Already deployed in over 50 stores around Japan, the VaakEye system constantly monitors security camera footage, detects suspicious activities and alerts staff, who can instantly review the footage and act on it. And the company is getting ready to launch Amazon-style auto-checkout as well.
Category: security – Page 138

Ocean plastic pollution costs the planet $2.5 trillion per year
It’s the first-ever quantification of the damage caused by plastic pollution on a global scale.
Global plastic pollution and the damage it causes to marine ecosystems now has a price tag attached to it. A team of researchers from the UK and Norway analyzed the many ways in which plastic pollution damages or destroys natural resources, and came up with a staggering figure – $2.5 billion – as the annual cost to society.
Much of our current understanding about plastic pollution is on a local level that cannot be interpreted easily on a global scale; and yet, this is a global threat. An estimated 8 million tons of plastic enter the oceans annually, and because of its material persistence and ability to disperse widely, must be viewed from a broader perspective if we hope to tackle it effectively. The researchers, whose study was just published in Marine Pollution Bulletin, looked at the many ways in which marine ecosystems benefit the planet, including food provision for billions of people, carbon storage, waste detoxification, and cultural benefits (recreational and spiritual). When these benefits are threatened by the presence of plastic, it “has the potential to significantly impact the wellbeing of humans across the globe, owing to the loss of food security, livelihoods, income and good health.”

This Neural Implant Accesses Your Brain Through the Jugular Vein
A permanent neural implant that reads brain activity and churns out text could prove to be a valuable medical tool, but it also could provide doctors with an unprecedented 24/7 stream of neural data.
Oxley recognizes that an endless feed of brain activity could be invaluable to medical researchers, but he doesn’t have plans to tap into that yet.
“[The Stentrode is] going to show us information that we hadn’t had before. Whether that helps us understand other things is not what we’re trying to do here,” he said, clarifying that Synchron’s primary goal is to get the new brain-computer interface working so that it can help paralyzed patients. “This is a novel data set, but this raises questions around privacy and security. That’s the patient’s data, and we can’t be mining that.”

20% of Industrial Control Systems Affected by Critical Vulnerabilities
Image: Business Wire
Over half of the 415 vulnerabilities found in industrial control systems (ICS) were assigned CVSS v.3.0 base scores over 7 which are designated to security issues of high or critical risk levels, with 20% of vulnerable ICS devices being impacted by critical security issues.
As detailed in Kaspersky’s “Threat landscape or industrial automation systems H2 2018”, “The largest number of vulnerabilities affect industrial control systems that control manufacturing processes at various enterprises (115), in the energy sector (110), and water supply (63).”

Deep Science AI joins Defendry to automatically detect crimes on camera
Deep Science AI made its debut on stage at Disrupt NY 2017, showing in a live demo how its computer vision system could spot a gun or mask in CCTV footage, potentially alerting a store or security provider to an imminent crime. The company has now been acquired in a friendly merger with Defendry, which is looking to deploy the tech more widely.
It’s a great example of a tech-focused company looking to get into the market, and a market-focused company looking for the right tech.
The idea was that if you have a chain of 20 stores, and 3 cameras at each store, and people can only reliably keep an eye on 8–10 feeds at a time, you’re looking at a significant personnel investment just to make sure those cameras aren’t pointless. If instead you used Deep Science AI’s middle layer that highlighted shady situations like guns drawn, one person could conceivably keep an eye on hundreds of feeds. It was a good pitch, though they didn’t take the cup that year.
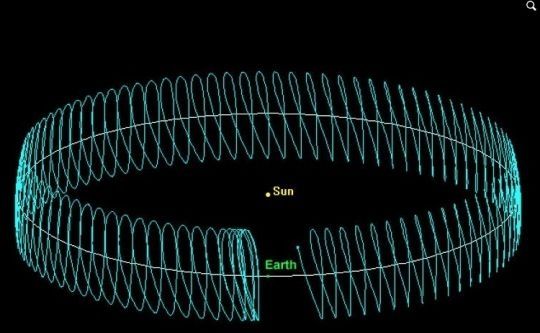
A SETI Search of Earth’s Co-orbitals
SETI for Bracewell probes? Yes please. Years ago Jill Tarter commented that looking for such probes would be worthwhile. These days we hear about Starshot, sending a fleet of lightweight probes to the nearest star within decades which brings into mind the obvious idea that maybe someone else did so long ago.
One objection to SETI is that it is not falsifiable — there is no point at which a lack of signals can prove that extraterrestrial civilizations do not exist. But there are some aspects of SETI that can be falsifiable. Consider a class of objects near enough for us to investigate not only with listening efforts but with probes, one small enough to be thoroughly covered, and one most people know almost nothing about. Could these offer a listening post for ‘Bracewell probes,’ a way of watching the development of our culture and reporting home to ETI? And if so, could we combine SETI with METI to advance both disciplines without compromising our own security?

