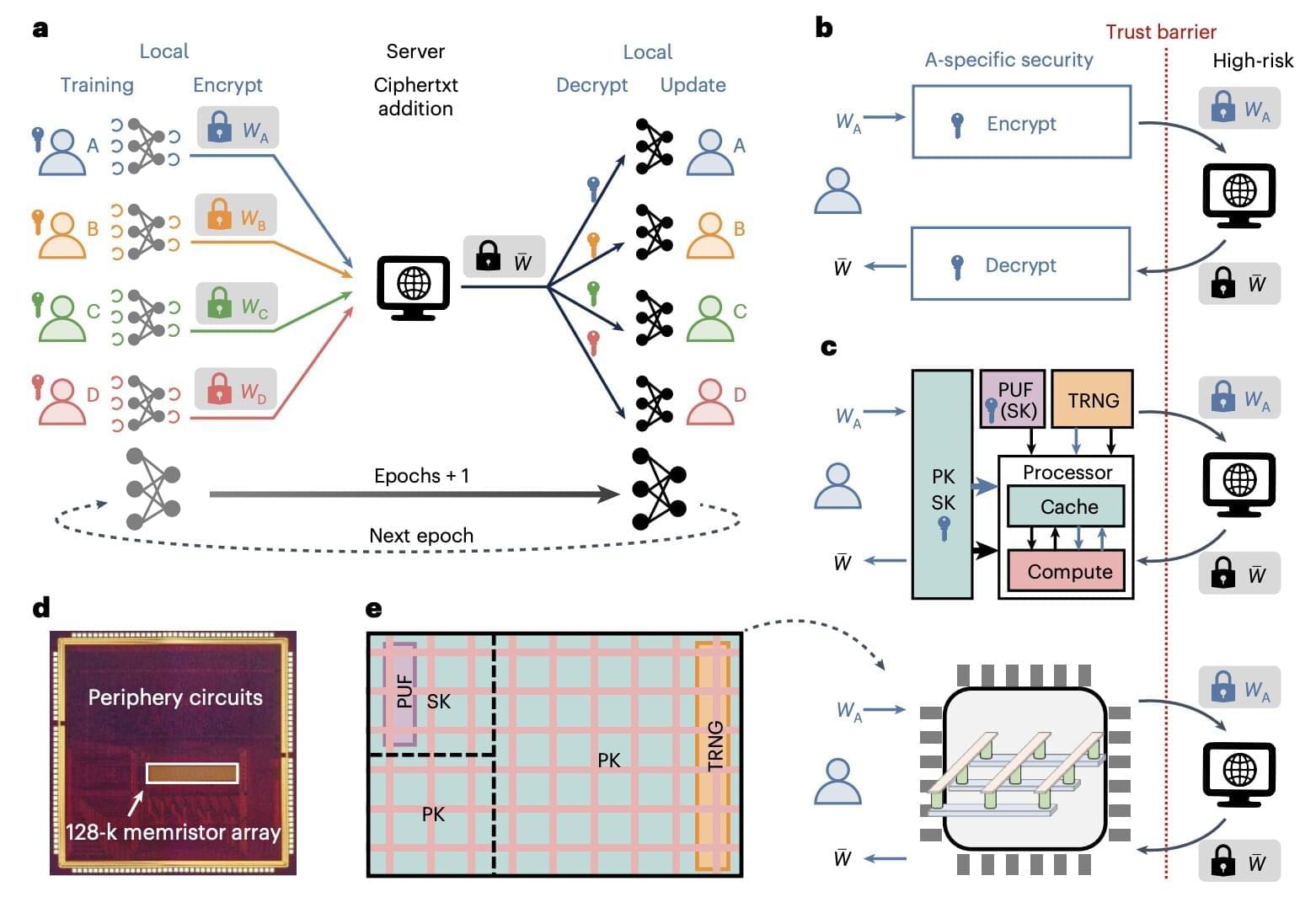
Researchers at Tsinghua University, the China Mobile Research Institute, and Hebei University recently developed a new compute-in-memory chip for federated learning, which is based on memristors, non-volatile electronic components that can both perform computations and store information, by adapting their resistance based on the electrical current that flowed through them in the past. Their proposed chip, outlined in a paper published in Nature Electronics, was found to boost both the efficiency and security of federated learning approaches.