A year in review.
This video is sponsored by ResearchHub — https://www.researchhub.com/?ref=eleanorsheeky.
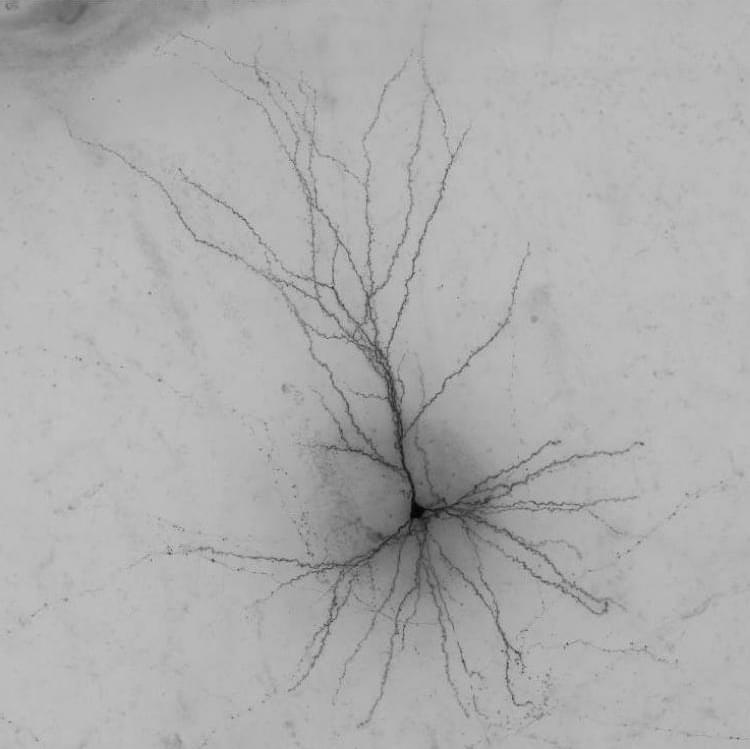
I’ve covered a lot of longevity science research this year so have summarised some of the key highlights here!!! Many breakthroughs & research I couldn’t cover — let me know what your favourite news this year was in the comments!!
Obviously, couldn’t go into as much detail for each topic, but you can find the full length videos in my playlist here: https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLnLFbRYd2NGEP1VxVkW8-Hy9xix-Y7wur.
Find me on Twitter — https://twitter.com/EleanorSheekey.