If the idea of nearby probes seems far-fetched today, it was even more so when Ronald Bracewell advanced his ‘sentinel hypothesis.’ Bracewell took the question of SETI and stood it on its ear. That was no mean feat in 1960, for SETI was just being born in that year through the efforts of Frank Drake at the Green Bank instrument in West Virginia. While Drake was, reasonably enough, asking whether we might pick up signs of an extraterrestrial civilization around another star, Bracewell had begun to wonder whether there might be a different way to study an alien culture. A long-lived probe could be planted in any system under investigation.
Prototype watch uses your body to prevent hacking of wearables and implants
We’re used to the security risks posed by someone hacking into our computers, tablets, and smartphones, but what about pacemakers and other implanted medical devices? To help prevent possible murder-by-hacker, engineers at Purdue University have come up with a watch-like device that turns the human body into its own network as a way to keep personal technology private.
Your body has internet—and now it can’t be hacked
Someone could hack into your pacemaker or insulin pump and potentially kill you, just by intercepting and analyzing wireless signals. This hasn’t happened in real life yet, but researchers have been demonstrating for at least a decade that it’s possible.
Before the first crime happens, Purdue University engineers have tightened security on the “internet of body.” Now, the network you didn’t know you had is only accessible by you and your devices, thanks to technology that keeps communication signals within the body itself.
The work appears in the journal Scientific Reports. Study authors include Shreyas Sen, an assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering at Purdue, and his students, Debayan Das, Shovan Maity and Baibhab Chatterjee.
Researchers turn liquid metal into a plasma
Scientists at the University of Rochester’s Laboratory for Laser Energetics have achieved a plasma research first. They were able to convert the liquid metal deuterium to the plasma state and directly observe the interaction threshold.
For the first time, researchers at the University of Rochester’s Laboratory for Laser Energetics (LLE) have found a way to turn a liquid metal into a plasma and to observe the temperature where a liquid under high-density conditions crosses over to a plasma state. Their observations, published in Physical Review Letters, have implications for better understanding stars and planets and could aid in the realization of controlled nuclear fusion — a promising alternative energy source whose realization has eluded scientists for decades. The research is supported by the US Department of Energy and the National Nuclear Security Administration.
What is a Plasma?
Plasmas consist of a hot soup of free moving electrons and ions — atoms that have lost their electrons — that easily conducts electricity. Although plasmas are not common naturally on Earth, they comprise most of the matter in the observable universe, such as the surface of the sun. Scientists are able to generate artificial plasmas here on Earth, typically by heating a gas to thousands of degrees Fahrenheit, which strips the atoms of their electrons. On a smaller scale, this is the same process that allows plasma TVs and neon signs to “glow”: electricity excites the atoms of a neon gas, causing neon to enter a plasma state and emit photons of light.
Two instruments as concrete alternatives to social networks taking advantage of our privacy
Keeping up with Meta’s scandals could easily be a part-time job. All joking aside, the development of its worldwide network ramifications helped decrease communication distances between individuals with an average of three and a half degrees of separation between its members in 2016.
As a reminder, this network and its numerous variations, which certainly don’t need to be named anymore, have enabled us to:
· reach our friends, family members, business collaborators, or partners;
· create and join discussion groups;
· organize events;promote icons and content in very different formats.
The downside is that all of this became possible the moment we agreed to join the online club for free. The benefit of accessing brand new and efficient communication tools has left us with no choice but to keep returning to a highly segmented network (comprising both acquaintances and close friends). Such a network, which includes more and more of our “friends,” convinces us to never really read the terms and conditions (boring, right?).
Yet, they clearly involve the real-time sale of our personal profiles and predictable behaviors the moment we tick the boxes just to get in.
Using a free service is very different from being the unwitting provider of a value stream (via analytics data and advertising marketplaces). We act in good faith, as we would in real life, but often accept advertising as the only way to endorse our cultural preferences regarding this or that innovative trend (even when there is little innovation and mostly an unsustainable waste of our limited resources, namely time and attention).
Today, privacy advocates are also thrilled by the broad variety of initiatives enabling us to stop dissipating our shared moments between our interlocutors AND third parties interfering with our conversations. How do we progressively upgrade the software without requiring everybody (who feels like it could be a good idea, of course) to get on board? We’re facing quite a pickle here, perhaps not as hard as gluing back together large blocks of melting ice, but still not trivial when considered at scale.
Here are two technological ways to connect with your peers outside of the “normative ways”,
plus one relying on one of the oldest networks, email. Here are their respective slogans:
· Delta Chat — Chat over email with encryption,
like Telegram or messaging apps owned by Meta but without the tracking or central control — https://delta.chat/en/
· Element — Own your conversations — https://element.io
(Its underlying protocols are now used by the French state for some of its administration services)
· Signal — Privacy is the default — https://signal.org
I invite you to try them out, share your insights, and support their contributors. Social challenges won’t be solved solely by switching communication tools.
However, conversations remain conversations; the better the host, the more comfortable and safe we feel in preserving a discussion that is as open, honest, and respectful as possible.