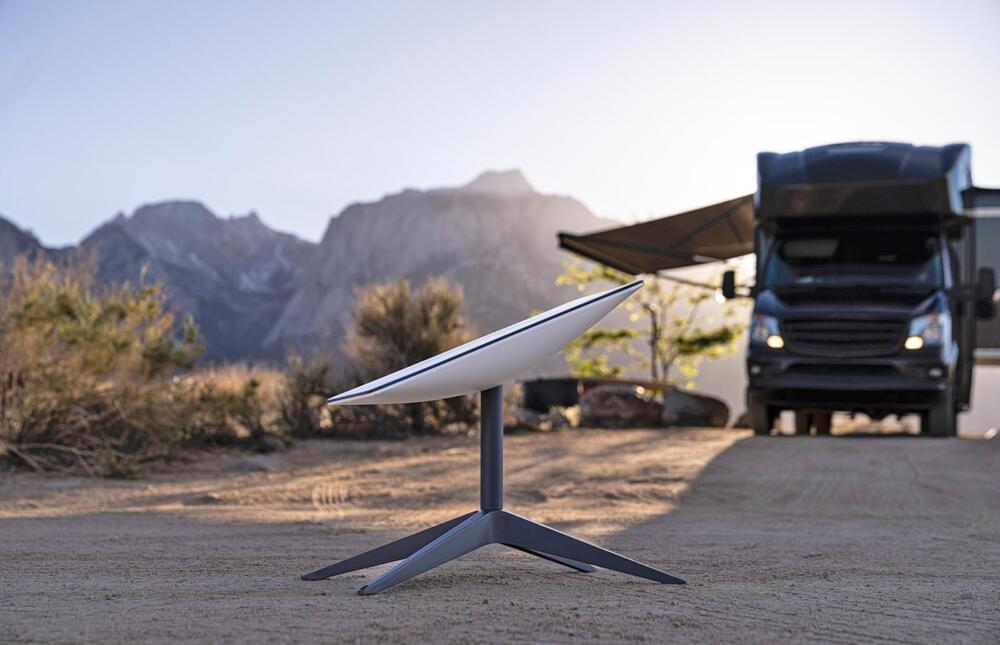
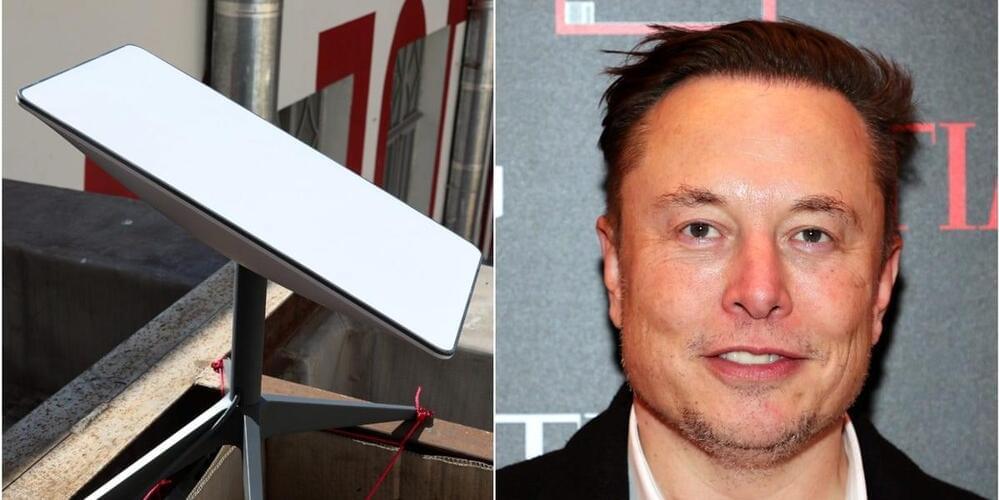
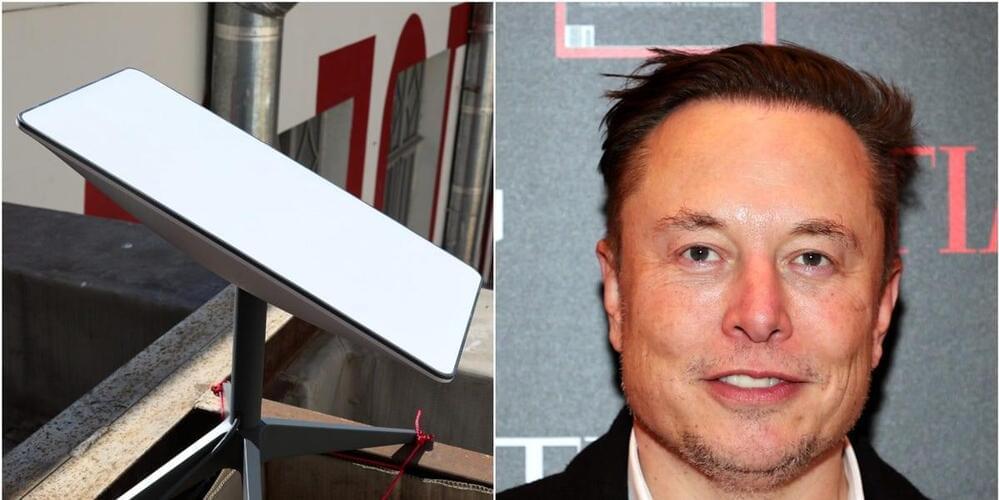
Starlink has launched a new product meant specifically for RV dwellers and those who can’t wait to get connected to the satellite internet service. While applying for a regular Starlink dish and service will put customers in a waitlist until 2023, Starlink for RVs is immediately available and will ship out to buyers right now. The downside? Network resources are always de-prioritized for it, and the service costs $135, which is $25 more than a regular Starlink connection.
In other words, the RV option costs just as much as a regular Starlink connection with the Portability feature introduced back in March that allows customers to use the service while they’re away from home. A regular connection requires one to have a home service first, though, and that may not be possible for some people. Another difference is that the product for RVs gives customers the ability to pause and un-pause service, so they can control when their billing starts and ends.
Since the network is de-prioritized for the RV service, though, users’ connection might be slow and intermittent in congested areas and during peak hours. “Stated speeds and uninterrupted use of the service are not guaranteed,” the company wrote in its Help page, clearly making sure interested customers understand that it’s prioritizing at-home users. One important thing to note for those looking into the RV option is that they can’t use Starlink while in motion at this time. SpaceX chief Elon Musk also added on Twitter that the dish is too big for cars, though that didn’t stop at least one user from bolting it onto their vehicle’s hood.